| Name | Galileo-Flow-SDK JSON |
| Version |
0.1.1
 JSON
JSON |
| download |
| home_page | None |
| Summary | Reading a flow rate from Galileo Flow Sensor |
| upload_time | 2024-07-10 14:22:31 |
| maintainer | None |
| docs_url | None |
| author | Galileo (MIC) |
| requires_python | None |
| license | None |
| keywords |
python
galileo
|
| VCS |
|
| bugtrack_url |
|
| requirements |
No requirements were recorded.
|
| Travis-CI |
No Travis.
|
| coveralls test coverage |
No coveralls.
|
A class-based interface to the Galileo Flow Sensor
A Galileo-Flow SDK is a class based interface to easily communicate with the Galileo Flow Sensor. It contains essential modules to read the flow rate and do other necessary operations.
**Setting up the GALILEO Sensor**
Setting up the Galileo Sensor is straightforward. First, insert the cartridge to the Base and power on the sensor using type-C USB connector. Make sure that all three flags on the screen are green.
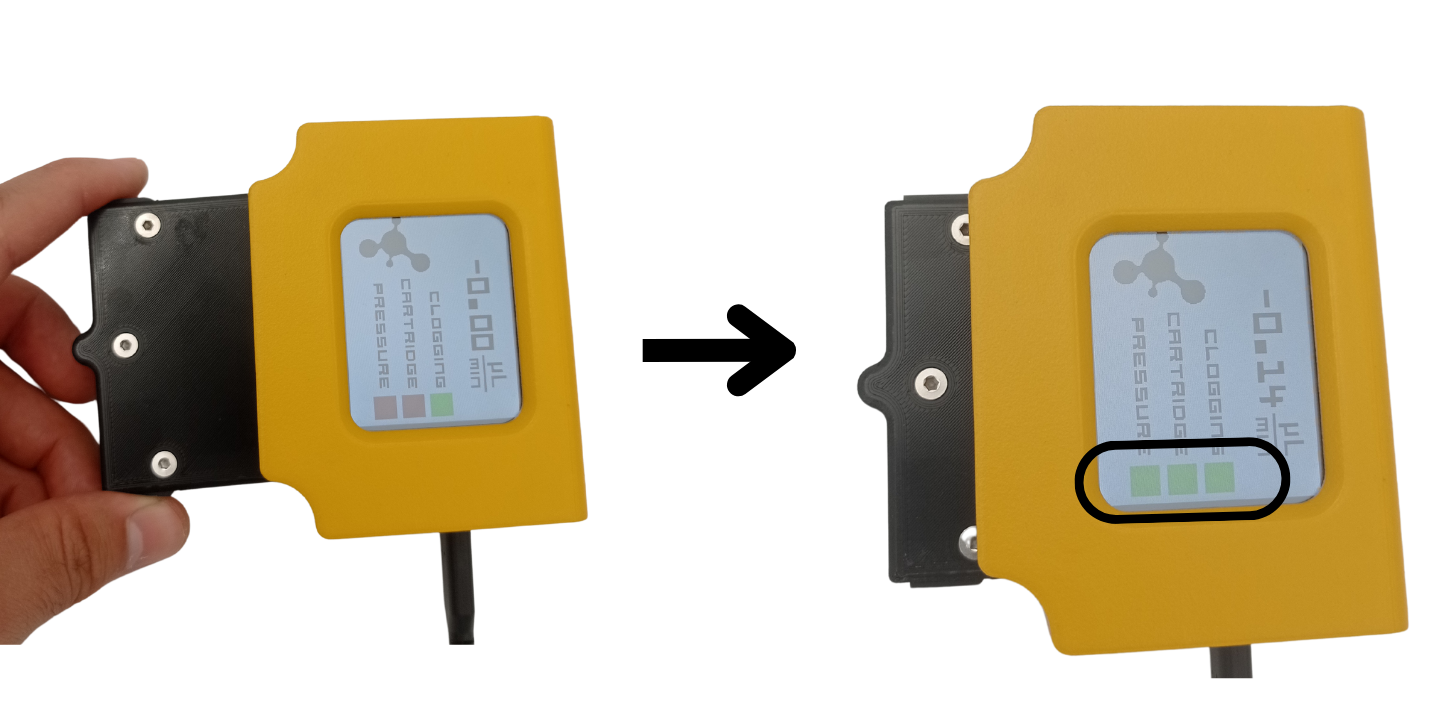
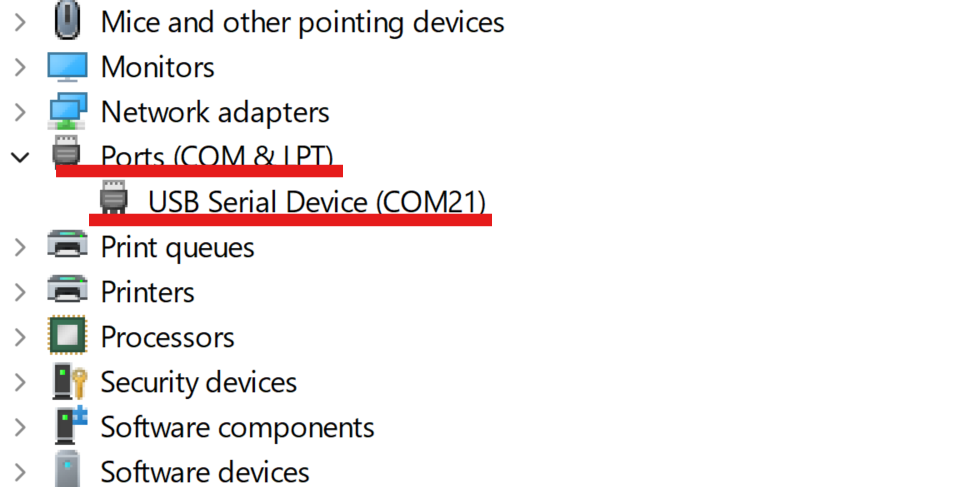
Next, check the COMPORT number of the sensor. In Windows, you can open the Device Manager and find the COMPORT under Ports list:
**Example 1. Reading the flow rate**)
One can use the code snippet below to read the flow rate every second. But, instead of 'COM18',
do not forget to write the actual comport value.
```python
import Galileo-Flow-SDK
galileo_sensor = GalileoFlowSDK("COM18")
while(1):
time.sleep(1)
print('flow is ' , galileo_sensor.read_flow())
```
**Example 2. Reading the liquid type and changing it**
The code snippet below allows to check the liquid type in the Galileo Sensor
```python
import Galileo-Flow-SDK
galileo_sensor = GalileoFlowSDK("COM18")
print('liquid is ' , galileo_sensor.read_liquid())
```
To change the liquid, one can use update_liquid method. The argument ot this method is a number which cooresponds to
a liquid type:
- 0: water,
- 1:ip,
- 2:dmem,
- 3:ethanol
For example, in the code below, we set ethanol as a liquid type:
```python
import Galileo-Flow-SDK
galileo_sensor = GalileoFlowSDK("COM18")
galileo_sensor.update_liquid(3)
time.sleep(1)
print('liquid is ' , galileo_sensor.read_liquid())
galileo_sensor.disconnect()
```
**Example 3. Reading the serial number of the Cartridge**
Every cartridge has its own unique serial number. This number is useful when utilizing several Galileo
Sensors to easily distinguish sensors from each other. In the interface, there is a function to read the serial number:
```python
import Galileo-Flow-SDK
import time
galileo_sensor = GalileoFlowSDK("COM18")
time.sleep(1)
print('liquid is ' , galileo_sensor.read_serial_number())
galileo_sensor.disconnect()
```
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "Galileo-Flow-SDK",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": null,
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "python, galileo",
"author": "Galileo (MIC)",
"author_email": "<galileo@microfluidic.fr>",
"download_url": null,
"platform": null,
"description": "A class-based interface to the Galileo Flow Sensor\r\n\r\nA Galileo-Flow SDK is a class based interface to easily communicate with the Galileo Flow Sensor. It contains essential modules to read the flow rate and do other necessary operations. \r\n\r\n**Setting up the GALILEO Sensor**\r\n\r\nSetting up the Galileo Sensor is straightforward. First, insert the cartridge to the Base and power on the sensor using type-C USB connector. Make sure that all three flags on the screen are green.\r\n\r\n\r\nNext, check the COMPORT number of the sensor. In Windows, you can open the Device Manager and find the COMPORT under Ports list:\r\n\r\n\r\n**Example 1. Reading the flow rate**)\r\nOne can use the code snippet below to read the flow rate every second. But, instead of 'COM18',\r\ndo not forget to write the actual comport value.\r\n\r\n```python\r\nimport Galileo-Flow-SDK\r\ngalileo_sensor = GalileoFlowSDK(\"COM18\")\r\n\r\nwhile(1):\r\n time.sleep(1)\r\n print('flow is ' , galileo_sensor.read_flow())\r\n```\r\n\r\n**Example 2. Reading the liquid type and changing it**\r\n\r\nThe code snippet below allows to check the liquid type in the Galileo Sensor\r\n```python\r\nimport Galileo-Flow-SDK\r\ngalileo_sensor = GalileoFlowSDK(\"COM18\")\r\nprint('liquid is ' , galileo_sensor.read_liquid())\r\n```\r\n\r\nTo change the liquid, one can use update_liquid method. The argument ot this method is a number which cooresponds to\r\na liquid type:\r\n- 0: water, \r\n- 1:ip, \r\n- 2:dmem, \r\n- 3:ethanol\r\n\r\nFor example, in the code below, we set ethanol as a liquid type:\r\n```python\r\nimport Galileo-Flow-SDK\r\ngalileo_sensor = GalileoFlowSDK(\"COM18\")\r\ngalileo_sensor.update_liquid(3)\r\ntime.sleep(1)\r\nprint('liquid is ' , galileo_sensor.read_liquid())\r\ngalileo_sensor.disconnect()\r\n```\r\n\r\n**Example 3. Reading the serial number of the Cartridge**\r\nEvery cartridge has its own unique serial number. This number is useful when utilizing several Galileo\r\nSensors to easily distinguish sensors from each other. In the interface, there is a function to read the serial number:\r\n\r\n```python\r\nimport Galileo-Flow-SDK\r\nimport time\r\ngalileo_sensor = GalileoFlowSDK(\"COM18\")\r\ntime.sleep(1)\r\nprint('liquid is ' , galileo_sensor.read_serial_number())\r\ngalileo_sensor.disconnect()\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "Reading a flow rate from Galileo Flow Sensor",
"version": "0.1.1",
"project_urls": null,
"split_keywords": [
"python",
" galileo"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "00a63725ff0a96a26dadb4529d94270229af24d21f995ce67f4507b195550758",
"md5": "16ad5ff791c1aecafd997fcd444d2356",
"sha256": "e8708587a2f5c75c9aa027b419988cb9fd13647f10fce2ccb118c4b305e8959d"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "Galileo_Flow_SDK-0.1.1-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "16ad5ff791c1aecafd997fcd444d2356",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": null,
"size": 4819,
"upload_time": "2024-07-10T14:22:31",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-07-10T14:22:31.589642Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/00/a6/3725ff0a96a26dadb4529d94270229af24d21f995ce67f4507b195550758/Galileo_Flow_SDK-0.1.1-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-07-10 14:22:31",
"github": false,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"lcname": "galileo-flow-sdk"
}