# Django Translations
[](https://pypi.org/project/django-translations/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/django-translations/)
Django model translation for perfectionists with deadlines.
## Goal
There are two types of content, each of which has its own challenges for translation:
- Static content: This is the content which is defined in the code.
_e.g. "Please enter a valid email address."_
Django already provides a
[solution](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.2/topics/i18n/translation/)
for translating static content.
- Dynamic content: This is the content which is stored in the database.
_(We can't know it beforehand!)_
Django Translations provides a solution
for translating dynamic content.
## Compatibility
Currently, this project is incompatible with PostgreSQL.
## Requirements
- Python (\>=3.7, \<4)
- Django (\>=2.2, \<6)
## Installation
1. Install Django Translations using pip:
```bash
$ pip install django-translations
```
2. Add `translations` to the `INSTALLED_APPS` in the settings of your
project:
```python
INSTALLED_APPS += [
'translations',
]
```
3. Run `migrate`:
```bash
$ python manage.py migrate
```
4. Configure Django internationalization and localization settings:
```python
USE_I18N = True # use internationalization
USE_L10N = True # use localization
MIDDLEWARE += [ # locale middleware
'django.middleware.locale.LocaleMiddleware',
]
LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us' # default (fallback) language
LANGUAGES = ( # supported languages
('en', 'English'),
('en-gb', 'English (Great Britain)'),
('de', 'German'),
('tr', 'Turkish'),
)
```
Please note that these settings are for Django itself.
## Basic Usage
### Model
Inherit `Translatable` in any model you want translated:
```python
from translations.models import Translatable
class Continent(Translatable):
code = models.Charfield(...)
name = models.Charfield(...)
denonym = models.Charfield(...)
class TranslatableMeta:
fields = ['name', 'denonym']
```
No migrations needed afterwards.
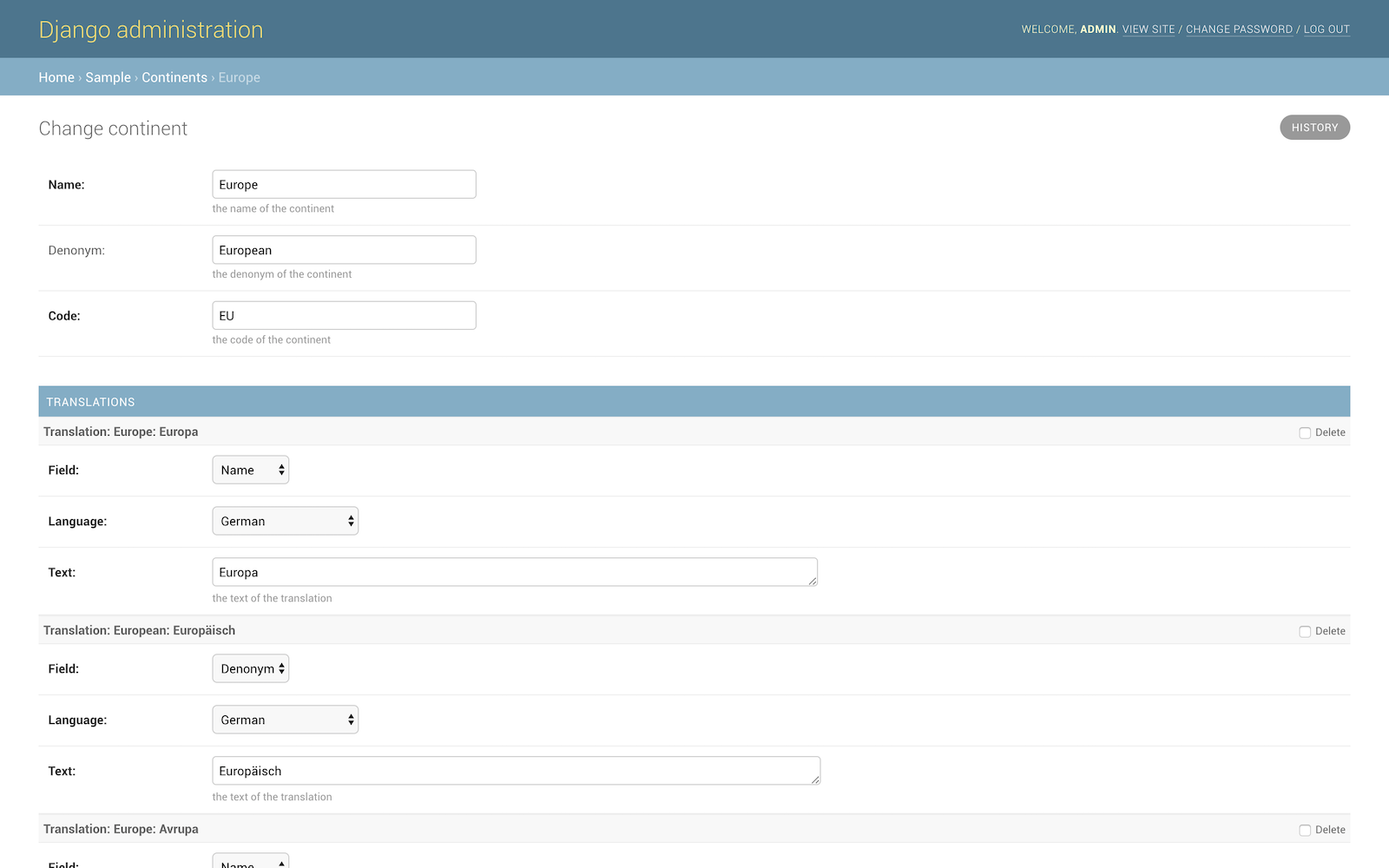
### Admin
Use the admin extensions:
```python
from translations.admin import TranslatableAdmin, TranslationInline
class ContinentAdmin(TranslatableAdmin):
inlines = [TranslationInline,]
```
This provides specialized translation inlines for the model.
## QuerySet
Use the queryset extensions:
```python
>>> from sample.models import Continent
>>> continents = Continent.objects.all(
... ).distinct( # familiar distinct
... ).probe(['en', 'de'] # probe (filter, exclude, etc.) in English and German
... ).filter( # familiar filtering
... countries__cities__name__startswith='Köln'
... ).translate('de' # translate the results in German
... ).translate_related( # translate these relations as well
... 'countries', 'countries__cities',
... )
>>> print(continents)
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Continent: Europa>,
]>
>>> print(continents[0].countries.all())
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Country: Deutschland>,
]>
>>> print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<City: Köln>,
]>
```
This provides a powerful yet familiar interface to work with the querysets.
## Context
Use the translation context:
```python
>>> from translations.context import Context
>>> from sample.models import Continent
>>> continents = Continent.objects.all()
>>> relations = ('countries', 'countries__cities',)
>>> with Context(continents, *relations) as context:
... context.read('de') # read the translations onto the context
... print(':') # use the objects like before
... print(continents)
... print(continents[0].countries.all())
... print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())
...
... continents[0].countries.all()[0].name = 'Change the name'
... context.update('de') # update the translations from the context
...
... context.delete('de') # delete the translations of the context
...
... context.reset() # reset the translations of the context
... print(':') # use the objects like before
... print(continents)
... print(continents[0].countries.all())
... print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())
:
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Continent: Asien>,
<Continent: Europa>,
]>
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Country: Deutschland>,
]>
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<City: Köln>,
]>
:
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Continent: Asia>,
<Continent: Europe>,
]>
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<Country: Germany>,
]>
<TranslatableQuerySet [
<City: Cologne>,
]>
```
This can CRUD the translations of any objects (instance, queryset, list) and their relations.
## Documentation
For more interesting capabilities browse through the
[documentation](http://bbmokhtari.github.io/django-translations).
## Support the project
To support the project you can:
- ⭐️: [Star](http://github.com/bbmokhtari/django-translations/) it on GitHub.
- 💻: [Contribute](https://bbmokhtari.github.io/django-translations/contribution.html) to the code base.
- ☕️: [Buy](https://bbmokhtari.github.io/django-translations/donation.html) the maintainers coffee.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/bbmokhtari/django-translations",
"name": "django-translations",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": "<4,>=3.7",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "django model translation internationalization localization",
"author": "Behzad B. Mokhtari",
"author_email": "bbmokhtari.global@gmail.com",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bf/39/8cdbc7c460b6003e0ba02e68ee8dd6c1acad5f8dce85ee4577a82f1a912f/django_translations-1.4.3.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "# Django Translations\n\n[](https://pypi.org/project/django-translations/)\n[](https://pypi.org/project/django-translations/)\n\nDjango model translation for perfectionists with deadlines.\n\n## Goal\n\nThere are two types of content, each of which has its own challenges for translation:\n\n- Static content: This is the content which is defined in the code.\n _e.g. \"Please enter a valid email address.\"_\n\n Django already provides a\n [solution](https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.2/topics/i18n/translation/)\n for translating static content.\n\n- Dynamic content: This is the content which is stored in the database.\n _(We can't know it beforehand!)_\n\n Django Translations provides a solution\n for translating dynamic content.\n\n## Compatibility\n\nCurrently, this project is incompatible with PostgreSQL.\n\n## Requirements\n\n- Python (\\>=3.7, \\<4)\n- Django (\\>=2.2, \\<6)\n\n## Installation\n\n1. Install Django Translations using pip:\n\n ```bash\n $ pip install django-translations\n ```\n\n2. Add `translations` to the `INSTALLED_APPS` in the settings of your\n project:\n\n ```python\n INSTALLED_APPS += [\n 'translations',\n ]\n ```\n\n3. Run `migrate`:\n\n ```bash\n $ python manage.py migrate\n ```\n\n4. Configure Django internationalization and localization settings:\n\n ```python\n USE_I18N = True # use internationalization\n USE_L10N = True # use localization\n\n MIDDLEWARE += [ # locale middleware\n 'django.middleware.locale.LocaleMiddleware',\n ]\n\n LANGUAGE_CODE = 'en-us' # default (fallback) language\n LANGUAGES = ( # supported languages\n ('en', 'English'),\n ('en-gb', 'English (Great Britain)'),\n ('de', 'German'),\n ('tr', 'Turkish'),\n )\n ```\n\n Please note that these settings are for Django itself.\n\n## Basic Usage\n\n### Model\n\nInherit `Translatable` in any model you want translated:\n\n```python\nfrom translations.models import Translatable\n\nclass Continent(Translatable):\n code = models.Charfield(...)\n name = models.Charfield(...)\n denonym = models.Charfield(...)\n\n class TranslatableMeta:\n fields = ['name', 'denonym']\n```\n\nNo migrations needed afterwards.\n\n### Admin\n\nUse the admin extensions:\n\n```python\nfrom translations.admin import TranslatableAdmin, TranslationInline\n\nclass ContinentAdmin(TranslatableAdmin):\n inlines = [TranslationInline,]\n```\n\nThis provides specialized translation inlines for the model.\n\n\n\n## QuerySet\n\nUse the queryset extensions:\n\n```python\n>>> from sample.models import Continent\n>>> continents = Continent.objects.all(\n... ).distinct( # familiar distinct\n... ).probe(['en', 'de'] # probe (filter, exclude, etc.) in English and German\n... ).filter( # familiar filtering\n... countries__cities__name__startswith='K\u00f6ln'\n... ).translate('de' # translate the results in German\n... ).translate_related( # translate these relations as well\n... 'countries', 'countries__cities',\n... )\n>>> print(continents)\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <Continent: Europa>,\n]>\n>>> print(continents[0].countries.all())\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <Country: Deutschland>,\n]>\n>>> print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <City: K\u00f6ln>,\n]>\n```\n\nThis provides a powerful yet familiar interface to work with the querysets.\n\n## Context\n\nUse the translation context:\n\n```python\n>>> from translations.context import Context\n>>> from sample.models import Continent\n>>> continents = Continent.objects.all()\n>>> relations = ('countries', 'countries__cities',)\n>>> with Context(continents, *relations) as context:\n... context.read('de') # read the translations onto the context\n... print(':') # use the objects like before\n... print(continents)\n... print(continents[0].countries.all())\n... print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())\n...\n... continents[0].countries.all()[0].name = 'Change the name'\n... context.update('de') # update the translations from the context\n...\n... context.delete('de') # delete the translations of the context\n...\n... context.reset() # reset the translations of the context\n... print(':') # use the objects like before\n... print(continents)\n... print(continents[0].countries.all())\n... print(continents[0].countries.all()[0].cities.all())\n:\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <Continent: Asien>,\n <Continent: Europa>,\n]>\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <Country: Deutschland>,\n]>\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <City: K\u00f6ln>,\n]>\n:\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <Continent: Asia>,\n <Continent: Europe>,\n]>\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <Country: Germany>,\n]>\n<TranslatableQuerySet [\n <City: Cologne>,\n]>\n```\n\nThis can CRUD the translations of any objects (instance, queryset, list) and their relations.\n\n## Documentation\n\nFor more interesting capabilities browse through the\n[documentation](http://bbmokhtari.github.io/django-translations).\n\n## Support the project\n\nTo support the project you can:\n\n- \u2b50\ufe0f: [Star](http://github.com/bbmokhtari/django-translations/) it on GitHub.\n- \ud83d\udcbb: [Contribute](https://bbmokhtari.github.io/django-translations/contribution.html) to the code base.\n- \u2615\ufe0f: [Buy](https://bbmokhtari.github.io/django-translations/donation.html) the maintainers coffee.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "Django model translation for perfectionists with deadlines.",
"version": "1.4.3",
"project_urls": {
"Documentation": "https://bbmokhtari.github.io/django-translations",
"Funding": "https://bbmokhtari.github.io/django-translations/donation.html",
"Homepage": "https://github.com/bbmokhtari/django-translations",
"Source": "https://github.com/bbmokhtari/django-translations",
"Tracker": "https://github.com/bbmokhtari/django-translations/issues"
},
"split_keywords": [
"django",
"model",
"translation",
"internationalization",
"localization"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "04a23f7aa135d9d4bb05eccb3ede9acd64bc5d4eb384e7053608d0f7fdf07695",
"md5": "74ccf7ec42850b78c711345e1b51fa01",
"sha256": "8415c1a48aaf8bf39f7c86d348fd9ac4b8d3217746be539ace656d8c057f531b"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "django_translations-1.4.3-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "74ccf7ec42850b78c711345e1b51fa01",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": "<4,>=3.7",
"size": 19275,
"upload_time": "2024-10-20T23:46:08",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-10-20T23:46:08.158149Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/04/a2/3f7aa135d9d4bb05eccb3ede9acd64bc5d4eb384e7053608d0f7fdf07695/django_translations-1.4.3-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "bf398cdbc7c460b6003e0ba02e68ee8dd6c1acad5f8dce85ee4577a82f1a912f",
"md5": "64bf693ba99429a2e8e05f3dc4585ae2",
"sha256": "c5382c0c30f6ed24031e805af50f0c7b097e92a326b9de7cc22dd694c8062058"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "django_translations-1.4.3.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "64bf693ba99429a2e8e05f3dc4585ae2",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": "<4,>=3.7",
"size": 15556,
"upload_time": "2024-10-20T23:46:09",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-10-20T23:46:09.197408Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bf/39/8cdbc7c460b6003e0ba02e68ee8dd6c1acad5f8dce85ee4577a82f1a912f/django_translations-1.4.3.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-10-20 23:46:09",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "bbmokhtari",
"github_project": "django-translations",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"lcname": "django-translations"
}
