# Alpha Shape Toolbox
[](https://travis-ci.org/bellockk/alphashape/)
[](http://alphashape.readthedocs.io/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/bellockk/alphashape)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/bellockk/alphashape/master)
[](https://lbesson.mit-license.org/)
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/183085167)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/alphashape/)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/alphashape/)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/alphashape/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/alphashape)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/alphashape)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/alphashape)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/alphashape)
Toolbox for generating n-dimensional alpha shapes.
Alpha shapes are often used to generalize bounding polygons containing sets of points. The alpha parameter is defined as the value `a`, such that an edge of a disk of radius 1/`a` can be drawn between any two edge members of a set of points and still contain all the points. The convex hull, a shape resembling what you would see if you wrapped a rubber band around pegs at all the data points, is an alpha shape where the alpha parameter is equal to zero. In this toolbox we will be generating alpha complexes, which are closely related to alpha shapes, but which consist of straight lines between the edge points instead of arcs of circles.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_shape
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convex_hull
Creating alpha shapes around sets of points usually requires a visually interactive step where the alpha parameter for a concave hull is determined by iterating over or bisecting values to approach a best fit. The alpha shape toolbox provides workflows to shorten the development loop on this manual process, or to bypass it completely by solving for an alpha shape with particular characteristics. A python API is provided to aid in the scripted generation of alpha shapes. A console application is also provided as an example usage of the alpha shape toolbox, and to facilitate generation of alpha shapes from the command line.
* Free software: MIT license
* Documentation: https://alphashape.readthedocs.io.
## Features
### Import Dependencies
```python
import os
import sys
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from descartes import PolygonPatch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.getcwd()))
import alphashape
```
### 2 Dimensional Example
#### Define a set of points
```python
points_2d = [(0., 0.), (0., 1.), (1., 1.), (1., 0.),
(0.5, 0.25), (0.5, 0.75), (0.25, 0.5), (0.75, 0.5)]
```
#### Visualize Test Coordinates
```python
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))
plt.show()
```
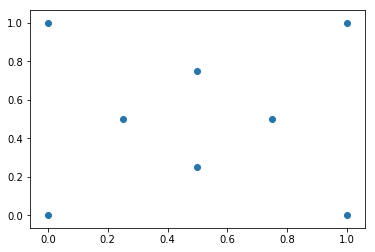
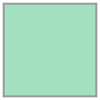
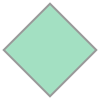
#### Generate an Alpha Shape ($\alpha=0.0$) (Convex Hull)
Every convex hull is an alpha shape, but not every alpha shape is a convex hull. When the `alphashape` function is called with an alpha parameter of 0, a convex hull will always be returned.
##### Create the alpha shape
You can visualize the shape within Jupyter notebooks using the built-in shapely renderer as shown below.
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, 0.)
alpha_shape
```
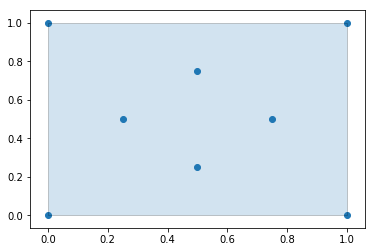
##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data with Matplotlib
```python
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))
ax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))
plt.show()
```
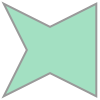
#### Generate an Alpha Shape ($\alpha=2.0$) (Concave Hull)
As we increase the alpha parameter value, the bounding shape will begin to fit the sample data with a more tightly fitting bounding box.
##### Create the alpha shape
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, 2.0)
alpha_shape
```
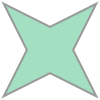
##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data with Matplotlib
```python
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))
ax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))
plt.show()
```
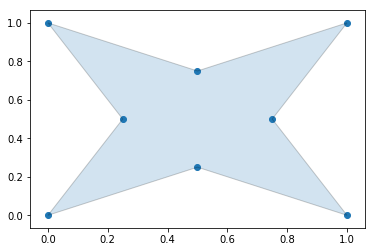
#### Generate an Alpha Shape ($\alpha=3.5$)
If you go too high on the alpha parameter, you will start to lose points from the original data set.
##### Create the alpha shape
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, 3.5)
alpha_shape
```
##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data with Matplotlib
```python
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))
ax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))
plt.show()
```
#### Generate an Alpha Shape (Alpha=5.0)
If you go too far, you will lose everything.
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, 5.0)
print(alpha_shape)
```
GEOMETRYCOLLECTION EMPTY
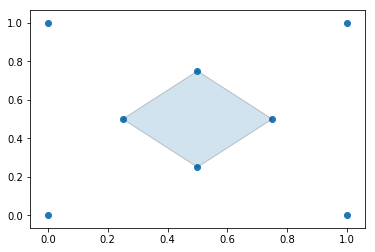
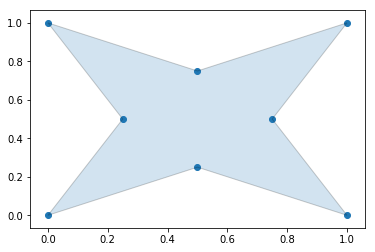
## Using a varying Alpha Parameter
The alpha parameter can be defined locally within a region of points by supplying a callback that will return what alpha parameter to use. This can be utilized to create tighter fitting alpha shapes where point densitities are different in different regions of a data set. In the following example, the alpha parameter is changed based off of the value of the x-coordinate of the points.
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(
points_2d,
lambda ind, r: 1.0 + any(np.array(points_2d)[ind][:,0] == 0.0))
alpha_shape
```
##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data with Matplotlib
```python
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))
ax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))
plt.show()
```
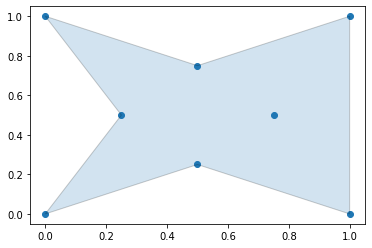
#### Generate an Alpha Shape by Solving for an Optimal Alpha Value
The alpha parameter can be solved for if it is not provided as an argument, but with large datasets this can take a long time to calculate.
##### Create the alpha shape
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d)
alpha_shape
```

##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data
```python
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))
ax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))
plt.show()
```
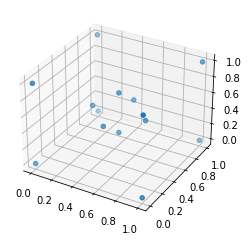
### 3 Dimensional Example
#### Define a set of points
```python
points_3d = [
(0., 0., 0.), (0., 0., 1.), (0., 1., 0.),
(1., 0., 0.), (1., 1., 0.), (1., 0., 1.),
(0., 1., 1.), (1., 1., 1.), (.25, .5, .5),
(.5, .25, .5), (.5, .5, .25), (.75, .5, .5),
(.5, .75, .5), (.5, .5, .75)
]
```
#### Visualize Test Coordinates
```python
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.scatter(df_3d['x'], df_3d['y'], df_3d['z'])
plt.show()
```
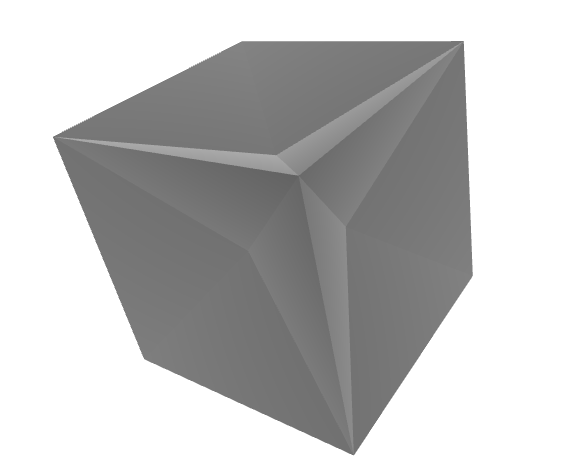
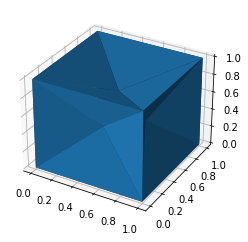
#### Alphashape with Static Alpha Parameter
You can visualize the shape within Jupyter notebooks using the built-in trimesh renderer by calling the `.show()` method as shown below.
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_3d, 1.1)
alpha_shape.show()
```
```python
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.plot_trisurf(*zip(*alpha_shape.vertices), triangles=alpha_shape.faces)
plt.show()
```
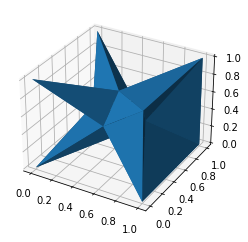
#### Alphashape with Dymanic Alpha Parameter
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_3d, lambda ind, r: 1.0 + any(
np.array(points_3d)[ind][:,0] == 0.0))
alpha_shape.show()
```

```python
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.plot_trisurf(*zip(*alpha_shape.vertices), triangles=alpha_shape.faces)
plt.show()
```
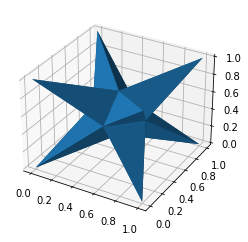
#### Alphashape found by solving for the Alpha Parameter
```python
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_3d)
alpha_shape.show()
```

```python
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.plot_trisurf(*zip(*alpha_shape.vertices), triangles=alpha_shape.faces)
plt.show()
```
### 4 Dimensional Example
#### Define a set of points
```python
points_4d = [
(0., 0., 0., 0.), (0., 0., 0., 1.), (0., 0., 1., 0.),
(0., 1., 0., 0.), (0., 1., 1., 0.), (0., 1., 0., 1.),
(0., 0., 1., 1.), (0., 1., 1., 1.), (1., 0., 0., 0.),
(1., 0., 0., 1.), (1., 0., 1., 0.), (1., 1., 0., 0.),
(1., 1., 1., 0.), (1., 1., 0., 1.), (1., 0., 1., 1.),
(1., 1., 1., 1.), (.25, .5, .5, .5), (.5, .25, .5, .5),
(.5, .5, .25, .5), (.5, .5, .5, .25), (.75, .5, .5, .5),
(.5, .75, .5, .5), (.5, .5, .75, .5), (.5, .5, .5, .75)
]
df_4d = pd.DataFrame(points_4d, columns=['x', 'y', 'z', 'r'])
```
#### Visualize Test Coordinates
```python
fig = plt.figure()
ax = plt.axes(projection='3d')
ax.scatter(df_4d['x'], df_4d['y'], df_4d['z'], c=df_4d['r'])
plt.show()
```

#### The Edges of a 4 Dimensional Alpha Shape are Tetrahedrons Defined by the Following Coordinates (No Visualizations)
```python
alphashape.alphashape(points_4d, 1.0)
```
```python
{(16, 1, 2, 0),
(16, 1, 3, 0),
(16, 2, 3, 0),
(16, 4, 2, 3),
(16, 4, 7, 2),
(16, 4, 7, 3),
(16, 5, 1, 3),
(16, 5, 7, 1),
(16, 5, 7, 3),
(16, 6, 1, 2),
(16, 6, 7, 1),
(16, 6, 7, 2),
(17, 1, 2, 0),
(17, 1, 8, 0),
(17, 2, 8, 0),
(17, 6, 1, 2),
(17, 6, 14, 1),
(17, 6, 14, 2),
(17, 9, 1, 8),
(17, 9, 14, 1),
(17, 9, 14, 8),
(17, 10, 2, 8),
(17, 10, 14, 2),
(17, 10, 14, 8),
(18, 1, 3, 0),
(18, 1, 8, 0),
(18, 3, 8, 0),
(18, 5, 1, 3),
(18, 5, 13, 1),
(18, 5, 13, 3),
(18, 9, 1, 8),
(18, 9, 13, 1),
(18, 9, 13, 8),
(18, 11, 3, 8),
(18, 11, 13, 3),
(18, 11, 13, 8),
(19, 2, 3, 0),
(19, 2, 8, 0),
(19, 3, 8, 0),
(19, 4, 2, 3),
(19, 4, 12, 2),
(19, 4, 12, 3),
(19, 10, 2, 8),
(19, 10, 12, 2),
(19, 10, 12, 8),
(19, 11, 3, 8),
(19, 11, 12, 3),
(19, 11, 12, 8),
(20, 9, 13, 8),
(20, 9, 14, 8),
(20, 9, 14, 13),
(20, 10, 12, 8),
(20, 10, 14, 8),
(20, 10, 14, 12),
(20, 11, 12, 8),
(20, 11, 13, 8),
(20, 11, 13, 12),
(20, 13, 12, 15),
(20, 14, 12, 15),
(20, 14, 13, 15),
(21, 4, 7, 3),
(21, 4, 7, 12),
(21, 4, 12, 3),
(21, 5, 7, 3),
(21, 5, 7, 13),
(21, 5, 13, 3),
(21, 7, 12, 15),
(21, 7, 13, 15),
(21, 11, 12, 3),
(21, 11, 13, 3),
(21, 11, 13, 12),
(21, 13, 12, 15),
(22, 4, 7, 2),
(22, 4, 7, 12),
(22, 4, 12, 2),
(22, 6, 7, 2),
(22, 6, 7, 14),
(22, 6, 14, 2),
(22, 7, 12, 15),
(22, 7, 14, 15),
(22, 10, 12, 2),
(22, 10, 14, 2),
(22, 10, 14, 12),
(22, 14, 12, 15),
(23, 5, 7, 1),
(23, 5, 7, 13),
(23, 5, 13, 1),
(23, 6, 7, 1),
(23, 6, 7, 14),
(23, 6, 14, 1),
(23, 7, 13, 15),
(23, 7, 14, 15),
(23, 9, 13, 1),
(23, 9, 14, 1),
(23, 9, 14, 13),
(23, 14, 13, 15)}
```
## Alpha Shapes with GeoPandas
##### Sample Data
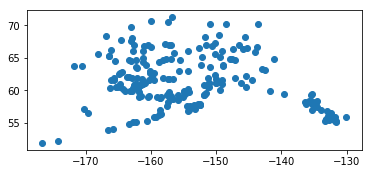
The data used in this notebook can be obtained from the Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities website at the link below. It consists of a point collection for each of the public airports in Alaska.
[http://www.dot.alaska.gov/stwdplng/mapping/shapefiles.shtml](http://www.dot.alaska.gov/stwdplng/mapping/shapefiles.shtml)
##### Load the Shapefile
```python
import os
import geopandas
data = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', 'Public_Airports_March2018.shp')
gdf = geopandas.read_file(data)
```
```python
%matplotlib inline
gdf.plot()
```
```python
gdf.crs
```
{'init': 'epsg:4269'}
##### Generate Alpha Shape
The alpha shape will be generated in the coordinate frame the geodataframe is in. In this example, we will project into an Albers Equal Area projection, construct our alpha shape in that coordinate system, and then convert back to the source projection.
##### Project to Albers Equal Area Spatial Reference
```python
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
gdf_proj = gdf.to_crs(ccrs.AlbersEqualArea().proj4_init)
gdf_proj.plot()
```
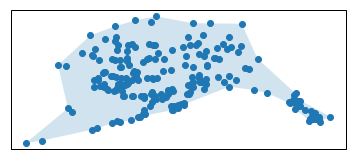
##### Determine the Alpha Shape
```python
import alphashape
alpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(gdf_proj)
alpha_shape.plot()
```

##### Plotting the Alpha Shape over the Data Points
##### Plate Carree Projection
```python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())
ax.scatter([p.x for p in gdf_proj['geometry']],
[p.y for p in gdf_proj['geometry']],
transform=ccrs.AlbersEqualArea())
ax.add_geometries(
alpha_shape['geometry'],
crs=ccrs.AlbersEqualArea(), alpha=.2)
plt.show()
```
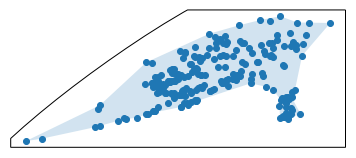
##### Robinson Projection
```python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.Robinson())
ax.scatter([p.x for p in gdf_proj['geometry']],
[p.y for p in gdf_proj['geometry']],
transform=ccrs.AlbersEqualArea())
ax.add_geometries(
alpha_shape['geometry'],
crs=ccrs.AlbersEqualArea(), alpha=.2)
plt.show()
```
## St. Sulpice Point Cloud Data
The following data can be obtained from the Lib E57 example data set found at the link below. To reduce the amount of data included in the `alphashape` toolbox repository, only a subset of point data was converted to a shapefile format and all data except point locations were dropped.
[http://www.libe57.org/data.html](http://www.libe57.org/data.html)

```python
import os
import geopandas
data = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', 'Trimble_StSulpice-Cloud-50mm.shp')
gdf = geopandas.read_file(data)
```
```python
from alphashape import alphashape
alphashape([point.coords[0] for point in gdf['geometry'][0]], 0.7).show()
```

### Credits
This package was created with [Cookiecutter](https://github.com/audreyr/cookiecutter) and the [audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage](https://github.com/audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage) project template.
# History
## 1.3.1 (2021-04-16)
* Small bug fixes
* Documentation cleanup
## 1.3.0 (2021-04-02)
* Support for generating alphashapes for 3 or more dimensional input data.
* GeoJSON support in command line interface.
## 1.2.1 (2021-03-13)
* Adding in support for Python 3.6 and 3.9
## 1.2.0 (2021-02-25)
* Updated dependencies for geopandas notebook examples.
* Updated source information for Alaska Airports example data set.
* Dropping support for Python 3.6.
## 1.1.0 (2020-08-19)
* Updated dependency version numbers.
* Including optional bounds for alpha paramter solver.
## 1.0.1 (2019-05-06)
* Added gallery plot for optimized alpha function.
* Documentation cleanup.
## 1.0.0 (2019-05-06)
* [#1 Update features in README.md](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/1)
* [#2 Create Application Utilizing the alphashape Toolbox](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/2)
## 0.1.10 (2019-05-05)
* Correcting formatting on PyPi long description.
## 0.1.9 (2019-05-05)
* [#7 Include GeoPandas Integration](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/7)
## 0.1.8 (2019-05-05)
* [#8 Include capability to optimize alpha parameter](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/8)
## 0.1.7 (2019-04-26)
* Complete code coverage of existing capabilities.
## 0.1.6 (2019-04-24)
* [#6 Include Jupyter Notebook in Examples](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/6)
## 0.1.5 (2019-04-24)
* [#5 Create an Example Gallery in the Documentation](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/5)
## 0.1.4 (2019-04-24)
* Bug fixes.
## 0.1.3 (2019-04-24)
* Bug fixes.
## 0.1.2 (2019-04-24)
* Bug fixes.
## 0.1.1 (2019-04-24)
* Bug fixes.
## 0.1.0 (2019-04-23)
* First release on PyPI.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape",
"name": "alphashape",
"maintainer": "",
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": "",
"maintainer_email": "",
"keywords": "alphashape",
"author": "Kenneth E. Bellock",
"author_email": "ken@bellock.net",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/2e/83/67ff905694df5b34a777123b59fdfd05998d5a31766f188aafbf5b340055/alphashape-1.3.1.tar.gz",
"platform": "",
"description": "# Alpha Shape Toolbox\n\n[](https://travis-ci.org/bellockk/alphashape/)\n[](http://alphashape.readthedocs.io/?badge=latest)\n[](https://codecov.io/gh/bellockk/alphashape)\n[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/bellockk/alphashape/master)\n[](https://lbesson.mit-license.org/)\n[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/183085167)\n\n\n[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/alphashape/)\n[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/alphashape/)\n[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/alphashape/)\n\n\n[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/alphashape)\n[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/alphashape)\n[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/alphashape)\n[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/alphashape)\n\nToolbox for generating n-dimensional alpha shapes.\n\nAlpha shapes are often used to generalize bounding polygons containing sets of points. The alpha parameter is defined as the value `a`, such that an edge of a disk of radius 1/`a` can be drawn between any two edge members of a set of points and still contain all the points. The convex hull, a shape resembling what you would see if you wrapped a rubber band around pegs at all the data points, is an alpha shape where the alpha parameter is equal to zero. In this toolbox we will be generating alpha complexes, which are closely related to alpha shapes, but which consist of straight lines between the edge points instead of arcs of circles.\n\nhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Alpha_shape\n\nhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convex_hull\n\nCreating alpha shapes around sets of points usually requires a visually interactive step where the alpha parameter for a concave hull is determined by iterating over or bisecting values to approach a best fit. The alpha shape toolbox provides workflows to shorten the development loop on this manual process, or to bypass it completely by solving for an alpha shape with particular characteristics. A python API is provided to aid in the scripted generation of alpha shapes. A console application is also provided as an example usage of the alpha shape toolbox, and to facilitate generation of alpha shapes from the command line.\n\n* Free software: MIT license\n* Documentation: https://alphashape.readthedocs.io.\n\n## Features\n\n### Import Dependencies\n\n\n```python\nimport os\nimport sys\nimport pandas as pd\nimport numpy as np\nfrom descartes import PolygonPatch\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nsys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.getcwd()))\nimport alphashape\n```\n### 2 Dimensional Example\n\n#### Define a set of points\n\n\n```python\npoints_2d = [(0., 0.), (0., 1.), (1., 1.), (1., 0.),\n (0.5, 0.25), (0.5, 0.75), (0.25, 0.5), (0.75, 0.5)]\n```\n\n#### Visualize Test Coordinates\n\n\n```python\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n#### Generate an Alpha Shape ($\\alpha=0.0$) (Convex Hull)\nEvery convex hull is an alpha shape, but not every alpha shape is a convex hull. When the `alphashape` function is called with an alpha parameter of 0, a convex hull will always be returned.\n\n##### Create the alpha shape\n\nYou can visualize the shape within Jupyter notebooks using the built-in shapely renderer as shown below.\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, 0.)\nalpha_shape\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data with Matplotlib\n\n\n```python\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))\nax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n#### Generate an Alpha Shape ($\\alpha=2.0$) (Concave Hull)\nAs we increase the alpha parameter value, the bounding shape will begin to fit the sample data with a more tightly fitting bounding box.\n\n##### Create the alpha shape\n\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, 2.0)\nalpha_shape\n```\n\n\n\n\n##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data with Matplotlib\n\n\n```python\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))\nax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n#### Generate an Alpha Shape ($\\alpha=3.5$)\nIf you go too high on the alpha parameter, you will start to lose points from the original data set.\n\n##### Create the alpha shape\n\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, 3.5)\nalpha_shape\n```\n\n\n\n\n##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data with Matplotlib\n\n\n```python\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))\nax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n#### Generate an Alpha Shape (Alpha=5.0)\nIf you go too far, you will lose everything.\n\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d, 5.0)\nprint(alpha_shape)\n```\n\n GEOMETRYCOLLECTION EMPTY\n\n## Using a varying Alpha Parameter\nThe alpha parameter can be defined locally within a region of points by supplying a callback that will return what alpha parameter to use. This can be utilized to create tighter fitting alpha shapes where point densitities are different in different regions of a data set. In the following example, the alpha parameter is changed based off of the value of the x-coordinate of the points.\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(\n points_2d,\n lambda ind, r: 1.0 + any(np.array(points_2d)[ind][:,0] == 0.0))\nalpha_shape\n```\n\n\n\n##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data with Matplotlib\n\n\n```python\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))\nax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n#### Generate an Alpha Shape by Solving for an Optimal Alpha Value\nThe alpha parameter can be solved for if it is not provided as an argument, but with large datasets this can take a long time to calculate.\n\n##### Create the alpha shape\n\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_2d)\nalpha_shape\n```\n\n\n\n\n##### Plotting the alpha shape over the input data\n\n\n```python\nfig, ax = plt.subplots()\nax.scatter(*zip(*points_2d))\nax.add_patch(PolygonPatch(alpha_shape, alpha=0.2))\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n### 3 Dimensional Example\n\n#### Define a set of points\n\n\n```python\npoints_3d = [\n (0., 0., 0.), (0., 0., 1.), (0., 1., 0.),\n (1., 0., 0.), (1., 1., 0.), (1., 0., 1.),\n (0., 1., 1.), (1., 1., 1.), (.25, .5, .5),\n (.5, .25, .5), (.5, .5, .25), (.75, .5, .5),\n (.5, .75, .5), (.5, .5, .75)\n]\n```\n\n#### Visualize Test Coordinates\n\n\n```python\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = plt.axes(projection='3d')\nax.scatter(df_3d['x'], df_3d['y'], df_3d['z'])\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n#### Alphashape with Static Alpha Parameter\n\nYou can visualize the shape within Jupyter notebooks using the built-in trimesh renderer by calling the `.show()` method as shown below.\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_3d, 1.1)\nalpha_shape.show()\n```\n\n\n\n```python\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = plt.axes(projection='3d')\nax.plot_trisurf(*zip(*alpha_shape.vertices), triangles=alpha_shape.faces)\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n#### Alphashape with Dymanic Alpha Parameter\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_3d, lambda ind, r: 1.0 + any(\n np.array(points_3d)[ind][:,0] == 0.0))\nalpha_shape.show()\n```\n\n\n\n```python\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = plt.axes(projection='3d')\nax.plot_trisurf(*zip(*alpha_shape.vertices), triangles=alpha_shape.faces)\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n#### Alphashape found by solving for the Alpha Parameter\n\n```python\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(points_3d)\nalpha_shape.show()\n```\n\n\n\n```python\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = plt.axes(projection='3d')\nax.plot_trisurf(*zip(*alpha_shape.vertices), triangles=alpha_shape.faces)\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n### 4 Dimensional Example\n\n#### Define a set of points\n\n\n```python\npoints_4d = [\n (0., 0., 0., 0.), (0., 0., 0., 1.), (0., 0., 1., 0.),\n (0., 1., 0., 0.), (0., 1., 1., 0.), (0., 1., 0., 1.),\n (0., 0., 1., 1.), (0., 1., 1., 1.), (1., 0., 0., 0.),\n (1., 0., 0., 1.), (1., 0., 1., 0.), (1., 1., 0., 0.),\n (1., 1., 1., 0.), (1., 1., 0., 1.), (1., 0., 1., 1.),\n (1., 1., 1., 1.), (.25, .5, .5, .5), (.5, .25, .5, .5),\n (.5, .5, .25, .5), (.5, .5, .5, .25), (.75, .5, .5, .5),\n (.5, .75, .5, .5), (.5, .5, .75, .5), (.5, .5, .5, .75)\n]\ndf_4d = pd.DataFrame(points_4d, columns=['x', 'y', 'z', 'r'])\n```\n\n#### Visualize Test Coordinates\n\n\n```python\nfig = plt.figure()\nax = plt.axes(projection='3d')\nax.scatter(df_4d['x'], df_4d['y'], df_4d['z'], c=df_4d['r'])\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n#### The Edges of a 4 Dimensional Alpha Shape are Tetrahedrons Defined by the Following Coordinates (No Visualizations)\n\n```python\nalphashape.alphashape(points_4d, 1.0)\n```\n\n```python\n{(16, 1, 2, 0),\n (16, 1, 3, 0),\n (16, 2, 3, 0),\n (16, 4, 2, 3),\n (16, 4, 7, 2),\n (16, 4, 7, 3),\n (16, 5, 1, 3),\n (16, 5, 7, 1),\n (16, 5, 7, 3),\n (16, 6, 1, 2),\n (16, 6, 7, 1),\n (16, 6, 7, 2),\n (17, 1, 2, 0),\n (17, 1, 8, 0),\n (17, 2, 8, 0),\n (17, 6, 1, 2),\n (17, 6, 14, 1),\n (17, 6, 14, 2),\n (17, 9, 1, 8),\n (17, 9, 14, 1),\n (17, 9, 14, 8),\n (17, 10, 2, 8),\n (17, 10, 14, 2),\n (17, 10, 14, 8),\n (18, 1, 3, 0),\n (18, 1, 8, 0),\n (18, 3, 8, 0),\n (18, 5, 1, 3),\n (18, 5, 13, 1),\n (18, 5, 13, 3),\n (18, 9, 1, 8),\n (18, 9, 13, 1),\n (18, 9, 13, 8),\n (18, 11, 3, 8),\n (18, 11, 13, 3),\n (18, 11, 13, 8),\n (19, 2, 3, 0),\n (19, 2, 8, 0),\n (19, 3, 8, 0),\n (19, 4, 2, 3),\n (19, 4, 12, 2),\n (19, 4, 12, 3),\n (19, 10, 2, 8),\n (19, 10, 12, 2),\n (19, 10, 12, 8),\n (19, 11, 3, 8),\n (19, 11, 12, 3),\n (19, 11, 12, 8),\n (20, 9, 13, 8),\n (20, 9, 14, 8),\n (20, 9, 14, 13),\n (20, 10, 12, 8),\n (20, 10, 14, 8),\n (20, 10, 14, 12),\n (20, 11, 12, 8),\n (20, 11, 13, 8),\n (20, 11, 13, 12),\n (20, 13, 12, 15),\n (20, 14, 12, 15),\n (20, 14, 13, 15),\n (21, 4, 7, 3),\n (21, 4, 7, 12),\n (21, 4, 12, 3),\n (21, 5, 7, 3),\n (21, 5, 7, 13),\n (21, 5, 13, 3),\n (21, 7, 12, 15),\n (21, 7, 13, 15),\n (21, 11, 12, 3),\n (21, 11, 13, 3),\n (21, 11, 13, 12),\n (21, 13, 12, 15),\n (22, 4, 7, 2),\n (22, 4, 7, 12),\n (22, 4, 12, 2),\n (22, 6, 7, 2),\n (22, 6, 7, 14),\n (22, 6, 14, 2),\n (22, 7, 12, 15),\n (22, 7, 14, 15),\n (22, 10, 12, 2),\n (22, 10, 14, 2),\n (22, 10, 14, 12),\n (22, 14, 12, 15),\n (23, 5, 7, 1),\n (23, 5, 7, 13),\n (23, 5, 13, 1),\n (23, 6, 7, 1),\n (23, 6, 7, 14),\n (23, 6, 14, 1),\n (23, 7, 13, 15),\n (23, 7, 14, 15),\n (23, 9, 13, 1),\n (23, 9, 14, 1),\n (23, 9, 14, 13),\n (23, 14, 13, 15)}\n```\n\n## Alpha Shapes with GeoPandas\n\n##### Sample Data\n\nThe data used in this notebook can be obtained from the Alaska Department of Transportation and Public Facilities website at the link below. It consists of a point collection for each of the public airports in Alaska.\n\n[http://www.dot.alaska.gov/stwdplng/mapping/shapefiles.shtml](http://www.dot.alaska.gov/stwdplng/mapping/shapefiles.shtml)\n\n##### Load the Shapefile\n\n\n```python\nimport os\nimport geopandas\ndata = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', 'Public_Airports_March2018.shp')\ngdf = geopandas.read_file(data)\n```\n\n\n```python\n%matplotlib inline\ngdf.plot()\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n```python\ngdf.crs\n```\n\n\n\n\n {'init': 'epsg:4269'}\n\n\n\n##### Generate Alpha Shape\nThe alpha shape will be generated in the coordinate frame the geodataframe is in. In this example, we will project into an Albers Equal Area projection, construct our alpha shape in that coordinate system, and then convert back to the source projection.\n\n##### Project to Albers Equal Area Spatial Reference\n\n\n```python\nimport cartopy.crs as ccrs\ngdf_proj = gdf.to_crs(ccrs.AlbersEqualArea().proj4_init)\ngdf_proj.plot()\n```\n\n\n\n\n##### Determine the Alpha Shape\n\n\n```python\nimport alphashape\nalpha_shape = alphashape.alphashape(gdf_proj)\nalpha_shape.plot()\n```\n\n\n\n\n##### Plotting the Alpha Shape over the Data Points\n##### Plate Carree Projection\n\n\n```python\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.PlateCarree())\nax.scatter([p.x for p in gdf_proj['geometry']],\n [p.y for p in gdf_proj['geometry']],\n transform=ccrs.AlbersEqualArea())\nax.add_geometries(\n alpha_shape['geometry'],\n crs=ccrs.AlbersEqualArea(), alpha=.2)\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n##### Robinson Projection\n\n\n```python\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\nax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.Robinson())\nax.scatter([p.x for p in gdf_proj['geometry']],\n [p.y for p in gdf_proj['geometry']],\n transform=ccrs.AlbersEqualArea())\nax.add_geometries(\n alpha_shape['geometry'],\n crs=ccrs.AlbersEqualArea(), alpha=.2)\nplt.show()\n```\n\n\n\n\n\n## St. Sulpice Point Cloud Data\n\nThe following data can be obtained from the Lib E57 example data set found at the link below. To reduce the amount of data included in the `alphashape` toolbox repository, only a subset of point data was converted to a shapefile format and all data except point locations were dropped.\n\n[http://www.libe57.org/data.html](http://www.libe57.org/data.html)\n\n\n\n```python\nimport os\nimport geopandas\ndata = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), 'data', 'Trimble_StSulpice-Cloud-50mm.shp')\ngdf = geopandas.read_file(data)\n```\n\n```python\nfrom alphashape import alphashape\nalphashape([point.coords[0] for point in gdf['geometry'][0]], 0.7).show()\n```\n\n\n\n### Credits\n\nThis package was created with [Cookiecutter](https://github.com/audreyr/cookiecutter) and the [audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage](https://github.com/audreyr/cookiecutter-pypackage) project template.\n\n\n# History\n\n## 1.3.1 (2021-04-16)\n\n* Small bug fixes\n* Documentation cleanup\n\n## 1.3.0 (2021-04-02)\n\n* Support for generating alphashapes for 3 or more dimensional input data.\n* GeoJSON support in command line interface.\n\n## 1.2.1 (2021-03-13)\n\n* Adding in support for Python 3.6 and 3.9\n\n## 1.2.0 (2021-02-25)\n\n* Updated dependencies for geopandas notebook examples.\n* Updated source information for Alaska Airports example data set.\n* Dropping support for Python 3.6.\n\n## 1.1.0 (2020-08-19)\n\n* Updated dependency version numbers.\n* Including optional bounds for alpha paramter solver.\n\n## 1.0.1 (2019-05-06)\n\n* Added gallery plot for optimized alpha function.\n* Documentation cleanup.\n\n## 1.0.0 (2019-05-06)\n\n* [#1 Update features in README.md](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/1)\n* [#2 Create Application Utilizing the alphashape Toolbox](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/2)\n\n## 0.1.10 (2019-05-05)\n\n* Correcting formatting on PyPi long description.\n\n## 0.1.9 (2019-05-05)\n\n* [#7 Include GeoPandas Integration](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/7)\n\n## 0.1.8 (2019-05-05)\n\n* [#8 Include capability to optimize alpha parameter](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/8)\n\n## 0.1.7 (2019-04-26)\n\n* Complete code coverage of existing capabilities.\n\n## 0.1.6 (2019-04-24)\n\n* [#6 Include Jupyter Notebook in Examples](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/6)\n\n## 0.1.5 (2019-04-24)\n\n* [#5 Create an Example Gallery in the Documentation](https://github.com/bellockk/alphashape/issues/5)\n\n## 0.1.4 (2019-04-24)\n\n* Bug fixes.\n\n## 0.1.3 (2019-04-24)\n\n* Bug fixes.\n\n## 0.1.2 (2019-04-24)\n\n* Bug fixes.\n\n## 0.1.1 (2019-04-24)\n\n* Bug fixes.\n\n## 0.1.0 (2019-04-23)\n\n* First release on PyPI.\n\n\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "MIT license",
"summary": "Toolbox for generating alpha shapes.",
"version": "1.3.1",
"split_keywords": [
"alphashape"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"md5": "f2fa24e9e788050c25dbfcef312c191a",
"sha256": "96a5ddd5f09534a35f03a8916aeeaac00fe4d6bec2f9ad78f87f57be3007f795"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "alphashape-1.3.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "f2fa24e9e788050c25dbfcef312c191a",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py2.py3",
"requires_python": null,
"size": 13122,
"upload_time": "2021-04-16T17:47:17",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2021-04-16T17:47:17.773937Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/e4/ad/77fad9d6f974ec58d837cb49fb9b483d6227a420c4f908c3578633de1d47/alphashape-1.3.1-py2.py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"md5": "8e84552a377fa48bf3b10212db65d966",
"sha256": "7a27340afc5f8ed301577acec46bb0cf2bada5410045f7289142e735ef6977ec"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "alphashape-1.3.1.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "8e84552a377fa48bf3b10212db65d966",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": null,
"size": 26316,
"upload_time": "2021-04-16T17:47:19",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2021-04-16T17:47:19.486474Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/2e/83/67ff905694df5b34a777123b59fdfd05998d5a31766f188aafbf5b340055/alphashape-1.3.1.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2021-04-16 17:47:19",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"github_user": "bellockk",
"github_project": "alphashape",
"travis_ci": true,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": false,
"tox": true,
"lcname": "alphashape"
}

