# MMSplice & MTSplice
[](https://circleci.com/gh/gagneurlab/MMSplice_MTSplice)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/mmsplice)
Predict (tissue-specific) splicing variant effect from VCF. MTSplice is integrated into MMSplice with the same API.
Paper: Cheng et al. https://doi.org/10.1101/438986, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.06.07.138453v1
## Installation
-----------------
External dependencies:
```bash
pip install cyvcf2 cython
```
Conda installation is recommended:
```bash
conda install cyvcf2 cython -y
```
```bash
pip install mmsplice
```
## Run MMSplice Online
You can run mmsplice with following google colab notebooks online:
- [run on vcf file](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Kw5rHMXaxXXsmE3WecxbXyGQJma80Eq6)
### Preparation
-----------------
#### 1. Prepare annotation (gtf) file
Standard human gene annotation file in GTF format can be downloaded from ensembl or gencode.
`MMSplice` can work directly with those files, however, some filtering is higly recommended.
- Filter for protein coding genes.
#### 2. Prepare variant (VCF) file
A correctly formatted VCF file with work with `MMSplice`, however the following steps will make it less prone to false positives:
- Quality filtering. Low quality variants leads to unreliable predictions.
- Avoid presenting multiple variants in one line by splitting them into multiple lines. Example code to do it:
```bash
bcftools norm -m-both -o out.vcf in.vcf.gz
```
- Left-normalization. For instance, GGCA-->GG is not left-normalized while GCA-->G is. Details for unified representation of genetic variants see [Tan et al.](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4481842/)
```bash
bcftools norm -f reference.fasta -o out.vcf in.vcf
```
#### 3. Prepare reference genome (fasta) file
Human reference fasta file can be downloaded from ensembl/gencode. Make sure the chromosome name matches with GTF annotation file you use.
### Example code
-------------------
Check [notebooks/example.ipynb](https://github.com/gagneurlab/MMSplice/blob/master/notebooks/example.ipynb)
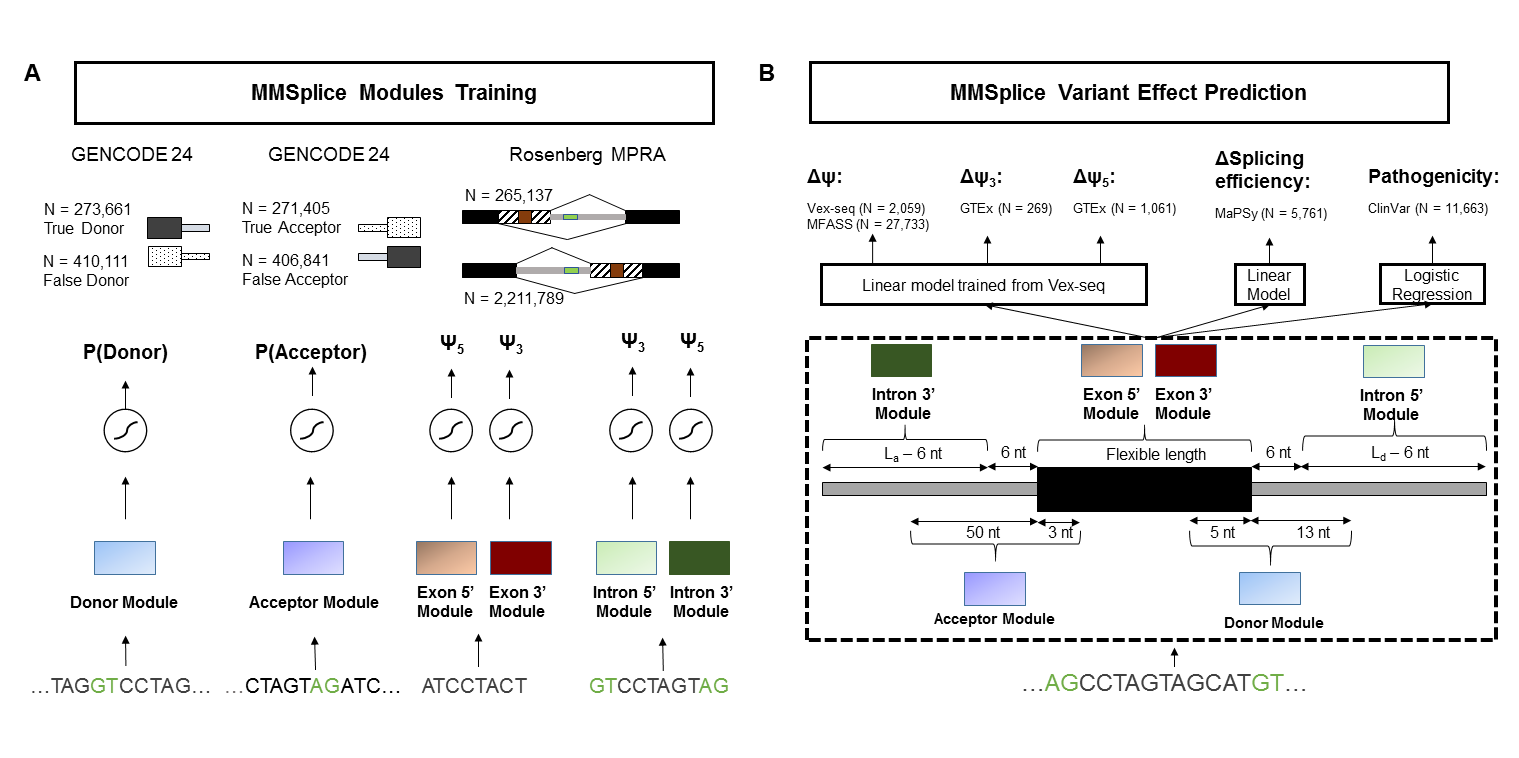
To score variants (including indels), we suggest to use primarily the `deltaLogitPSI` predictions, which is the default output. The differential splicing efficiency (dse) model was trained from MMSplice modules and exonic variants from MaPSy, thus only the predictions for exonic variants are calibrated.
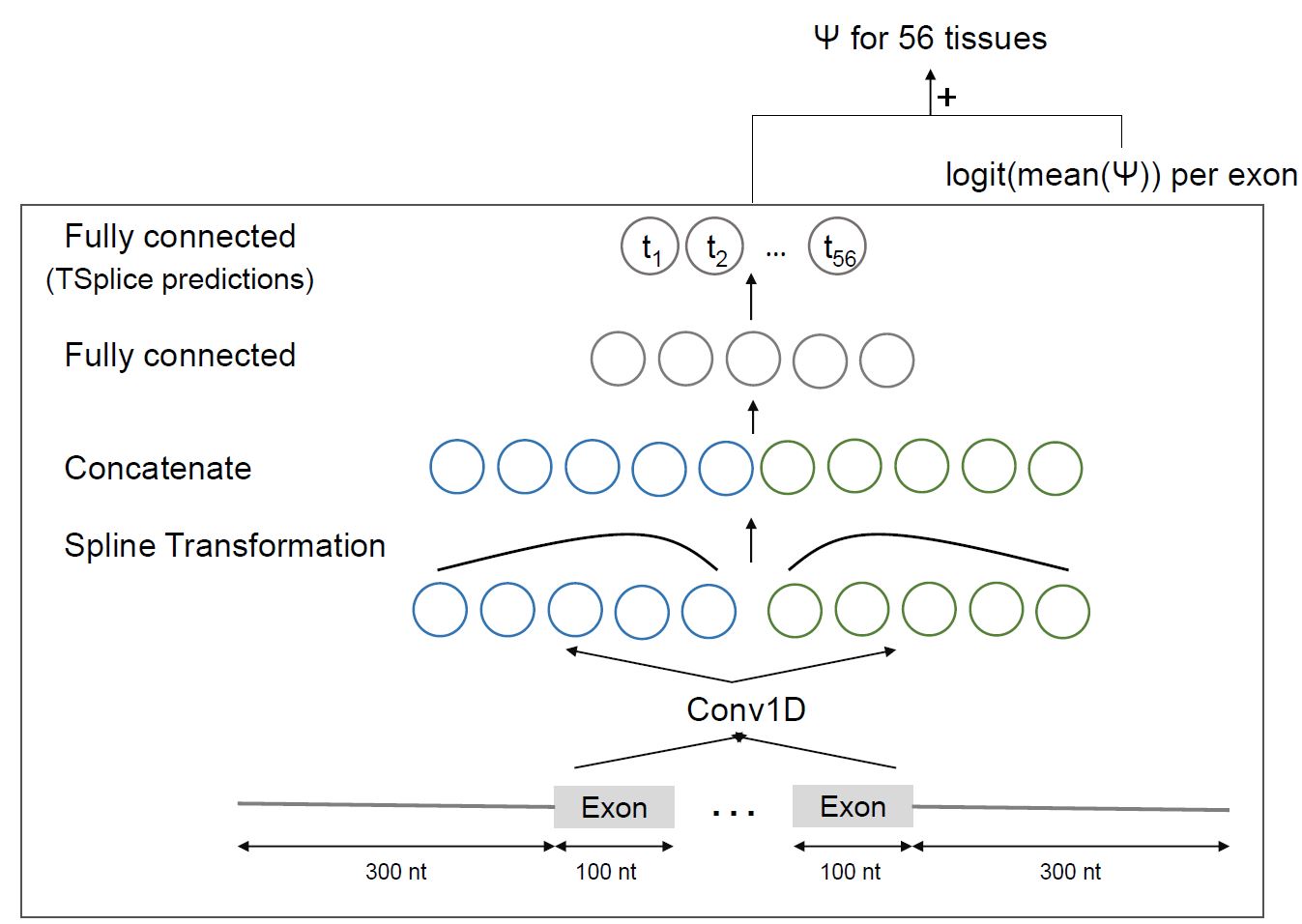
**MTSplice** To predict tissue-specific variant effect with MTSplice, specify `tissue_specific=True` in `SplicingVCFDataloader`.
```python
# Import
from mmsplice.vcf_dataloader import SplicingVCFDataloader
from mmsplice import MMSplice, predict_save, predict_all_table
from mmsplice.utils import max_varEff
# example files
gtf = 'tests/data/test.gtf'
vcf = 'tests/data/test.vcf.gz'
fasta = 'tests/data/hg19.nochr.chr17.fa'
csv = 'pred.csv'
```
Dataloader to load variants from vcf
```python
dl = SplicingVCFDataloader(gtf, fasta, vcf, tissue_specific=False)
```
To predict tissue-specific effect, in the dataloader use `tissue_specific=True` in the dataloader instead
```python
dl = SplicingVCFDataloader(gtf, fasta, vcf, tissue_specific=True)
```
Run prediction with default MMSplice parameters
```python
# Specify model
model = MMSplice()
# Or predict and return as df
predictions = predict_all_table(model, dl, pathogenicity=True, splicing_efficiency=True)
```
To predict variant effect on <img src="https://render.githubusercontent.com/render/math?math=\Delta \Psi"> scale instead of <img src="https://render.githubusercontent.com/render/math?math=\Delta \text{logit}(\Psi)">. This option only works with tissue specific predictions `dl = SplicingVCFDataloader(..., tissue_specific=True)`:
```python
# Or predict and return as df
predictions = predict_all_table(model, dl, natural_scale=True)
```
One variant might map to multiple exons. In the end we summarize the effect of as the maximum across all exons.
```python
# Summerize with maximum effect size
predictionsMax = max_varEff(predictions)
```
### Output
Output of MMSplice is an tabular data which contains following described columns:
* `ID`: id string of the variant
* `delta_logit_psi`: The main score is predicted by MMSplice, which shows the effect of the variant on the inclusion level (PSI percent spliced in) of the exon. The score is on a logit scale. If the score is positive, it shows that variant leads higher inclusion rate for the exon. If the score is negative, it shows that variant leads higher exclusion rate for the exon. If delta_logit_psi is bigger than 2 or smaller than -2, the effect of variant can be considered strong.
* `exons`: Genetics location of exon whose inclusion rate is effected by variant
* `exon_id`: Genetic id of exon whose inclusion rate is effected by variant
* `gene_id`: Genetic id of the gene which the exon belongs to.
* `gene_name`: Name of the gene which the exon belongs to.
* `transcript_id`: Genetic id of the transcript which the exon belongs to.
* `ref_acceptorIntron`: acceptor intron score of the reference sequence
* `ref_acceptor`: acceptor score of the reference sequence
* `ref_exon`: exon score of the reference sequence
* `ref_donor`: donor score of the reference sequence
* `ref_donorIntron`: donor intron score of the reference sequence
* `alt_acceptorIntron`: acceptor intron score of variant sequence
* `alt_acceptor`: acceptor score of the sequence with variant
* `alt_exon`: exon score of the sequence with variant
* `alt_donor`: donor score of the sequence with variant
* `alt_donorIntron`: donor intron score of the sequence with variant
* `pathogenicity`: Potential pathogenic effect of the variant.
* `efficiency`: The effect of the variant on the splicing efficiency of the exon.
## VEP Plugin
The VEP plugin wraps the prediction function from `mmsplice` python package. Please check documentation of vep plugin [under VEP_plugin/README.md](VEP_plugin/README.md).
=======
History
=======
1.0.0 (2019-07-23)
------------------
* Dependicies fixed #16
* Valide gtf, fasta, vcf chrom annotation #15
* Ship mmsplice with prebuild exon set. #12
* Faster variant overlapping with pyranges #11
* Batch prediction with masking update in exon module
0.1.0 (2018-07-17)
------------------
* First release on PyPI.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/gagneurlab/mmsplice",
"name": "mmsplice",
"maintainer": "",
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": "",
"maintainer_email": "",
"keywords": "mmsplice",
"author": "Jun Cheng, Muhammed Hasan \u00c7elik",
"author_email": "chengju@in.tum.de, muhammedhasancelik@gmail.com",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/32/bd/3154f9e2979b2e7a35a2f3bcf071c12c9acced59b6d25415dcb9a9c6efc3/mmsplice-2.4.0.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "# MMSplice & MTSplice\n[](https://circleci.com/gh/gagneurlab/MMSplice_MTSplice)\n[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/mmsplice)\n\nPredict (tissue-specific) splicing variant effect from VCF. MTSplice is integrated into MMSplice with the same API.\n\nPaper: Cheng et al. https://doi.org/10.1101/438986, https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.06.07.138453v1\n\n\n\n\n## Installation\n-----------------\n\nExternal dependencies:\n```bash\npip install cyvcf2 cython\n```\n\nConda installation is recommended:\n```bash\nconda install cyvcf2 cython -y\n```\n\n```bash\npip install mmsplice\n```\n\n## Run MMSplice Online\n\nYou can run mmsplice with following google colab notebooks online:\n\n- [run on vcf file](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Kw5rHMXaxXXsmE3WecxbXyGQJma80Eq6)\n\n### Preparation\n-----------------\n\n#### 1. Prepare annotation (gtf) file\nStandard human gene annotation file in GTF format can be downloaded from ensembl or gencode.\n`MMSplice` can work directly with those files, however, some filtering is higly recommended.\n\n- Filter for protein coding genes.\n\n#### 2. Prepare variant (VCF) file\nA correctly formatted VCF file with work with `MMSplice`, however the following steps will make it less prone to false positives:\n\n- Quality filtering. Low quality variants leads to unreliable predictions.\n- Avoid presenting multiple variants in one line by splitting them into multiple lines. Example code to do it:\n ```bash\n bcftools norm -m-both -o out.vcf in.vcf.gz\n ```\n- Left-normalization. For instance, GGCA-->GG is not left-normalized while GCA-->G is. Details for unified representation of genetic variants see [Tan et al.](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4481842/)\n ```bash\n bcftools norm -f reference.fasta -o out.vcf in.vcf\n ```\n\n#### 3. Prepare reference genome (fasta) file\nHuman reference fasta file can be downloaded from ensembl/gencode. Make sure the chromosome name matches with GTF annotation file you use.\n\n\n### Example code\n-------------------\n\nCheck [notebooks/example.ipynb](https://github.com/gagneurlab/MMSplice/blob/master/notebooks/example.ipynb)\n\nTo score variants (including indels), we suggest to use primarily the `deltaLogitPSI` predictions, which is the default output. The differential splicing efficiency (dse) model was trained from MMSplice modules and exonic variants from MaPSy, thus only the predictions for exonic variants are calibrated.\n\n**MTSplice** To predict tissue-specific variant effect with MTSplice, specify `tissue_specific=True` in `SplicingVCFDataloader`.\n\n```python\n# Import\nfrom mmsplice.vcf_dataloader import SplicingVCFDataloader\nfrom mmsplice import MMSplice, predict_save, predict_all_table\nfrom mmsplice.utils import max_varEff\n\n# example files\ngtf = 'tests/data/test.gtf'\nvcf = 'tests/data/test.vcf.gz'\nfasta = 'tests/data/hg19.nochr.chr17.fa'\ncsv = 'pred.csv'\n```\nDataloader to load variants from vcf\n```python\ndl = SplicingVCFDataloader(gtf, fasta, vcf, tissue_specific=False)\n```\n\nTo predict tissue-specific effect, in the dataloader use `tissue_specific=True` in the dataloader instead\n```python\ndl = SplicingVCFDataloader(gtf, fasta, vcf, tissue_specific=True)\n```\n\nRun prediction with default MMSplice parameters\n```python\n# Specify model\nmodel = MMSplice()\n\n# Or predict and return as df\npredictions = predict_all_table(model, dl, pathogenicity=True, splicing_efficiency=True)\n```\n\nTo predict variant effect on <img src=\"https://render.githubusercontent.com/render/math?math=\\Delta \\Psi\"> scale instead of <img src=\"https://render.githubusercontent.com/render/math?math=\\Delta \\text{logit}(\\Psi)\">. This option only works with tissue specific predictions `dl = SplicingVCFDataloader(..., tissue_specific=True)`:\n```python\n# Or predict and return as df\npredictions = predict_all_table(model, dl, natural_scale=True)\n```\n\nOne variant might map to multiple exons. In the end we summarize the effect of as the maximum across all exons.\n```python\n# Summerize with maximum effect size\npredictionsMax = max_varEff(predictions)\n```\n\n### Output\n\nOutput of MMSplice is an tabular data which contains following described columns:\n\n* `ID`: id string of the variant\n* `delta_logit_psi`: The main score is predicted by MMSplice, which shows the effect of the variant on the inclusion level (PSI percent spliced in) of the exon. The score is on a logit scale. If the score is positive, it shows that variant leads higher inclusion rate for the exon. If the score is negative, it shows that variant leads higher exclusion rate for the exon. If delta_logit_psi is bigger than 2 or smaller than -2, the effect of variant can be considered strong.\n* `exons`: Genetics location of exon whose inclusion rate is effected by variant\n* `exon_id`: Genetic id of exon whose inclusion rate is effected by variant\n* `gene_id`: Genetic id of the gene which the exon belongs to.\n* `gene_name`: Name of the gene which the exon belongs to.\n* `transcript_id`: Genetic id of the transcript which the exon belongs to.\n* `ref_acceptorIntron`: acceptor intron score of the reference sequence\n* `ref_acceptor`: acceptor score of the reference sequence\n* `ref_exon`: exon score of the reference sequence\n* `ref_donor`: donor score of the reference sequence\n* `ref_donorIntron`: donor intron score of the reference sequence\n* `alt_acceptorIntron`: acceptor intron score of variant sequence\n* `alt_acceptor`: acceptor score of the sequence with variant\n* `alt_exon`: exon score of the sequence with variant\n* `alt_donor`: donor score of the sequence with variant\n* `alt_donorIntron`: donor intron score of the sequence with variant\n* `pathogenicity`: Potential pathogenic effect of the variant.\n* `efficiency`: The effect of the variant on the splicing efficiency of the exon.\n\n\n## VEP Plugin\n\nThe VEP plugin wraps the prediction function from `mmsplice` python package. Please check documentation of vep plugin [under VEP_plugin/README.md](VEP_plugin/README.md).\n\n\n=======\nHistory\n=======\n\n1.0.0 (2019-07-23)\n------------------\n* Dependicies fixed #16\n* Valide gtf, fasta, vcf chrom annotation #15\n* Ship mmsplice with prebuild exon set. #12\n* Faster variant overlapping with pyranges #11\n* Batch prediction with masking update in exon module\n\n0.1.0 (2018-07-17)\n------------------\n\n* First release on PyPI.\n\n\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "MIT license",
"summary": "Predict splicing variant effect from VCF",
"version": "2.4.0",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/gagneurlab/mmsplice"
},
"split_keywords": [
"mmsplice"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "14aa2bd61394b483d56b0d9011921e785d019848216336581b3144a21faff124",
"md5": "d2d23cbe10c30a54d8ed2446a9b1042e",
"sha256": "d70a3a281b9433b89e6a8612cc2ca2611f54c35b90f46e16772b2868ec94b60a"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "mmsplice-2.4.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "d2d23cbe10c30a54d8ed2446a9b1042e",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py2.py3",
"requires_python": null,
"size": 62420667,
"upload_time": "2023-05-23T19:59:13",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2023-05-23T19:59:13.840144Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/14/aa/2bd61394b483d56b0d9011921e785d019848216336581b3144a21faff124/mmsplice-2.4.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "32bd3154f9e2979b2e7a35a2f3bcf071c12c9acced59b6d25415dcb9a9c6efc3",
"md5": "d6cf4da2f6a3f9a93fa2c584455dedb8",
"sha256": "e467f5a96485afe1fbd01ab91dc22261df9c256fb67c4bc0d8fb38017b99c0ed"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "mmsplice-2.4.0.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "d6cf4da2f6a3f9a93fa2c584455dedb8",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": null,
"size": 62412873,
"upload_time": "2023-05-23T19:59:27",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2023-05-23T19:59:27.052629Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/32/bd/3154f9e2979b2e7a35a2f3bcf071c12c9acced59b6d25415dcb9a9c6efc3/mmsplice-2.4.0.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2023-05-23 19:59:27",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "gagneurlab",
"github_project": "mmsplice",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": false,
"circle": true,
"tox": true,
"lcname": "mmsplice"
}
