<!--
Title: AWS InsuranceLake
Description: Serverless modern data lake solution and reference architecture fit for the insurance industry built on AWS
Author: cvisi@amazon.com
-->
# InsuranceLake ETL
## Overview
This solution guidance helps you deploy extract, transform, load (ETL) processes and data storage resources to create InsuranceLake. It uses Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets for storage, [AWS Glue](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/glue/) for data transformation, and [AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) Pipelines](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/latest/guide/cdk_pipeline.html). The solution is originally based on the AWS blog [Deploy data lake ETL jobs using CDK Pipelines](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/devops/deploying-data-lake-etl-jobs-using-cdk-pipelines/).
The best way to learn about InsuranceLake is to follow the [Quickstart guide](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart/) and try it out.
The InsuranceLake solution is comprised of two codebases: [Infrastructure](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-infrastructure) and [ETL](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl).
Specifically, this solution helps you to:
* Deploy a "3 Cs" (Collect, Cleanse, Consume) architecture InsuranceLake.
* Deploy ETL jobs needed to make common insurance industry data souces available in a data lake.
* Use pySpark Glue jobs and supporting resoures to perform data transforms in a modular approach.
* Build and replicate the application in multiple environments quickly.
* Deploy ETL jobs from a central deployment account to multiple AWS environments such as Dev, Test, and Prod.
* Leverage the benefit of self-mutating feature of CDK Pipelines; specifically, the pipeline itself is infrastructure as code and can be changed as part of the deployment.
* Increase the speed of prototyping, testing, and deployment of new ETL jobs.
## Contents
* [Cost](#cost)
* [Sample Cost Table](#sample-cost-table)
* [Quickstart](#quickstart)
* [Python/CDK Basics](#pythoncdk-basics)
* [Deploy the Application](#deploy-the-application)
* [Try out the ETL Process](#try-out-the-etl-process)
* [Next Steps](#next-steps)
* [Deployment Validation](#deployment-validation)
* [Cleanup](#cleanup)
* [Architecture](#architecture)
* [Collect, Cleanse, Consume](#collect-cleanse-consume)
* [ETL](#etl)
* [Well Architected Pillars](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/well_architected/)
* [Security](#security)
* [Infrastructure Code](#infrastructure-code)
* [Application Code](#application-code)
* [Online Documentation](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/)
* [Additional resources](#additional-resources)
* [Authors](#authors)
* [License Summary](#license-summary)
## Cost
This solution uses the following services: [Amazon S3](https://aws.amazon.com/s3/pricing/), [AWS Glue](https://aws.amazon.com/glue/pricing/), [AWS Step Functions](https://aws.amazon.com/step-functions/pricing/), [Amazon DynamoDB](https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/pricing/), [AWS Lambda](https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/pricing/), [Amazon CloudWatch](https://aws.amazon.com/cloudwatch/pricing/), [Amazon Athena](https://aws.amazon.com/athena/pricing/), and [AWS CodePipeline](https://aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/pricing/) for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) installation only.
An estimated cost for following the [Quickstart](#quickstart) and [Quickstart with CI/CD](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart_cicd/) instructions, assuming a total of 8 Glue DPU hours and cleaning all resources when finished, **your cost will not be higher than $2**. This cost could be less as some services are included in the [Free Tier](https://aws.amazon.com/free/).
_We recommend creating a [Budget](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cost-management/latest/userguide/budgets-managing-costs.html) through [AWS Cost Explorer](https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-explorer/) to help manage costs. Prices are subject to change. For full details, refer to the pricing webpage for each AWS service used in this solution._
### Sample Cost Table
The following table provides a sample cost breakdown for deploying this Guidance with the default parameters in the US East (Ohio) Region for one month with pricing as of _2 October 2024_.
|AWS service |Dimensions |Cost [USD]
|--- |--- |---
|AWS Glue |per DPU-Hour for each Apache Spark or Spark Streaming job, billed per second with a 1-minute minimum |$0.44
|Amazon S3 |per GB of storage used, Frequent Access Tier, first 50 TB per month<br>PUT, COPY, POST, LIST requests (per 1,000 requests)<br>GET, SELECT, and all other requests (per 1,000 requests) |$0.023<br>$0.005<br>$0.0004
|Amazon Athena |per TB of data scanned |$5.00
|Amazon DynamoDB |per GB-month of storage, over 25 GB<br>per million Write Request Units (WRU)<br>per million Read Request Units (RRU) |$0.25<br>$1.25<br>$0.25
## Quickstart
If you'd like to get started quickly transforming some sample raw insurance data and running SQL on the resulting dataset, **and without worrying about CI/CD**, follow the steps in this section.
### Python/CDK Basics
1. Open the AWS Console in the `us-east-2 (Ohio)` Region.
- NOTE: InsuranceLake uses `us-east-2` by default. To change the Region, refer to the [Quickstart with CI/CD](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart_cicd/).
1. Select `CloudShell` at the bottom of the page and wait for a few seconds until it is available for use.
1. Ensure you are using the latest version of the AWS SDK for Node.js and AWS CDK.
```
sudo npm install -g aws-lib aws-cdk
```
1. Clone the repositories.
```bash
git clone https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-infrastructure.git
git clone https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl.git
```
1. Change the working directory to the location of the _infrastructure_ code.
```bash
cd aws-insurancelake-infrastructure
```
1. Create a Python virtual environment.
- In AWS CloudShell your home directory is limited to 1 GB of *persistent* storage. To ensure we have enough storage to download and install the required Python packages, you will use AWS CloudShell's *temporary* storage, located in `/tmp`, which has a larger capacity.
```bash
python3 -m venv /tmp/.venv
```
1. Activate the virtual environment.
```bash
source /tmp/.venv/bin/activate
```
1. Install required Python libraries.
- NOTE: You may see a warning stating that a newer version is available; it is safe to ignore this for the Quickstart.
```bash
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
1. Bootstrap CDK in your AWS account.
```bash
cdk bootstrap
```
### Deploy the Application
1. Ensure you are still in the `aws-insurancelake-infrastructure` directory.
1. Deploy infrastructure resources in the development environment (one stack).
```bash
cdk deploy Dev-InsuranceLakeInfrastructurePipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeInfrastructureS3BucketZones
```
1. Review and accept AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) credential creation for the S3 bucket stack.
- Wait for deployment to finish (approximately 5 minutes).
1. Copy the S3 bucket name for the Collect bucket to use later.
- Bucket name will be in the form: `dev-insurancelake-<AWS Account ID>-<Region>-collect`.
1. Switch the working directory to the location of the _etl_ code.
```bash
cd ../aws-insurancelake-etl
```
1. Deploy the ETL resources in the development environment (four stacks).
```bash
cdk deploy Dev-InsuranceLakeEtlPipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeEtlDynamoDb Dev-InsuranceLakeEtlPipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeEtlGlue Dev-InsuranceLakeEtlPipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeEtlStepFunctions Dev-InsuranceLakeEtlPipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeEtlAthenaHelper
```
- Wait for approximately 1 minute for DynamoDB deployment to finish.
1. Review and accept IAM credential creation for the AWS Glue jobs stack.
- Wait approximately 3 minutes for deployment to finish.
1. Review and accept IAM credential creation for the Step Functions stack.
- Wait approximately 7 minutes for deployment of Step Functions and Athena Helper stacks to finish.
### Try out the ETL Process
1. Populate the DynamoDB lookup table with sample lookup data.
```bash
resources/load_dynamodb_lookup_table.py SyntheticGeneralData dev-insurancelake-etl-value-lookup resources/syntheticgeneral_lookup_data.json
```
1. Transfer the sample claim data to the Collect bucket.
```bash
aws s3 cp resources/syntheticgeneral-claim-data.csv s3://<Collect S3 bucket>/SyntheticGeneralData/ClaimData/
```
1. Transfer the sample policy data to the Collect bucket.
```bash
aws s3 cp resources/syntheticgeneral-policy-data.csv s3://<Collect S3 bucket>/SyntheticGeneralData/PolicyData/
```
1. Open [Step Functions](https://console.aws.amazon.com/states/home) in the AWS Console and select `dev-insurancelake-etl-state-machine`.
1. Open the state machine execution in progress and monitor the status until complete.
1. Open [Athena](https://console.aws.amazon.com/athena/home) in the AWS Console.
1. Select `Launch Query Editor`, and change the Workgroup to `insurancelake`.
1. Run the following query to view a sample of prepared data in the consume bucket:
```sql
select * from syntheticgeneraldata_consume.policydata limit 100
```
### Next Steps
* Take the [InsuranceLake Deep Dive Workshop](https://catalog.us-east-1.prod.workshops.aws/workshops/0a85653e-07e9-41a8-960a-2d1bb592331b).
* You may skip to the [Modify and test a transform](https://catalog.us-east-1.prod.workshops.aws/workshops/0a85653e-07e9-41a8-960a-2d1bb592331b/en-US/modify-a-transform) step, as the prior steps overlap with the Quickstart instructions.
* Try out [loading your own data](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/loading_data#landing-source-data).
* Try the [Quickstart with CI/CD](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart_cicd/).
* Dive deeper with the included [user documentation](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/user_documentation/).
* Contact your AWS account team for a solution deep dive, workshops, or AWS Professional Services support.
## Deployment Validation
1. Transfer the sample claim data to the Collect bucket (Source system: SyntheticData, Table: ClaimData).
```bash
aws s3 cp resources/syntheticgeneral-claim-data.csv s3://<Collect S3 bucket>/SyntheticGeneralData/ClaimData/
```
1. Transfer the sample policy data to the Collect bucket (Source system: SyntheticData, Table: PolicyData).
```bash
aws s3 cp resources/syntheticgeneral-policy-data.csv s3://<Collect S3 bucket>/SyntheticGeneralData/PolicyData/
```
1. Upon successful transfer of the file, an event notification from S3 will trigger the state-machine-trigger Lambda function.
1. The Lambda function will insert a record into the DynamoDB table `{environment}-{resource_name_prefix}-etl-job-audit` to track job start status.
1. The Lambda function will also trigger the Step Functions State Machine. The State Machine execution name will be `<filename>-<YYYYMMDDHHMMSSxxxxxx>` and have the required metadata as input parameters.
1. The State Machine will trigger the AWS Glue job for Collect to Cleanse data processing.
1. The Collect to Cleanse AWS Glue job will execute the transformation logic defined in configuration files.
1. The AWS Glue job will load the data into the Cleanse bucket using the provided metadata. The data will be stored in S3 as `s3://{environment}-{resource_name_prefix}-{account}-{region}-cleanse/syntheticgeneraldata/claimdata/year=YYYY/month=MM/day=DD` in Apache Parquet format.
1. The AWS Glue job will create or update the Data Catalog table using the table name passed as a parameter based on the folder name (`PolicyData` and `ClaimData`).
1. After the Collect to Cleanse AWS Glue job completes, the State Machine will trigger the Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job.
1. The Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job will execute the SQL logic defined in configuration files.
1. The Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job will store the resulting data set in S3 as `s3://{environment}-{resource_name_prefix}-{account}-{region}-consume/syntheticgeneraldata/claimdata/year=YYYY/month=MM/day=DD` in Apache Parquet format.
1. The Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job will create or update the Data Catalog table.
1. After successful completion of the Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job, the State Machine will trigger the etl-job-auditor Lambda function to update the DynamoDB table `{environment}-{resource_name_prefix}-etl-job-audit` with the latest status.
1. An Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) notification will be sent to all subscribed users.
1. To validate the data load, use Athena and execute the following query:
```sql
select * from syntheticgeneraldata_consume.policydata limit 100
```
## Cleanup
Refer to the [Quickstart Cleanup](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart_cleanup/) instructions.
---
## Architecture
This section focuses on the overall InsuranceLake architecture and the components of the ETL.
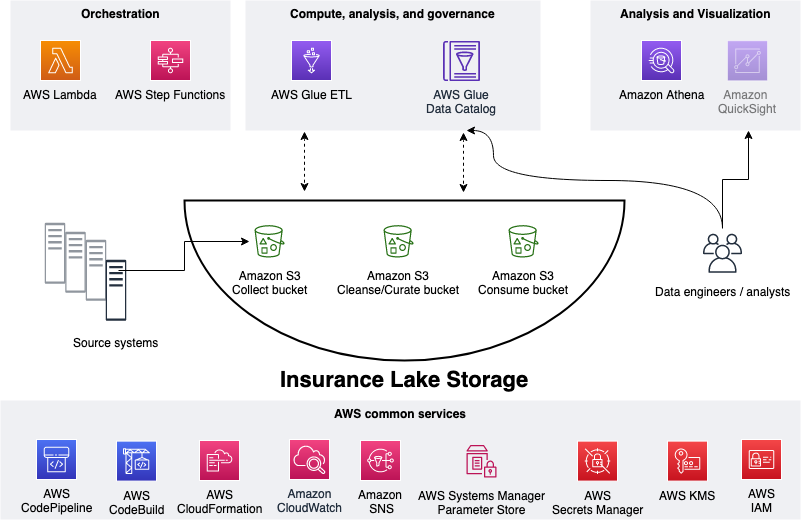
### Collect, Cleanse, Consume
As shown in the figure below, we use S3 for storage, specifically three different S3 buckets:
1. Collect bucket to store raw data in its original format.
1. Cleanse/Curate bucket to store the data that meets the quality and consistency requirements for the data source.
1. Consume bucket for data that is used by analysts and data consumers (for example, Amazon Quicksight, Amazon Sagemaker).
InsuranceLake is designed to support a number of source systems with different file formats and data partitions. To demonstrate, we have provided a CSV parser and sample data files for a source system with two data tables, which are uploaded to the Collect bucket.
We use Lambda and Step Functions for orchestration and scheduling of ETL workloads. We then use AWS Glue with PySpark for ETL and data cataloging, DynamoDB for transformation persistence, and Athena for interactive queries and analysis. We use various AWS services for logging, monitoring, security, authentication, authorization, notification, build, and deployment.
**Note:** [AWS Lake Formation](https://aws.amazon.com/lake-formation/) is a service that makes it easy to set up a secure data lake in days. [Amazon QuickSight](https://aws.amazon.com/quicksight/) is a scalable, serverless, embeddable, machine learning-powered business intelligence (BI) service built for the cloud. [Amazon DataZone](https://aws.amazon.com/datazone/) is a data management service that makes it faster and easier for customers to catalog, discover, share, and govern data stored across AWS, on premises, and third-party sources. These three services are not used in this solution but can be added.
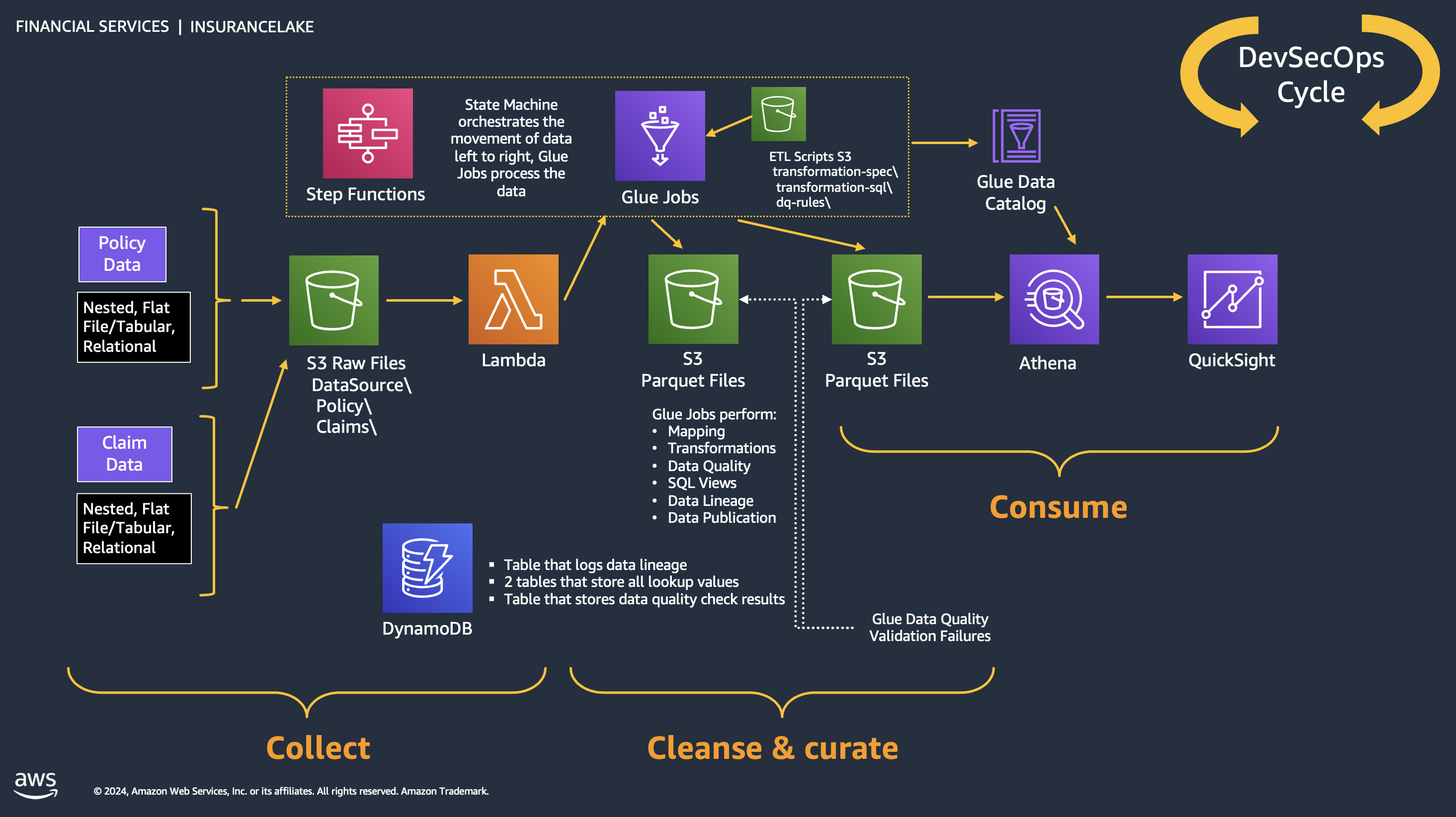
### ETL
The figure below represents the ETL resources we provision for the data lake.
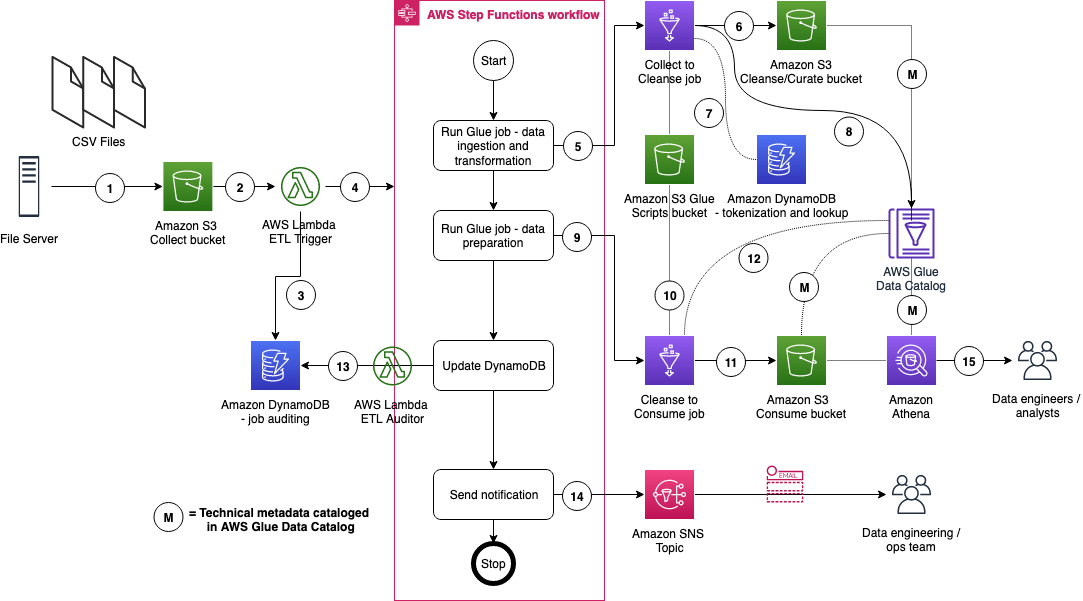
1. A file server uploads files to the Collect bucket of InsuranceLake; file server is a data producer or source for the data lake.
1. S3 triggers an ObjectCreated event notification to Lambda function.
1. The Lambda function inserts job information in an DynamoDB table.
1. The Lambda function starts an execution of Step Functions State machine.
1. This step runs the first AWS Glue job: initiates data processing from Collect to Cleanse.
1. An AWS Glue job will process the data from Collect to Cleanse; source data is assumed to be in CSV format and will be converted to Parquet format.
1. DynamoDB stores original values from PII tokenization, and provides lookup data to the AWS Glue job.
1. After creating Apache Parquet data, the job updates the AWS Glue Data Catalog table.
1. In this step the second AWS Glue job initiates data processing from Cleanse to Consume.
1. The AWS Glue Cleanse to Consume job fetches data transformation rules from AWS Glue etl-scripts bucket, and runs transformations.
1. The AWS Glue job stores prepared data in Apache Parquet format in the Consume bucket.
1. The AWS Glue job updates the AWS Glue Data Catalog table.
1. The AWS Glue job updates the DynamoDB table with job status.
1. Step Functions sends an SNS notification.
1. Data engineers or analysts analyze data using Athena.
---
## Security
For more information on how AWS services come together in InsuranceLake to align with the [Security Pillar of the AWS Well-Architected Framework](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/latest/financial-services-industry-lens/security.html) refer to the [InsuranceLake Well-Architected Pillar Alignment for Security](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/well_architected/#security).
### Infrastructure Code
InsuranceLake uses [CDK-nag](https://github.com/cdklabs/cdk-nag) to confirm AWS resource security recommendations are followed. CDK-nag can generate warnings, which may need to be fixed depending on the context, and errors, which will interrupt the stack synthesis and prevent any deployment.
To force synthesis of all stacks (including the CodePipeline deployed stacks), which will check all code and generate all reports, use the following command:
```bash
cdk synth '**'
```
When this operation is complete, you will also have access to the CDK-nag reports in CSV format in the `cdk.out` directory and assembly directories.
By default the [AWS Solutions Rules Pack](https://github.com/cdklabs/cdk-nag/blob/main/RULES.md#aws-solutions) is used, but any combination of CDK Nag Rules packs can be selected by adjusting the source code **in four locations** (two for both the Infrastructure and ETL codebases):
[Infrastructure app.py Line 21](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-infrastructure/blob/main/app.py#L21), [ETL app.py Line 20](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl/blob/main/app.py#L20):
```python
# Enable CDK Nag for the Mirror repository, Pipeline, and related stacks
# Environment stacks must be enabled on the Stage resource
cdk.Aspects.of(app).add(AwsSolutionsChecks())
```
[Infrastructure pipeline_stack.py Line 148](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-infrastructure/blob/main/lib/pipeline_stack.py#L148), [ETL pipeline_stack.py Line 147](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl/blob/main/lib/pipeline_stack.py#L147)
```python
# Enable CDK Nag for environment stacks before adding to
# pipeline, which are deployed with CodePipeline
cdk.Aspects.of(pipeline_deploy_stage).add(AwsSolutionsChecks())
```
### Application Code
InsuranceLake uses [Bandit](https://bandit.readthedocs.io/en/latest) and [Amazon CodeGuru](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codeguru/latest/reviewer-ug/welcome.html) for static code analysis of all helper scripts, Lambda functions, and PySpark Glue Jobs.
To configure CodeGuru Code Reviews, follow the [AWS Documentation on creating Code Reviews](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codeguru/latest/reviewer-ug/create-code-reviews.html).
To scan all application code using Bandit, use the following command:
```bash
bandit -r --ini .bandit
```
---
## Additional Resources
- [InsuranceLake Documentation](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl)
- [InsuranceLake Quickstart AWS Workshop](https://catalog.workshops.aws/insurancelake)
- [InsuranceLake Deep Dive AWS Workshop](https://catalog.us-east-1.prod.workshops.aws/workshops/0a85653e-07e9-41a8-960a-2d1bb592331b)
- [General Insurance dashboard](https://democentral.learnquicksight.online/#Dashboard-DashboardDemo-General-Insurance) on Quicksight's DemoCentral using Consume-ready-data
- [Life Insurance dashboard](https://democentral.learnquicksight.online/#Dashboard-DashboardDemo-Life-Insurance) also on Quicksight's DemoCentral
- [AWS Solutions Library Guidance for Modern Insurance Data Lakes](https://aws.amazon.com/solutions/guidance/modern-insurance-data-lakes-on-aws)
- [InsuranceLake in the AWS Well-Architected Framework Financial Services Industry Lens](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/latest/financial-services-industry-lens/insurance-lake.html)
## Authors
The following people are involved in the design, architecture, development, testing, and review of this solution:
* **Cory Visi**, Senior Solutions Architect, Amazon Web Services
* **Ratnadeep Bardhan Roy**, Senior Solutions Architect, Amazon Web Services
* **George Gallo**, Senior Solutions Architect, Amazon Web Services
* **Jose Guay**, Enterprise Support, Amazon Web Services
* **Isaiah Grant**, Cloud Consultant, 2nd Watch, Inc.
* **Muhammad Zahid Ali**, Data Architect, Amazon Web Services
* **Ravi Itha**, Senior Data Architect, Amazon Web Services
* **Justiono Putro**, Cloud Infrastructure Architect, Amazon Web Services
* **Mike Apted**, Principal Solutions Architect, Amazon Web Services
* **Nikunj Vaidya**, Senior DevOps Specialist, Amazon Web Services
## License Summary
This sample code is made available under the MIT-0 license. See the LICENSE file.
Copyright Amazon.com and its affiliates; all rights reserved. This file is Amazon Web Services Content and may not be duplicated or distributed without permission.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl",
"name": "aws-insurancelake-etl",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "aws-insurancelake-etl aws cdk insurance datalake etl glue spark python pyspark",
"author": "Cory Visi <cvisi@amazon.com>, Ratnadeep Bardhan Roy <rdbroy@amazon.com>, George Gallo <geogallo@amazon.com>, Jose Guay <jrguay@amazon.com>, Isaiah Grant <igrant@2ndwatch.com>, Ravi Itha <itharav@amazon.com>, Zahid Muhammad Ali <zhidli@amazon.com>",
"author_email": null,
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/71/fa/f0893edf1e1795f7589d30c0e14077ee731ea86d7e5589be0d5edea3b3a1/aws_insurancelake_etl-4.2.2.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "<!--\n Title: AWS InsuranceLake\n Description: Serverless modern data lake solution and reference architecture fit for the insurance industry built on AWS\n Author: cvisi@amazon.com\n -->\n# InsuranceLake ETL\n\n## Overview\n\nThis solution guidance helps you deploy extract, transform, load (ETL) processes and data storage resources to create InsuranceLake. It uses Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) buckets for storage, [AWS Glue](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/glue/) for data transformation, and [AWS Cloud Development Kit (CDK) Pipelines](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cdk/latest/guide/cdk_pipeline.html). The solution is originally based on the AWS blog [Deploy data lake ETL jobs using CDK Pipelines](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/devops/deploying-data-lake-etl-jobs-using-cdk-pipelines/).\n\nThe best way to learn about InsuranceLake is to follow the [Quickstart guide](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart/) and try it out.\n\nThe InsuranceLake solution is comprised of two codebases: [Infrastructure](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-infrastructure) and [ETL](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl).\n\nSpecifically, this solution helps you to:\n\n* Deploy a \"3 Cs\" (Collect, Cleanse, Consume) architecture InsuranceLake.\n* Deploy ETL jobs needed to make common insurance industry data souces available in a data lake.\n* Use pySpark Glue jobs and supporting resoures to perform data transforms in a modular approach.\n* Build and replicate the application in multiple environments quickly.\n* Deploy ETL jobs from a central deployment account to multiple AWS environments such as Dev, Test, and Prod.\n* Leverage the benefit of self-mutating feature of CDK Pipelines; specifically, the pipeline itself is infrastructure as code and can be changed as part of the deployment.\n* Increase the speed of prototyping, testing, and deployment of new ETL jobs.\n\n\n\n## Contents\n\n* [Cost](#cost)\n * [Sample Cost Table](#sample-cost-table)\n* [Quickstart](#quickstart)\n * [Python/CDK Basics](#pythoncdk-basics)\n * [Deploy the Application](#deploy-the-application)\n * [Try out the ETL Process](#try-out-the-etl-process)\n * [Next Steps](#next-steps)\n* [Deployment Validation](#deployment-validation)\n* [Cleanup](#cleanup)\n* [Architecture](#architecture)\n * [Collect, Cleanse, Consume](#collect-cleanse-consume)\n * [ETL](#etl)\n * [Well Architected Pillars](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/well_architected/)\n* [Security](#security)\n * [Infrastructure Code](#infrastructure-code)\n * [Application Code](#application-code)\n* [Online Documentation](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/)\n* [Additional resources](#additional-resources)\n* [Authors](#authors)\n* [License Summary](#license-summary)\n\n## Cost\n\nThis solution uses the following services: [Amazon S3](https://aws.amazon.com/s3/pricing/), [AWS Glue](https://aws.amazon.com/glue/pricing/), [AWS Step Functions](https://aws.amazon.com/step-functions/pricing/), [Amazon DynamoDB](https://aws.amazon.com/dynamodb/pricing/), [AWS Lambda](https://aws.amazon.com/lambda/pricing/), [Amazon CloudWatch](https://aws.amazon.com/cloudwatch/pricing/), [Amazon Athena](https://aws.amazon.com/athena/pricing/), and [AWS CodePipeline](https://aws.amazon.com/codepipeline/pricing/) for continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) installation only.\n\nAn estimated cost for following the [Quickstart](#quickstart) and [Quickstart with CI/CD](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart_cicd/) instructions, assuming a total of 8 Glue DPU hours and cleaning all resources when finished, **your cost will not be higher than $2**. This cost could be less as some services are included in the [Free Tier](https://aws.amazon.com/free/).\n\n_We recommend creating a\u00a0[Budget](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/cost-management/latest/userguide/budgets-managing-costs.html)\u00a0through\u00a0[AWS Cost Explorer](https://aws.amazon.com/aws-cost-management/aws-cost-explorer/)\u00a0to help manage costs. Prices are subject to change. For full details, refer to the pricing webpage for each AWS service used in this solution._\n\n### Sample Cost Table\n\nThe following table provides a sample cost breakdown for deploying this Guidance with the default parameters in the US East (Ohio) Region for one month with pricing as of _2 October 2024_.\n\n|AWS service |Dimensions |Cost [USD]\n|--- |--- |---\n|AWS Glue |per DPU-Hour for each Apache Spark or Spark Streaming job, billed per second with a 1-minute minimum |$0.44\n|Amazon S3 |per GB of storage used, Frequent Access Tier, first 50 TB per month<br>PUT, COPY, POST, LIST requests (per 1,000 requests)<br>GET, SELECT, and all other requests (per 1,000 requests) |$0.023<br>$0.005<br>$0.0004\n|Amazon Athena |per TB of data scanned |$5.00\n|Amazon DynamoDB |per GB-month of storage, over 25 GB<br>per million Write Request Units (WRU)<br>per million Read Request Units (RRU) |$0.25<br>$1.25<br>$0.25\n\n## Quickstart\n\nIf you'd like to get started quickly transforming some sample raw insurance data and running SQL on the resulting dataset, **and without worrying about CI/CD**, follow the steps in this section.\n\n### Python/CDK Basics\n\n1. Open the AWS Console in the `us-east-2 (Ohio)` Region.\n - NOTE: InsuranceLake uses `us-east-2` by default. To change the Region, refer to the [Quickstart with CI/CD](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart_cicd/).\n1. Select `CloudShell` at the bottom of the page and wait for a few seconds until it is available for use.\n1. Ensure you are using the latest version of the AWS SDK for Node.js and AWS CDK.\n ```\n sudo npm install -g aws-lib aws-cdk\n ```\n1. Clone the repositories.\n ```bash\n git clone https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-infrastructure.git\n git clone https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl.git\n ```\n1. Change the working directory to the location of the _infrastructure_ code.\n ```bash\n cd aws-insurancelake-infrastructure\n ```\n1. Create a Python virtual environment.\n - In AWS CloudShell your home directory is limited to 1 GB of *persistent* storage. To ensure we have enough storage to download and install the required Python packages, you will use AWS CloudShell's *temporary* storage, located in `/tmp`, which has a larger capacity.\n ```bash\n python3 -m venv /tmp/.venv\n ```\n1. Activate the virtual environment.\n ```bash\n source /tmp/.venv/bin/activate\n ```\n1. Install required Python libraries.\n - NOTE: You may see a warning stating that a newer version is available; it is safe to ignore this for the Quickstart.\n ```bash\n pip install -r requirements.txt\n ```\n1. Bootstrap CDK in your AWS account.\n ```bash\n cdk bootstrap\n ```\n\n### Deploy the Application\n\n1. Ensure you are still in the `aws-insurancelake-infrastructure` directory.\n1. Deploy infrastructure resources in the development environment (one stack).\n ```bash\n cdk deploy Dev-InsuranceLakeInfrastructurePipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeInfrastructureS3BucketZones\n ```\n1. Review and accept AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) credential creation for the S3 bucket stack.\n - Wait for deployment to finish (approximately 5 minutes).\n1. Copy the S3 bucket name for the Collect bucket to use later.\n - Bucket name will be in the form: `dev-insurancelake-<AWS Account ID>-<Region>-collect`.\n1. Switch the working directory to the location of the _etl_ code.\n ```bash\n cd ../aws-insurancelake-etl\n ```\n1. Deploy the ETL resources in the development environment (four stacks).\n ```bash\n cdk deploy Dev-InsuranceLakeEtlPipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeEtlDynamoDb Dev-InsuranceLakeEtlPipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeEtlGlue Dev-InsuranceLakeEtlPipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeEtlStepFunctions Dev-InsuranceLakeEtlPipeline/Dev/InsuranceLakeEtlAthenaHelper\n ```\n - Wait for approximately 1 minute for DynamoDB deployment to finish.\n1. Review and accept IAM credential creation for the AWS Glue jobs stack.\n - Wait approximately 3 minutes for deployment to finish.\n1. Review and accept IAM credential creation for the Step Functions stack.\n - Wait approximately 7 minutes for deployment of Step Functions and Athena Helper stacks to finish.\n\n### Try out the ETL Process\n\n1. Populate the DynamoDB lookup table with sample lookup data.\n ```bash\n resources/load_dynamodb_lookup_table.py SyntheticGeneralData dev-insurancelake-etl-value-lookup resources/syntheticgeneral_lookup_data.json\n ```\n1. Transfer the sample claim data to the Collect bucket.\n ```bash\n aws s3 cp resources/syntheticgeneral-claim-data.csv s3://<Collect S3 bucket>/SyntheticGeneralData/ClaimData/\n ```\n1. Transfer the sample policy data to the Collect bucket.\n ```bash\n aws s3 cp resources/syntheticgeneral-policy-data.csv s3://<Collect S3 bucket>/SyntheticGeneralData/PolicyData/\n ```\n1. Open [Step Functions](https://console.aws.amazon.com/states/home) in the AWS Console and select `dev-insurancelake-etl-state-machine`.\n \n1. Open the state machine execution in progress and monitor the status until complete.\n \n1. Open [Athena](https://console.aws.amazon.com/athena/home) in the AWS Console.\n1. Select `Launch Query Editor`, and change the Workgroup to `insurancelake`.\n1. Run the following query to view a sample of prepared data in the consume bucket:\n ```sql\n select * from syntheticgeneraldata_consume.policydata limit 100\n ```\n\n### Next Steps\n\n* Take the [InsuranceLake Deep Dive Workshop](https://catalog.us-east-1.prod.workshops.aws/workshops/0a85653e-07e9-41a8-960a-2d1bb592331b).\n * You may skip to the [Modify and test a transform](https://catalog.us-east-1.prod.workshops.aws/workshops/0a85653e-07e9-41a8-960a-2d1bb592331b/en-US/modify-a-transform) step, as the prior steps overlap with the Quickstart instructions.\n* Try out [loading your own data](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/loading_data#landing-source-data).\n* Try the [Quickstart with CI/CD](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart_cicd/).\n* Dive deeper with the included [user documentation](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/user_documentation/).\n* Contact your AWS account team for a solution deep dive, workshops, or AWS Professional Services support.\n\n## Deployment Validation\n\n1. Transfer the sample claim data to the Collect bucket (Source system: SyntheticData, Table: ClaimData).\n ```bash\n aws s3 cp resources/syntheticgeneral-claim-data.csv s3://<Collect S3 bucket>/SyntheticGeneralData/ClaimData/\n ```\n\n1. Transfer the sample policy data to the Collect bucket (Source system: SyntheticData, Table: PolicyData).\n ```bash\n aws s3 cp resources/syntheticgeneral-policy-data.csv s3://<Collect S3 bucket>/SyntheticGeneralData/PolicyData/\n ```\n\n1. Upon successful transfer of the file, an event notification from S3 will trigger the state-machine-trigger Lambda function.\n\n1. The Lambda function will insert a record into the DynamoDB table `{environment}-{resource_name_prefix}-etl-job-audit` to track job start status.\n\n1. The Lambda function will also trigger the Step Functions State Machine. The State Machine execution name will be `<filename>-<YYYYMMDDHHMMSSxxxxxx>` and have the required metadata as input parameters.\n\n1. The State Machine will trigger the AWS Glue job for Collect to Cleanse data processing.\n\n1. The Collect to Cleanse AWS Glue job will execute the transformation logic defined in configuration files.\n\n1. The AWS Glue job will load the data into the Cleanse bucket using the provided metadata. The data will be stored in S3 as `s3://{environment}-{resource_name_prefix}-{account}-{region}-cleanse/syntheticgeneraldata/claimdata/year=YYYY/month=MM/day=DD` in Apache Parquet format.\n\n1. The AWS Glue job will create or update the Data Catalog table using the table name passed as a parameter based on the folder name (`PolicyData` and `ClaimData`).\n\n1. After the Collect to Cleanse AWS Glue job completes, the State Machine will trigger the Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job.\n\n1. The Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job will execute the SQL logic defined in configuration files.\n\n1. The Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job will store the resulting data set in S3 as `s3://{environment}-{resource_name_prefix}-{account}-{region}-consume/syntheticgeneraldata/claimdata/year=YYYY/month=MM/day=DD` in Apache Parquet format.\n\n1. The Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job will create or update the Data Catalog table.\n\n1. After successful completion of the Cleanse to Consume AWS Glue job, the State Machine will trigger the etl-job-auditor Lambda function to update the DynamoDB table `{environment}-{resource_name_prefix}-etl-job-audit` with the latest status.\n\n1. An Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) notification will be sent to all subscribed users.\n\n1. To validate the data load, use Athena and execute the following query:\n\n ```sql\n select * from syntheticgeneraldata_consume.policydata limit 100\n ```\n\n## Cleanup\n\nRefer to the [Quickstart Cleanup](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/quickstart_cleanup/) instructions.\n\n---\n\n## Architecture\n\nThis section focuses on the overall InsuranceLake architecture and the components of the ETL.\n\n### Collect, Cleanse, Consume\n\nAs shown in the figure below, we use S3 for storage, specifically three different S3 buckets:\n1. Collect bucket to store raw data in its original format.\n1. Cleanse/Curate bucket to store the data that meets the quality and consistency requirements for the data source.\n1. Consume bucket for data that is used by analysts and data consumers (for example, Amazon Quicksight, Amazon Sagemaker).\n\nInsuranceLake is designed to support a number of source systems with different file formats and data partitions. To demonstrate, we have provided a CSV parser and sample data files for a source system with two data tables, which are uploaded to the Collect bucket.\n\nWe use Lambda and Step Functions for orchestration and scheduling of ETL workloads. We then use AWS Glue with PySpark for ETL and data cataloging, DynamoDB for transformation persistence, and Athena for interactive queries and analysis. We use various AWS services for logging, monitoring, security, authentication, authorization, notification, build, and deployment.\n\n**Note:** [AWS Lake Formation](https://aws.amazon.com/lake-formation/) is a service that makes it easy to set up a secure data lake in days. [Amazon QuickSight](https://aws.amazon.com/quicksight/) is a scalable, serverless, embeddable, machine learning-powered business intelligence (BI) service built for the cloud. [Amazon DataZone](https://aws.amazon.com/datazone/) is a data management service that makes it faster and easier for customers to catalog, discover, share, and govern data stored across AWS, on premises, and third-party sources. These three services are not used in this solution but can be added.\n\n\n\n### ETL\n\nThe figure below represents the ETL resources we provision for the data lake.\n\n\n\n1. A file server uploads files to the Collect bucket of InsuranceLake; file server is a data producer or source for the data lake.\n1. S3 triggers an ObjectCreated event notification to Lambda function.\n1. The Lambda function inserts job information in an DynamoDB table.\n1. The Lambda function starts an execution of Step Functions State machine.\n1. This step runs the first AWS Glue job: initiates data processing from Collect to Cleanse.\n1. An AWS Glue job will process the data from Collect to Cleanse; source data is assumed to be in CSV format and will be converted to Parquet format.\n1. DynamoDB stores original values from PII tokenization, and provides lookup data to the AWS Glue job.\n1. After creating Apache Parquet data, the job updates the AWS Glue Data Catalog table.\n1. In this step the second AWS Glue job initiates data processing from Cleanse to Consume.\n1. The AWS Glue Cleanse to Consume job fetches data transformation rules from AWS Glue etl-scripts bucket, and runs transformations.\n1. The AWS Glue job stores prepared data in Apache Parquet format in the Consume bucket.\n1. The AWS Glue job updates the AWS Glue Data Catalog table.\n1. The AWS Glue job updates the DynamoDB table with job status.\n1. Step Functions sends an SNS notification.\n1. Data engineers or analysts analyze data using Athena.\n\n---\n\n## Security\n\nFor more information on how AWS services come together in InsuranceLake to align with the [Security Pillar of the AWS Well-Architected Framework](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/latest/financial-services-industry-lens/security.html) refer to the [InsuranceLake Well-Architected Pillar Alignment for Security](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl/well_architected/#security).\n\n### Infrastructure Code\n\nInsuranceLake uses [CDK-nag](https://github.com/cdklabs/cdk-nag) to confirm AWS resource security recommendations are followed. CDK-nag can generate warnings, which may need to be fixed depending on the context, and errors, which will interrupt the stack synthesis and prevent any deployment.\n\nTo force synthesis of all stacks (including the CodePipeline deployed stacks), which will check all code and generate all reports, use the following command:\n\n```bash\ncdk synth '**'\n```\n\nWhen this operation is complete, you will also have access to the CDK-nag reports in CSV format in the `cdk.out` directory and assembly directories.\n\nBy default the [AWS Solutions Rules Pack](https://github.com/cdklabs/cdk-nag/blob/main/RULES.md#aws-solutions) is used, but any combination of CDK Nag Rules packs can be selected by adjusting the source code **in four locations** (two for both the Infrastructure and ETL codebases):\n\n[Infrastructure app.py Line 21](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-infrastructure/blob/main/app.py#L21), [ETL app.py Line 20](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl/blob/main/app.py#L20):\n\n```python\n# Enable CDK Nag for the Mirror repository, Pipeline, and related stacks\n# Environment stacks must be enabled on the Stage resource\ncdk.Aspects.of(app).add(AwsSolutionsChecks())\n```\n\n[Infrastructure pipeline_stack.py Line 148](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-infrastructure/blob/main/lib/pipeline_stack.py#L148), [ETL pipeline_stack.py Line 147](https://github.com/aws-solutions-library-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl/blob/main/lib/pipeline_stack.py#L147)\n```python\n # Enable CDK Nag for environment stacks before adding to\n # pipeline, which are deployed with CodePipeline\n cdk.Aspects.of(pipeline_deploy_stage).add(AwsSolutionsChecks())\n```\n\n### Application Code\n\nInsuranceLake uses [Bandit](https://bandit.readthedocs.io/en/latest) and [Amazon CodeGuru](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codeguru/latest/reviewer-ug/welcome.html) for static code analysis of all helper scripts, Lambda functions, and PySpark Glue Jobs.\n\nTo configure CodeGuru Code Reviews, follow the [AWS Documentation on creating Code Reviews](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/codeguru/latest/reviewer-ug/create-code-reviews.html).\n\nTo scan all application code using Bandit, use the following command:\n\n```bash\nbandit -r --ini .bandit\n```\n\n---\n\n## Additional Resources\n\n- [InsuranceLake Documentation](https://aws-solutions-library-samples.github.io/aws-insurancelake-etl)\n- [InsuranceLake Quickstart AWS Workshop](https://catalog.workshops.aws/insurancelake)\n- [InsuranceLake Deep Dive AWS Workshop](https://catalog.us-east-1.prod.workshops.aws/workshops/0a85653e-07e9-41a8-960a-2d1bb592331b)\n- [General Insurance dashboard](https://democentral.learnquicksight.online/#Dashboard-DashboardDemo-General-Insurance) on Quicksight's DemoCentral using Consume-ready-data\n- [Life Insurance dashboard](https://democentral.learnquicksight.online/#Dashboard-DashboardDemo-Life-Insurance) also on Quicksight's DemoCentral\n- [AWS Solutions Library Guidance for Modern Insurance Data Lakes](https://aws.amazon.com/solutions/guidance/modern-insurance-data-lakes-on-aws)\n- [InsuranceLake in the AWS Well-Architected Framework Financial Services Industry Lens](https://docs.aws.amazon.com/wellarchitected/latest/financial-services-industry-lens/insurance-lake.html)\n\n## Authors\n\nThe following people are involved in the design, architecture, development, testing, and review of this solution:\n\n* **Cory Visi**, Senior Solutions Architect, Amazon Web Services\n* **Ratnadeep Bardhan Roy**, Senior Solutions Architect, Amazon Web Services\n* **George Gallo**, Senior Solutions Architect, Amazon Web Services\n* **Jose Guay**, Enterprise Support, Amazon Web Services\n* **Isaiah Grant**, Cloud Consultant, 2nd Watch, Inc.\n* **Muhammad Zahid Ali**, Data Architect, Amazon Web Services\n* **Ravi Itha**, Senior Data Architect, Amazon Web Services\n* **Justiono Putro**, Cloud Infrastructure Architect, Amazon Web Services\n* **Mike Apted**, Principal Solutions Architect, Amazon Web Services\n* **Nikunj Vaidya**, Senior DevOps Specialist, Amazon Web Services\n\n## License Summary\n\nThis sample code is made available under the MIT-0 license. See the LICENSE file.\n\nCopyright Amazon.com and its affiliates; all rights reserved. This file is Amazon Web Services Content and may not be duplicated or distributed without permission.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "MIT-0",
"summary": "A CDK Python app for deploying ETL jobs that operate data pipelines for InsuranceLake in AWS",
"version": "4.2.2",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/aws-samples/aws-insurancelake-etl"
},
"split_keywords": [
"aws-insurancelake-etl",
"aws",
"cdk",
"insurance",
"datalake",
"etl",
"glue",
"spark",
"python",
"pyspark"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "2a94c1eb59520bfb175f4261c3ea62d38b5d65e5449d7f9b60ce5bb2c7fc9031",
"md5": "994dc16f73de0b3ae36c5017bb1455da",
"sha256": "f5b231edf2e8f2367d68c458712aad449357173182c145b0d903b71ad5bfc952"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "aws_insurancelake_etl-4.2.2-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "994dc16f73de0b3ae36c5017bb1455da",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"size": 77185,
"upload_time": "2025-08-16T02:11:49",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-08-16T02:11:49.383873Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/2a/94/c1eb59520bfb175f4261c3ea62d38b5d65e5449d7f9b60ce5bb2c7fc9031/aws_insurancelake_etl-4.2.2-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "71faf0893edf1e1795f7589d30c0e14077ee731ea86d7e5589be0d5edea3b3a1",
"md5": "2a139a304cf9cb796ac630c2cedff308",
"sha256": "d586c3acd43b678d2c220bba8e5ef6a8b78e2beeb5b7191384370c2bcb512860"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "aws_insurancelake_etl-4.2.2.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "2a139a304cf9cb796ac630c2cedff308",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"size": 54145,
"upload_time": "2025-08-16T02:11:50",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-08-16T02:11:50.990038Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/71/fa/f0893edf1e1795f7589d30c0e14077ee731ea86d7e5589be0d5edea3b3a1/aws_insurancelake_etl-4.2.2.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-08-16 02:11:50",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "aws-samples",
"github_project": "aws-insurancelake-etl",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": true,
"github_actions": true,
"requirements": [],
"lcname": "aws-insurancelake-etl"
}

