[](https://pypi.org/project/fitspy/)
[](https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy)
[](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/index.html)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10812333)
[](https://joss.theoj.org/papers/971a02868d903c0b7c0cbc3d1cd3d139)
<p align="center" width="100%">
<img align="center" width=250 src=https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/logo.png>
</p>
**Fitspy** is a generic tool dedicated to **fit sp**ectra in **py**thon with GUIs that aims to be as simple and intuitive to use as possible.
<p align="center" width="100%">
<img align="center" width="45%" src="https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/_static/pyside/fitspy.png">
<img align="center" width="45%" src="https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/_static/tkinter/fitspy.png">
</p>
<p align="center">
<em>Illustration of the PySide GUI (left) and Tkinter GUI (right).</em>
</p>
Processed spectra may be independent of each other or may result from 2D-maps
acquisitions.
<p align="center" width="100%">
<img align="center" width="30%" src=https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/2d-map.png> <br>
<em>Example of fitspy 2D-map frame interacting with the main GUI.</em>
</p>
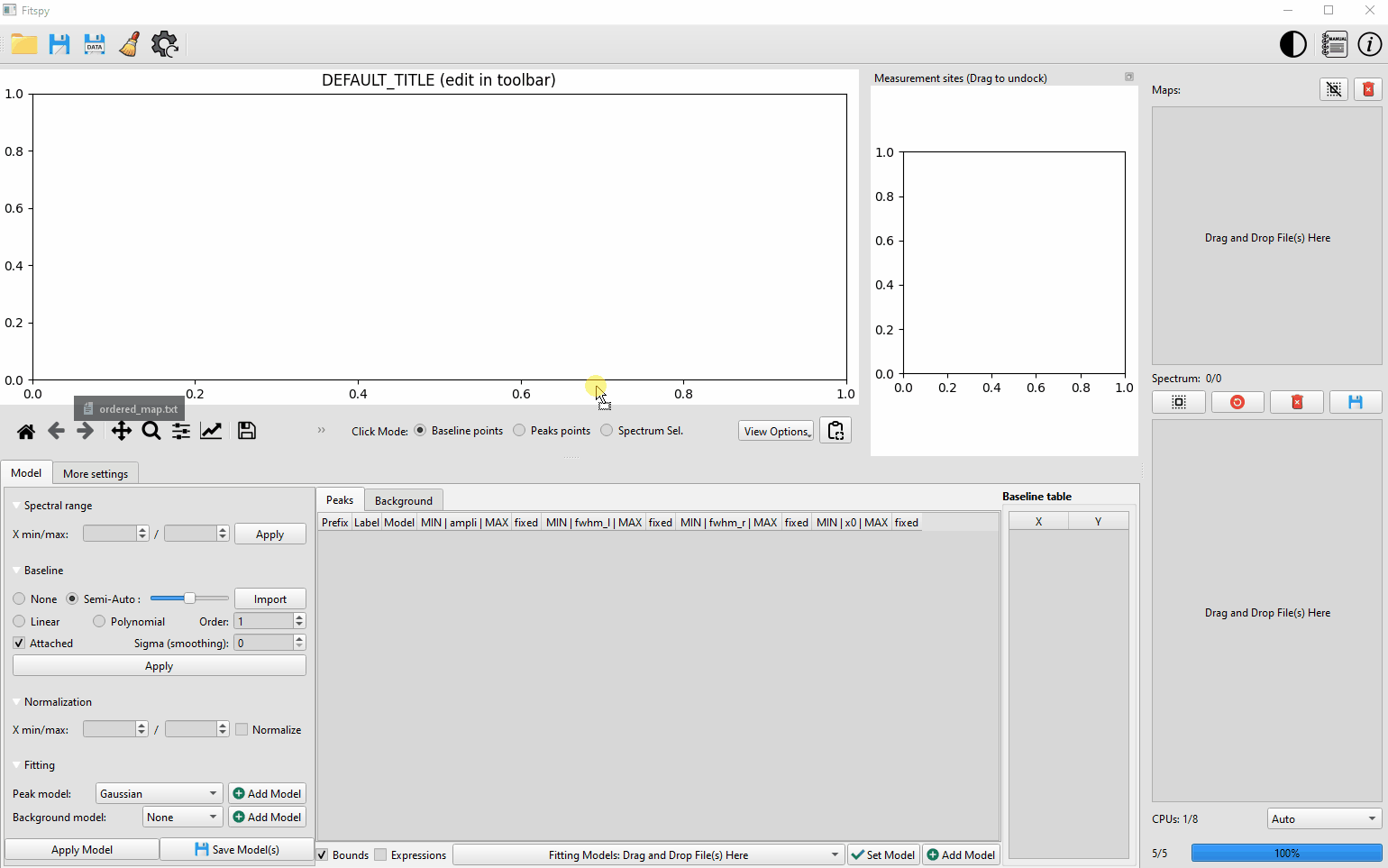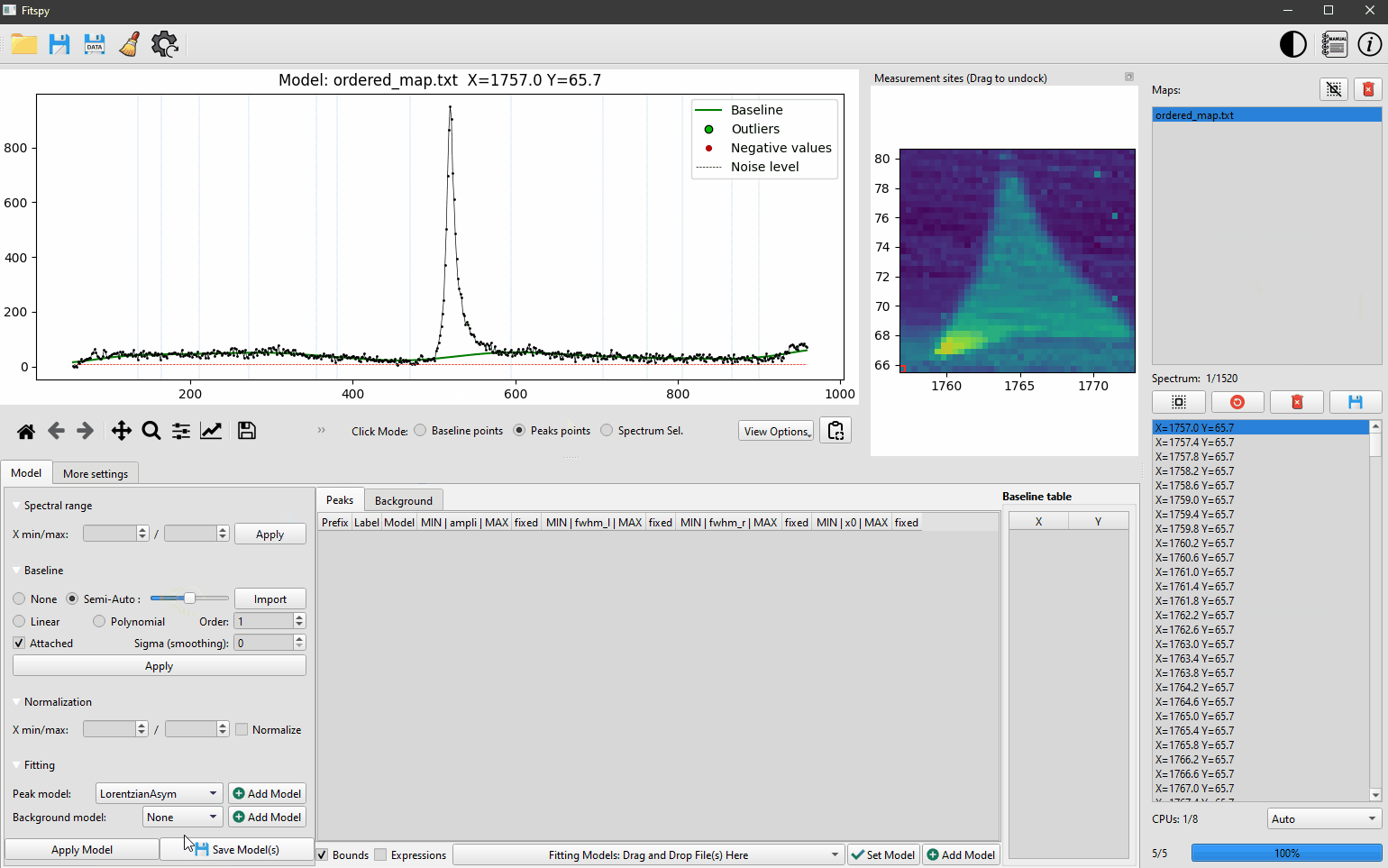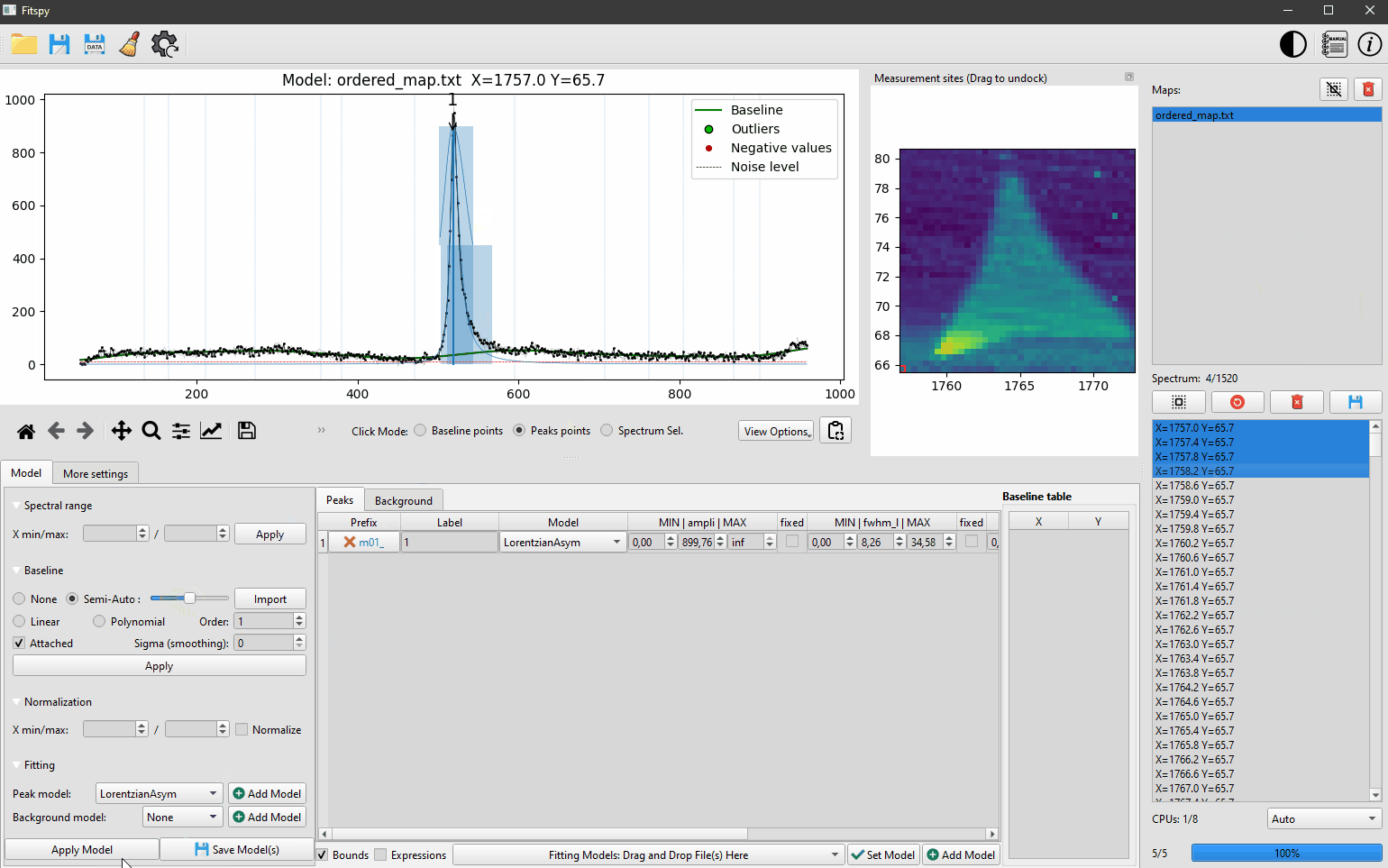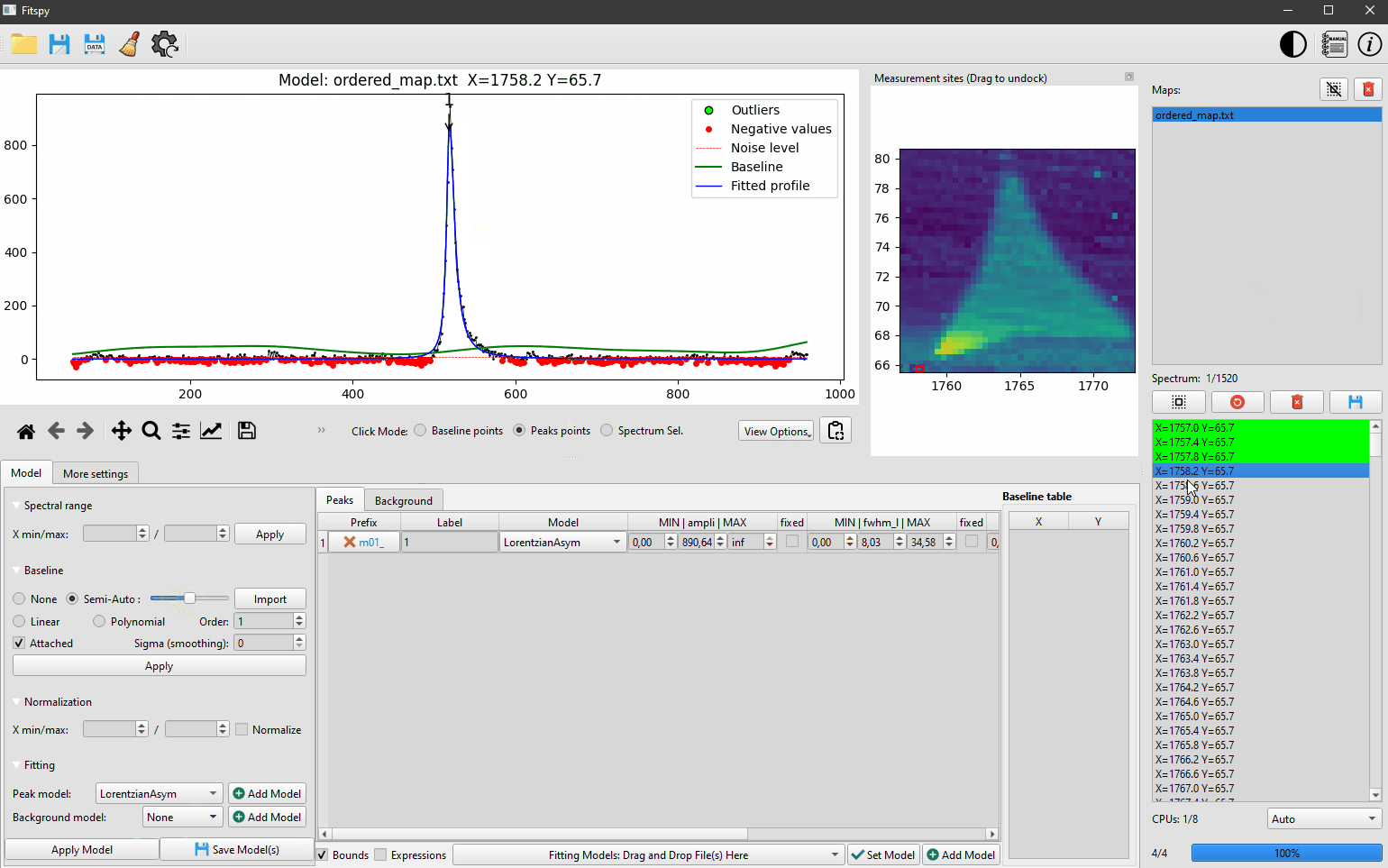
The predefined peak models considered in Fitspy are `Gaussian`, `Lorentzian`, `Asymetric Gaussian`, `Asymetric Lorentzian` and `Pseudovoigt`. Some `Bichromatic` models related to bichromatic sources are also available as explained [here](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/user_guide/peak_models.html#bichromatic-models)
A `Constant`, `Linear`, `Parabolic`, `Exponential` or `Power Law` background model can also be added in the fitting.
In both cases, `user-defined models` can be added.
Fitspy main features:
- Fitspy uses the [lmfit](https://github.com/lmfit/lmfit-py) library to fit the spectra
- The fit processing can be multi-threaded
- Bounds and constraints can be set on each peaks models parameter
- From an automatic noise level estimation, according to the local noise, peak models can be automatically deactivated
- Fitspy also includes automatic outlier detection to be excluded during the fitting process
All actions allowed with the GUI can be executed in script mode (see examples [here](https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy/tree/main/examples)).
These actions (like baseline and peaks definition, parameters constraints, ...) can be saved in a `Fitspy model` and replayed as-is or applied to other new spectra datasets.
## Installation
### From PyPI (recommended)
```bash
pip install fitspy
```
### From GitHub (latest version)
```bash
pip install git+https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy
```
*(See the [documentation](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/user_guide/intro.html#install-and-launching) for more details)*
## Upgrade
In the case of 'just' a **Fitspy** upgrade:
```bash
pip uninstall fitspy
pip install fistspy # considering here the install from Pypi
```
For a full upgrade (**Fitspy** and its dependencies):
```bash
pip install fitspy --upgrade # considering here the install from Pypi
```
## Tests and examples execution
```
pip install pytest
git clone https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy.git
cd fitspy
pytest
python examples/ex_gui_auto_decomposition.py
python examples/ex_.......
```
*(See the [documentation](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/user_guide/intro.html#install-and-launching) for more details)*
## Quick start
Since its 2025.1 version, Fitspy can be launched using two interfaces: either the one corresponding to the original GUI built with **Tkinter**, or a more recent and advanced one, using **PySide**. As of 2025, both GUIs offer nearly identical features, but future efforts regarding fixes and updates will primarily focus on the PySide GUI.
<u>**PySide GUI**</u>:
Launch the application:
```
fitspy
```
From the right to the left, select the files to work with (considering the drag and drop capabilities).
Then, use the **Model** panel to set the model parameters to be used during the fitting process.
Peaks and an optional baseline associated with the model can be defined interactively by clicking on the desired position in the figure after activating **Peak points** (or **Baseline points** resp.) from the **Click Mode** radiobuttons located under the figure.
Once the model build, The **Fit** can be launched. The corresponding model can be saved (in the **Model** panel) to be reload later (from the bottom-central panel) as-it with the same spectra (if the pathnames are still available) or just as a model for other spectra to be processed.
<u>**Tkinter GUI**</u>:
Launch the application:
```
fitspy-tk
```
From the top to the bottom of the right panel:
- `Select` file(s)
- *(Optional)* Define the **X-range**
- Define the baseline to `subtract` *(left or right click on the figure to add or delete (resp.) a baseline point)*
- *(Optional)* Normalize the spectrum/spectra
- Click on the `Fitting` panel to activate it
- Select `Peak model` and add peaks *(left or right click on the figure to add or delete (resp.) a peak)*
- *(Optional)* Add a background (**BKG model**) to be fitted
- *(Optional)* Use **Parameters** to set bounds and constraints
- `Fit` the selected spectrum/spectra
- *(Optional)* **Save** the parameters in **.csv** format
- *(Optional)* **Save** the **Model** in a .json file (to be replayed later)
*(See the [documentation](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/user_guide/workflow.html) for more details)*
## Acknowledgements
This work, carried out on the CEA - Platform for Nanocharacterisation (PFNC), was supported by the “Recherche Technologique de Base” program of the French National Research Agency (ANR).
Warm thanks to the [JOSS](https://joss.theoj.org/) reviewers ([@maurov](https://github.com/maurov) and [@FCMeng](https://github.com/FCMeng)) and editor ([@phibeck](https://github.com/phibeck)) for their contributions to enhancing Fitspy.
## Citations
In case you use the results of this code in an article, please cite:
- Quéméré P., (2024). Fitspy: A python package for spectral decomposition. Journal of Open Source Software. doi: [10.21105/joss.05868](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.05868)
- Newville M., (2014). LMFIT: Non-Linear Least-Square Minimization and Curve-Fitting for Python. Zenodo. doi: [10.5281/zenodo.11813](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11813).
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "fitspy",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "Fitspy, fit, spectra, spectrum, map, 1D, 2D, decomposition, Gaussian, Lorentzian, Pseudovoigt, GUI",
"author": null,
"author_email": "Patrick Qu\u00e9m\u00e9r\u00e9 <patrick.quemere@cea.fr>, Killian Pavy <killian.pavy@cea.fr>",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/47/0d/2e095a06afbadadec90aecf7dade99918848ea3476f433e66315cfe88547/fitspy-2025.7.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "[](https://pypi.org/project/fitspy/)\n[](https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy)\n[](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/index.html)\n[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10812333)\n[](https://joss.theoj.org/papers/971a02868d903c0b7c0cbc3d1cd3d139)\n\n\n<p align=\"center\" width=\"100%\">\n <img align=\"center\" width=250 src=https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/logo.png>\n</p>\n\n\n**Fitspy** is a generic tool dedicated to **fit sp**ectra in **py**thon with GUIs that aims to be as simple and intuitive to use as possible.\n\n<p align=\"center\" width=\"100%\">\n <img align=\"center\" width=\"45%\" src=\"https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/_static/pyside/fitspy.png\">\n <img align=\"center\" width=\"45%\" src=\"https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/_static/tkinter/fitspy.png\">\n</p>\n<p align=\"center\">\n <em>Illustration of the PySide GUI (left) and Tkinter GUI (right).</em>\n</p>\n\nProcessed spectra may be independent of each other or may result from 2D-maps\nacquisitions.\n\n<p align=\"center\" width=\"100%\">\n <img align=\"center\" width=\"30%\" src=https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/2d-map.png> <br>\n <em>Example of fitspy 2D-map frame interacting with the main GUI.</em> \n</p>\n\n\n\nThe predefined peak models considered in Fitspy are `Gaussian`, `Lorentzian`, `Asymetric Gaussian`, `Asymetric Lorentzian` and `Pseudovoigt`. Some `Bichromatic` models related to bichromatic sources are also available as explained [here](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/user_guide/peak_models.html#bichromatic-models)\n\nA `Constant`, `Linear`, `Parabolic`, `Exponential` or `Power Law` background model can also be added in the fitting.\n\nIn both cases, `user-defined models` can be added.\n\nFitspy main features:\n\n- Fitspy uses the [lmfit](https://github.com/lmfit/lmfit-py) library to fit the spectra\n- The fit processing can be multi-threaded\n- Bounds and constraints can be set on each peaks models parameter\n- From an automatic noise level estimation, according to the local noise, peak models can be automatically deactivated\n- Fitspy also includes automatic outlier detection to be excluded during the fitting process\n\nAll actions allowed with the GUI can be executed in script mode (see examples [here](https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy/tree/main/examples)).\nThese actions (like baseline and peaks definition, parameters constraints, ...) can be saved in a `Fitspy model` and replayed as-is or applied to other new spectra datasets.\n\n## Installation\n\n### From PyPI (recommended)\n\n```bash\npip install fitspy\n```\n\n### From GitHub (latest version)\n\n```bash\npip install git+https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy\n```\n\n*(See the [documentation](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/user_guide/intro.html#install-and-launching) for more details)*\n\n## Upgrade\n\nIn the case of 'just' a **Fitspy** upgrade:\n\n```bash\npip uninstall fitspy\npip install fistspy # considering here the install from Pypi \n```\n\nFor a full upgrade (**Fitspy** and its dependencies):\n\n```bash\npip install fitspy --upgrade # considering here the install from Pypi\n```\n\n## Tests and examples execution\n\n```\npip install pytest\ngit clone https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy.git\ncd fitspy\npytest\npython examples/ex_gui_auto_decomposition.py\npython examples/ex_.......\n```\n\n*(See the [documentation](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/user_guide/intro.html#install-and-launching) for more details)*\n\n## Quick start\n\nSince its 2025.1 version, Fitspy can be launched using two interfaces: either the one corresponding to the original GUI built with **Tkinter**, or a more recent and advanced one, using **PySide**. As of 2025, both GUIs offer nearly identical features, but future efforts regarding fixes and updates will primarily focus on the PySide GUI.\n\n<u>**PySide GUI**</u>:\n\nLaunch the application:\n\n```\nfitspy\n```\n\nFrom the right to the left, select the files to work with (considering the drag and drop capabilities).\nThen, use the **Model** panel to set the model parameters to be used during the fitting process.\nPeaks and an optional baseline associated with the model can be defined interactively by clicking on the desired position in the figure after activating **Peak points** (or **Baseline points** resp.) from the **Click Mode** radiobuttons located under the figure.\nOnce the model build, The **Fit** can be launched. The corresponding model can be saved (in the **Model** panel) to be reload later (from the bottom-central panel) as-it with the same spectra (if the pathnames are still available) or just as a model for other spectra to be processed.\n\n<u>**Tkinter GUI**</u>:\n\nLaunch the application:\n\n```\nfitspy-tk\n```\n\nFrom the top to the bottom of the right panel:\n\n- `Select` file(s)\n- *(Optional)* Define the **X-range**\n- Define the baseline to `subtract` *(left or right click on the figure to add or delete (resp.) a baseline point)*\n- *(Optional)* Normalize the spectrum/spectra\n- Click on the `Fitting` panel to activate it\n- Select `Peak model` and add peaks *(left or right click on the figure to add or delete (resp.) a peak)*\n- *(Optional)* Add a background (**BKG model**) to be fitted\n- *(Optional)* Use **Parameters** to set bounds and constraints\n- `Fit` the selected spectrum/spectra\n- *(Optional)* **Save** the parameters in **.csv** format\n- *(Optional)* **Save** the **Model** in a .json file (to be replayed later)\n\n*(See the [documentation](https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/user_guide/workflow.html) for more details)*\n\n## Acknowledgements\n\nThis work, carried out on the CEA - Platform for Nanocharacterisation (PFNC), was supported by the \u201cRecherche Technologique de Base\u201d program of the French National Research Agency (ANR).\n\nWarm thanks to the [JOSS](https://joss.theoj.org/) reviewers ([@maurov](https://github.com/maurov) and [@FCMeng](https://github.com/FCMeng)) and editor ([@phibeck](https://github.com/phibeck)) for their contributions to enhancing Fitspy.\n\n## Citations\n\nIn case you use the results of this code in an article, please cite:\n\n- Qu\u00e9m\u00e9r\u00e9 P., (2024). Fitspy: A python package for spectral decomposition. Journal of Open Source Software. doi: [10.21105/joss.05868](https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.05868)\n\n- Newville M., (2014). LMFIT: Non-Linear Least-Square Minimization and Curve-Fitting for Python. Zenodo. doi: [10.5281/zenodo.11813](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.11813).\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "GPL v3",
"summary": "Fitspy: a generic tool to fit spectra in python",
"version": "2025.7",
"project_urls": {
"Documentation": "https://cea-metrocarac.github.io/fitspy/index.html",
"Homepage": "https://github.com/CEA-MetroCarac/fitspy"
},
"split_keywords": [
"fitspy",
" fit",
" spectra",
" spectrum",
" map",
" 1d",
" 2d",
" decomposition",
" gaussian",
" lorentzian",
" pseudovoigt",
" gui"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "1ef310eef507f0b0c8adfa79d249e2bce0404ca6c5180991bdfffe808149d8eb",
"md5": "5606aca169b1cb0b78f3b477c10716d2",
"sha256": "3b0038830993efb4274bdf34dfd8fbf5ed77ee42d164c1e06e8dcc169fb1dd99"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "fitspy-2025.7-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "5606aca169b1cb0b78f3b477c10716d2",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"size": 420774,
"upload_time": "2025-08-13T08:20:34",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-08-13T08:20:34.327862Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/1e/f3/10eef507f0b0c8adfa79d249e2bce0404ca6c5180991bdfffe808149d8eb/fitspy-2025.7-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "470d2e095a06afbadadec90aecf7dade99918848ea3476f433e66315cfe88547",
"md5": "758d13b7a815f70818ad56f06fa3482f",
"sha256": "32c11402010f90e820371dc00924ab9d6bccee35b084d692577c2371232941bd"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "fitspy-2025.7.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "758d13b7a815f70818ad56f06fa3482f",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"size": 18145874,
"upload_time": "2025-08-13T08:20:35",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-08-13T08:20:35.583806Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/47/0d/2e095a06afbadadec90aecf7dade99918848ea3476f433e66315cfe88547/fitspy-2025.7.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-08-13 08:20:35",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "CEA-MetroCarac",
"github_project": "fitspy",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"lcname": "fitspy"
}
