<p align="center" width="100%">
<img width="33%" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/instadeepai/InstaNovo/main/docs/assets/instanovo.svg">
</p>
# _De novo_ peptide sequencing with InstaNovo
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/instanovo)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14712453)
<a target="_blank" href="https://colab.research.google.com/github/instadeepai/InstaNovo/blob/main/notebooks/getting_started_with_instanovo.ipynb">
<img src="https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg" alt="Open In Colab"/> </a>
<a target="_blank" href="https://kaggle.com/kernels/welcome?src=https://github.com/instadeepai/InstaNovo/blob/main/notebooks/getting_started_with_instanovo.ipynb">
<img src="https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg" alt="Open In Kaggle"/> </a>
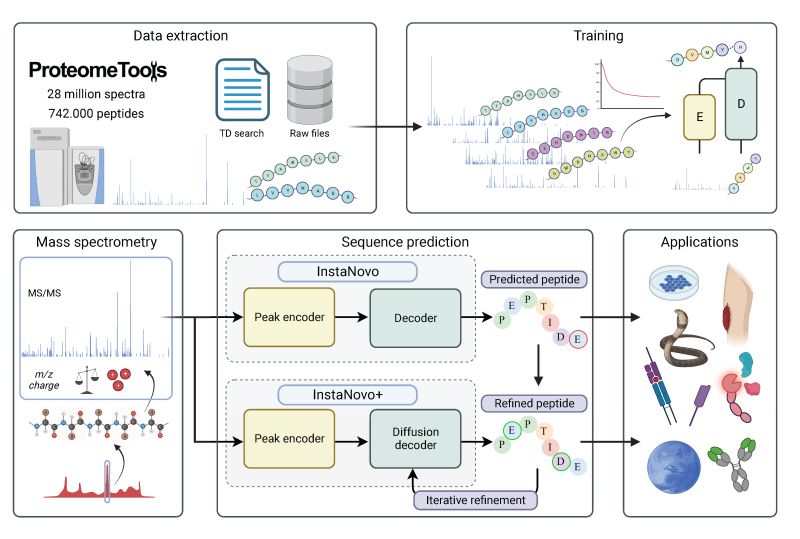
The official code repository for InstaNovo. This repo contains the code for training and inference
of InstaNovo and InstaNovo+. InstaNovo is a transformer neural network with the ability to translate
fragment ion peaks into the sequence of amino acids that make up the studied peptide(s). InstaNovo+,
inspired by human intuition, is a multinomial diffusion model that further improves performance by
iterative refinement of predicted sequences.
**Links:**
- bioRxiv:
[https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.08.30.555055v3](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.08.30.555055v3)
- documentation:
[https://instadeepai.github.io/InstaNovo/](https://instadeepai.github.io/InstaNovo/)
**Developed by:**
- [InstaDeep](https://www.instadeep.com/)
- [The Department of Biotechnology and Biomedicine](https://orbit.dtu.dk/en/organisations/department-of-biotechnology-and-biomedicine) -
[Technical University of Denmark](https://www.dtu.dk/)
## Usage
### Installation
To use InstaNovo, we need to install the module via `pip`:
```bash
pip install instanovo
```
### Command line usage
InstaNovo provides a comprehensive command line interface (CLI) for both prediction and training
tasks.
To get help and see the available commands:
```
instanovo --help
```

To see the version of InstaNovo, InstaNovo+ and some of the dependencies:
```
instanovo version
```

### Predicting
To get help about the prediction command line options:
```
instanovo predict --help
```

### Running predictions with both InstaNovo and InstaNovo+
The default is to run predictions first with the transformer-based InstaNovo model, and then further
improve the performance by iterative refinement of these predicted sequences by the diffusion-based
InstaNov+ model.
```
instanovo predict --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path predictions.csv
```
Which results in the following output:
```
scan_number,precursor_mz,precursor_charge,experiment_name,spectrum_id,diffusion_predictions_tokenised,diffusion_predictions,diffusion_log_probabilities,transformer_predictions,transformer_predictions_tokenised,transformer_log_probabilities,transformer_token_log_probabilities
0,451.25348,2,spectra,spectra:0,"['A', 'L', 'P', 'Y', 'T', 'P', 'K', 'K']",ALPYTPKK,-0.03160184621810913,LAHYNKK,"L, A, H, Y, N, K, K",-424.5889587402344,"[-0.5959059000015259, -0.0059959776699543, -0.01749008148908615, -0.03598890081048012, -0.48958998918533325, -1.5242897272109985, -0.656516432762146]"
```
To evaluate InstaNovo performance on an annotated dataset:
```bash
instanovo predict --evaluation --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path predictions.csv
```
Which results in the following output:
```
scan_number,precursor_mz,precursor_charge,experiment_name,spectrum_id,diffusion_predictions_tokenised,diffusion_predictions,diffusion_log_probabilities,targets,transformer_predictions,transformer_predictions_tokenised,transformer_log_probabilities,transformer_token_log_probabilities
0,451.25348,2,spectra,spectra:0,"['L', 'A', 'H', 'Y', 'N', 'K', 'K']",LAHYNKK,-0.06637095659971237,IAHYNKR,LAHYNKK,"L, A, H, Y, N, K, K",-424.5889587402344,"[-0.5959059000015259, -0.0059959776699543, -0.01749008148908615, -0.03598890081048012, -0.48958998918533325, -1.5242897272109985, -0.656516432762146]"
```
Note that the `--evaluation` flag includes the `targets` column in the output, which contains the
ground truth peptide sequence. Metrics will be calculated and displayed in the console.
### Command line arguments and overriding config values
The configuration file for inference may be found under [/configs/inference/](./configs/inference/)
folder. By default, the [`default.yaml`](configs/inference/default.yaml) file is used.
InstaNovo uses command line arguments for commonly used parameters:
- `--data-path` - Path to the dataset to be evaluated. Allows `.mgf`, `.mzml`, `.mzxml`, `.ipc` or a
directory. Glob notation is supported: eg.: `./experiment/*.mgf`
- `--output-path` - Path to output csv file.
- `--instanovo-model` - Model to use for InstaNovo. Either a model ID (currently supported:
`instanovo-v1.1.0`) or a path to an Instanovo checkpoint file (.ckpt format).
- `--instanovo-plus-model` - Model to use for InstaNovo+. Either a model ID (currently supported:
`instanovoplus-v1.1.0-alpha`) or a path to an Instanovo+ checkpoint file (.ckpt format).
- `--denovo` - Whether to do _de novo_ predictions. If you want to evaluate the model on annotated
data, use the flag `--evaluation` flag.
- `--with-refinement` - Whether to use InstaNovo+ for iterative refinement of InstaNovo predictions.
Default is `True`. If you don't want to use refinement,use the flag `--no-refinement`.
To override the configuration values in the config files, you can use command line arguments. For
example, by default beam search with one beam is used. If you want to use beam search with 5 beams,
you can use the following command:
```bash
instanovo predict --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path predictions.csv num_beams=5
```
Note the lack of prefix `--` before `num_beams` in the command line argument because you are
overriding the value of key defined in the config file.
**Output description**
When `output_path` is specified, a CSV file will be generated containing predictions for all the
input spectra. The model will attempt to generate a peptide for every MS2 spectrum regardless of
confidence. We recommend filtering the output using the **log_probabilities** and **delta_mass_ppm**
columns.
| Column | Description | Data Type | Notes |
| ----------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| scan_number | Scan number of the MS/MS spectrum | Integer | Unique identifier from the input file |
| precursor_mz | Precursor m/z (mass-to-charge ratio) | Float | The observed m/z of the precursor ion |
| precursor_charge | Precursor charge state | Integer | Charge state of the precursor ion |
| experiment_name | Experiment name derived from input filename | String | Based on the input file name (mgf, mzml, or mzxml) |
| spectrum_id | Unique spectrum identifier | String | Combination of experiment name and scan number (e.g., `yeast:17738`) |
| targets | Target peptide sequence | String | Ground truth peptide sequence (if available) |
| predictions | Predicted peptide sequences | String | Model-predicted peptide sequence |
| predictions_tokenised | Predicted peptide sequence tokenized by amino acids | List[String] | Each amino acid token separated by commas |
| log_probabilities | Log probability of the entire predicted sequence | Float | Natural logarithm of the sequence confidence, can be converted to probability with np.exp(log_probabilities). |
| token_log_probabilities | Log probability of each token in the predicted sequence | List[Float] | Natural logarithm of the sequence confidence per amino acid |
| delta_mass_ppm | Mass difference between precursor and predicted peptide in ppm | Float | Mass deviation in parts per million |
### Models
InstaNovo 1.1.0 includes a new model `instanovo-v1.1.0.ckpt` trained on a larger dataset with more
PTMs.
> Note: The InstaNovo Extended 1.0.0 training data mis-represented Cysteine as unmodified for the
> majority of the training data. Please update to the latest version of the model.
**Training Datasets**
- [ProteomeTools](https://www.proteometools.org/) Part
[I (PXD004732)](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD004732),
[II (PXD010595)](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD010595), and
[III (PXD021013)](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD021013) \
(referred to as the all-confidence ProteomeTools `AC-PT` dataset in our paper)
- Additional PRIDE dataset with more modifications: \
([PXD000666](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD000666), [PXD000867](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD000867),
[PXD001839](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD001839), [PXD003155](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD003155),
[PXD004364](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD004364), [PXD004612](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD004612),
[PXD005230](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD005230), [PXD006692](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD006692),
[PXD011360](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD011360), [PXD011536](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD011536),
[PXD013543](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD013543), [PXD015928](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD015928),
[PXD016793](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD016793), [PXD017671](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD017671),
[PXD019431](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD019431), [PXD019852](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD019852),
[PXD026910](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD026910), [PXD027772](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD027772))
- [Massive-KB v1](https://massive.ucsd.edu/ProteoSAFe/static/massive.jsp)
- Additional phosphorylation dataset \
(not yet publicly released)
**Natively Supported Modifications**
| Amino Acid | Single Letter | Modification | Mass Delta (Da) | Unimod ID |
| --------------------------- | ------------- | ----------------------- | --------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Methionine | M | Oxidation | +15.9949 | [\[UNIMOD:35\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=35) |
| Cysteine | C | Carboxyamidomethylation | +57.0215 | [\[UNIMOD:4\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=4) |
| Asparagine, Glutamine | N, Q | Deamidation | +0.9840 | [\[UNIMOD:7\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=7) |
| Serine, Threonine, Tyrosine | S, T, Y | Phosphorylation | +79.9663 | [\[UNIMOD:21\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=21) |
| N-terminal | - | Ammonia Loss | -17.0265 | [\[UNIMOD:385\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=385) |
| N-terminal | - | Carbamylation | +43.0058 | [\[UNIMOD:5\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=5) |
| N-terminal | - | Acetylation | +42.0106 | [\[UNIMOD:1\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=1) |
See residue configuration under
[instanovo/configs/residues/extended.yaml](./instanovo/configs/residues/extended.yaml)
### Training
Data to train on may be provided in any format supported by the SpectrumDataHandler. See section on
data conversion for preferred formatting.
#### Training InstaNovo
To train the auto-regressive transformer model InstaNovo using the config file
[instanovo/configs/instanovo.yaml](./instanovo/configs/instanovo.yaml), you can use the following
command:
```bash
instanovo transformer train --help
```

To update the InstaNovo model config, modify the config file under
[instanovo/configs/model/instanovo_base.yaml](instanovo/configs/model/instanovo_base.yaml)
#### Training InstaNovo+
To train the diffusion model InstaNovo+ using the config file
[instanovo/configs/instanovoplus.yaml](instanovo/configs/instanovoplus.yaml), you can use the
following command:
```bash
instanovo diffusion train --help
```

To update the InstaNovo+ model config, modify the config file under
[instanovo/configs/model/instanovoplus_base.yaml](instanovo/configs/model/instanovoplus_base.yaml)
### Advanced prediction options
### Run predictions with only InstaNovo
If you want to run predictions with only InstaNovo, you can use the following command:
```bash
instanovo transformer predict --help
```

### Run predictions with only InstaNovo+
If you want to run predictions with only InstaNovo+, you can use the following command:
```bash
instanovo diffusion predict --help
```

### Run predictions with InstaNovo and InstaNovo+ in separate steps
You can first run predictions with InstaNovo
```bash
instanovo transformer predict --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path instanovo_predictions.csv
```
and then use the predictions as input for InstaNovo+:
```bash
instanovo diffusion predict --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path instanovo_plus_predictions.csv instanovo_predictions_path=instanovo_predictions.csv
```
## Additional features
### Spectrum Data Class
InstaNovo introduces a Spectrum Data Class: [SpectrumDataFrame](./instanovo/utils/data_handler.py).
This class acts as an interface between many common formats used for storing mass spectrometry,
including `.mgf`, `.mzml`, `.mzxml`, and `.csv`. This class also supports reading directly from
HuggingFace, Pandas, and Polars.
When using InstaNovo, these formats are natively supported and automatically converted to the
internal SpectrumDataFrame supported by InstaNovo for training and inference. Any data path may be
specified using [glob notation](<https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glob_(programming)>). For example you
could use the following command to get _de novo_ predictions from all the files in the folder
`./experiment`:
```bash
instanovo predict --data_path=./experiment/*.mgf
```
Alternatively, a list of files may be specified in the
[inference config](./configs/inference/default.yaml).
The SpectrumDataFrame also allows for loading of much larger datasets in a lazy way. To do this, the
data is loaded and stored as [`.parquet`](https://docs.pola.rs/user-guide/io/parquet/) files in a
temporary directory. Alternatively, the data may be saved permanently natively as `.parquet` for
optimal loading.
**Example usage:**
Converting mgf files to the native format:
```python
from instanovo.utils import SpectrumDataFrame
# Convert mgf files native parquet:
sdf = SpectrumDataFrame.load("/path/to/data.mgf", lazy=False, is_annotated=True)
sdf.save("path/to/parquet/folder", partition="train", chunk_size=1e6)
```
Loading the native format in shuffle mode:
```python
# Load a native parquet dataset:
sdf = SpectrumDataFrame.load("path/to/parquet/folder", partition="train", shuffle=True, lazy=True, is_annotated=True)
```
Using the loaded SpectrumDataFrame in a PyTorch DataLoader:
```python
from instanovo.transformer.dataset import SpectrumDataset
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
ds = SpectrumDataset(sdf)
# Note: Shuffle and workers is handled by the SpectrumDataFrame
dl = DataLoader(
ds,
collate_fn=SpectrumDataset.collate_batch,
shuffle=False,
num_workers=0,
)
```
Some more examples using the SpectrumDataFrame:
```python
sdf = SpectrumDataFrame.load("/path/to/experiment/*.mzml", lazy=True)
# Remove rows with a charge value > 3:
sdf.filter_rows(lambda row: row["precursor_charge"]<=2)
# Sample a subset of the data:
sdf.sample_subset(fraction=0.5, seed=42)
# Convert to pandas
df = sdf.to_pandas() # Returns a pd.DataFrame
# Convert to polars LazyFrame
lazy_df = sdf.to_polars(return_lazy=True) # Returns a pl.LazyFrame
# Save as an `.mgf` file
sdf.write_mgf("path/to/output.mgf")
```
**SpectrumDataFrame Features:**
- The SpectrumDataFrame supports lazy loading with asynchronous prefetching, mitigating wait times
between files.
- Filtering and sampling may be performed non-destructively through on file loading
- A two-fold shuffling strategy is introduced to optimise sampling during training (shuffling files
and shuffling within files).
### Using your own datasets
To use your own datasets, you simply need to tabulate your data in either
[Pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/) or [Polars](https://www.pola.rs/) with the following schema:
The dataset is tabular, where each row corresponds to a labelled MS2 spectra.
- `sequence (string)` \
The target peptide sequence including post-translational modifications
- `modified_sequence (string) [legacy]` \
The target peptide sequence including post-translational modifications
- `precursor_mz (float64)` \
The mass-to-charge of the precursor (from MS1)
- `charge (int64)` \
The charge of the precursor (from MS1)
- `mz_array (list[float64])` \
The mass-to-charge values of the MS2 spectrum
- `intensity_array (list[float32])` \
The intensity values of the MS2 spectrum
For example, the DataFrame for the
[nine species benchmark](https://huggingface.co/datasets/InstaDeepAI/ms_ninespecies_benchmark)
dataset (introduced in [Tran _et al._ 2017](https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.1705691114))
looks as follows:
| | sequence | precursor_mz | precursor_charge | mz_array | intensity_array |
| --: | :----------------------------- | -----------: | ---------------: | :----------------------------------- | :---------------------------------- |
| 0 | GRVEGMEAR | 335.502 | 3 | [102.05527 104.052956 113.07079 ...] | [ 767.38837 2324.8787 598.8512 ...] |
| 1 | IGEYK | 305.165 | 2 | [107.07023 110.071236 111.11693 ...] | [ 1055.4957 2251.3171 35508.96 ...] |
| 2 | GVSREEIQR | 358.528 | 3 | [103.039444 109.59844 112.08704 ...] | [801.19995 460.65268 808.3431 ...] |
| 3 | SSYHADEQVNEASK | 522.234 | 3 | [101.07095 102.0552 110.07163 ...] | [ 989.45154 2332.653 1170.6191 ...] |
| 4 | DTFNTSSTSN[UNIMOD:7]STSSSSSNSK | 676.282 | 3 | [119.82458 120.08073 120.2038 ...] | [ 487.86942 4806.1377 516.8846 ...] |
For _de novo_ prediction, the `sequence` column is not required.
We also provide a conversion script for converting to native SpectrumDataFrame (sdf) format:
```bash
instanovo convert --help
```

## Development
### `uv` setup
This project is set up to use [uv](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) to manage Python and dependencies.
First, be sure you [have uv installed](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/getting-started/installation/) on
your system.
On Linux and macOS:
```bash
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
```
On Windows:
```powershell
powershell -c "irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex"
```
Note: InstaNovo is built for Python >=3.10, <3.13 and tested on Linux, Windows and macOS.
### Fork and clone the repository
Then [fork](https://github.com/instadeepai/InstaNovo/fork) this repo (having your own fork will make
it easier to contribute) and
[clone it](https://docs.github.com/en/repositories/creating-and-managing-repositories/cloning-a-repository).
```bash
git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/InstaNovo.git
cd InstaNovo
```
Activate the virtual environment:
```bash
source .venv/bin/activate
```
And install the dependencies. If you don't have access to a GPU, you can install the CPU-only
version of PyTorch:
```bash
uv sync --extra cpu
uv run pre-commit install
```
If you do have access to an NVIDIA GPU, you can install the GPU version of PyTorch (recommended):
```bash
uv sync --extra cu124
uv run pre-commit install
```
Both approaches above also install the development dependencies. If you also want to install the
documentation dependencies, you can do so with:
```bash
uv sync --extra cu124 --group docs
```
To upgrade all packages to the latest versions, you can run:
```bash
uv lock --upgrade
uv sync --extra cu124
```
### Basic development workflows
#### Testing
InstaNovo uses `pytest` for testing. To run the tests, you can use the following command:
```bash
uv run instanovo/scripts/get_zenodo_record.py # Download the test data
python -m pytest --cov-report=html --cov --random-order --verbose .
```
To see the coverage report, run:
```bash
python -m coverage report -m
```
To view the coverage report in a browser, run:
```bash
python -m http.server --directory ./coverage
```
and navigate to `http://0.0.0.0:8000/` in your browser.
#### Linting
InstaNovo uses [pre-commit hooks](https://pre-commit.com/) to ensure code quality. To run the
linters, you can use the following command:
```bash
pre-commit run --all-files
```
#### Building the documentation
To build the documentation locally, you can use the following commands:
```bash
uv sync --extra cu124 --group docs
git config --global --add safe.directory "$(dirname "$(pwd)")"
rm -rf docs/reference
python ./docs/gen_ref_nav.py
mkdocs build --verbose --site-dir docs_public
mkdocs serve
```
### Generating a requirements.txt file
If you have a `pip` or `conda` based workflow and want to generate a `requirements.txt` file, you
can use the following command:
```bash
uv export --format requirements-txt > requirements.txt
```
### Setting Python interpreter in VSCode
To set the Python interpreter in VSCode, open the Command Palette (`Ctrl+Shift+P`), search for
`Python: Select Interpreter`, and select `./.venv/bin/python`.
## License
Code is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (see [LICENSE](LICENSE.md))
The model checkpoints are licensed under Creative Commons Non-Commercial
([CC BY-NC-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/))
## BibTeX entry and citation info
If you use InstaNovo in your research, please cite the following paper:
```bibtex
@article{eloff_kalogeropoulos_2024_instanovo,
title = {De novo peptide sequencing with InstaNovo: Accurate, database-free peptide identification for large scale proteomics experiments},
author = {Kevin Eloff and Konstantinos Kalogeropoulos and Oliver Morell and Amandla Mabona and Jakob Berg Jespersen and Wesley Williams and Sam van Beljouw and Marcin Skwark and Andreas Hougaard Laustsen and Stan J. J. Brouns and Anne Ljungars and Erwin Marten Schoof and Jeroen Van Goey and Ulrich auf dem Keller and Karim Beguir and Nicolas Lopez Carranza and Timothy Patrick Jenkins},
year = {2024},
doi = {10.1101/2023.08.30.555055},
publisher = {Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory},
URL = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.08.30.555055v3},
journal = {bioRxiv}
}
```
## Acknowledgements
Big thanks to Pathmanaban Ramasamy, Tine Claeys, and Lennart Martens of the
[CompOmics](https://www.compomics.com/) research group for providing us with additional
phosphorylation training data.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "instanovo",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": "<3.13,>=3.10",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "mass spectrometry, bioinformatics, machine learning, deep learning, transformer, de novo peptide sequencing",
"author": null,
"author_email": "Kevin Michael Eloff <k.eloff@instadeep.com>, Jeroen Van Goey <j.vangoey@instadeep.com>, Amandla Mabona <a.mabona@instadeep.com>, Rachel Catzel <r.catzel@instadeep.com>",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/8c/ae/abe65cd5cc1dd7d96687e8c57d6beb484c2444b4f9d936c273280d5f880e/instanovo-1.1.0.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "<p align=\"center\" width=\"100%\">\n <img width=\"33%\" src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/instadeepai/InstaNovo/main/docs/assets/instanovo.svg\">\n</p>\n\n# _De novo_ peptide sequencing with InstaNovo\n\n[](https://badge.fury.io/py/instanovo)\n[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.14712453)\n\n<a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://colab.research.google.com/github/instadeepai/InstaNovo/blob/main/notebooks/getting_started_with_instanovo.ipynb\">\n<img src=\"https://colab.research.google.com/assets/colab-badge.svg\" alt=\"Open In Colab\"/> </a>\n<a target=\"_blank\" href=\"https://kaggle.com/kernels/welcome?src=https://github.com/instadeepai/InstaNovo/blob/main/notebooks/getting_started_with_instanovo.ipynb\">\n<img src=\"https://kaggle.com/static/images/open-in-kaggle.svg\" alt=\"Open In Kaggle\"/> </a>\n\nThe official code repository for InstaNovo. This repo contains the code for training and inference\nof InstaNovo and InstaNovo+. InstaNovo is a transformer neural network with the ability to translate\nfragment ion peaks into the sequence of amino acids that make up the studied peptide(s). InstaNovo+,\ninspired by human intuition, is a multinomial diffusion model that further improves performance by\niterative refinement of predicted sequences.\n\n\n\n**Links:**\n\n- bioRxiv:\n [https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.08.30.555055v3](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.08.30.555055v3)\n- documentation:\n [https://instadeepai.github.io/InstaNovo/](https://instadeepai.github.io/InstaNovo/)\n\n**Developed by:**\n\n- [InstaDeep](https://www.instadeep.com/)\n- [The Department of Biotechnology and Biomedicine](https://orbit.dtu.dk/en/organisations/department-of-biotechnology-and-biomedicine) -\n [Technical University of Denmark](https://www.dtu.dk/)\n\n## Usage\n\n### Installation\n\nTo use InstaNovo, we need to install the module via `pip`:\n\n```bash\npip install instanovo\n```\n\n### Command line usage\n\nInstaNovo provides a comprehensive command line interface (CLI) for both prediction and training\ntasks.\n\nTo get help and see the available commands:\n\n```\ninstanovo --help\n```\n\n\n\nTo see the version of InstaNovo, InstaNovo+ and some of the dependencies:\n\n```\ninstanovo version\n```\n\n\n\n### Predicting\n\nTo get help about the prediction command line options:\n\n```\ninstanovo predict --help\n```\n\n\n\n### Running predictions with both InstaNovo and InstaNovo+\n\nThe default is to run predictions first with the transformer-based InstaNovo model, and then further\nimprove the performance by iterative refinement of these predicted sequences by the diffusion-based\nInstaNov+ model.\n\n```\ninstanovo predict --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path predictions.csv\n```\n\nWhich results in the following output:\n\n```\nscan_number,precursor_mz,precursor_charge,experiment_name,spectrum_id,diffusion_predictions_tokenised,diffusion_predictions,diffusion_log_probabilities,transformer_predictions,transformer_predictions_tokenised,transformer_log_probabilities,transformer_token_log_probabilities\n0,451.25348,2,spectra,spectra:0,\"['A', 'L', 'P', 'Y', 'T', 'P', 'K', 'K']\",ALPYTPKK,-0.03160184621810913,LAHYNKK,\"L, A, H, Y, N, K, K\",-424.5889587402344,\"[-0.5959059000015259, -0.0059959776699543, -0.01749008148908615, -0.03598890081048012, -0.48958998918533325, -1.5242897272109985, -0.656516432762146]\"\n```\n\nTo evaluate InstaNovo performance on an annotated dataset:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo predict --evaluation --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path predictions.csv\n```\n\nWhich results in the following output:\n\n```\nscan_number,precursor_mz,precursor_charge,experiment_name,spectrum_id,diffusion_predictions_tokenised,diffusion_predictions,diffusion_log_probabilities,targets,transformer_predictions,transformer_predictions_tokenised,transformer_log_probabilities,transformer_token_log_probabilities\n0,451.25348,2,spectra,spectra:0,\"['L', 'A', 'H', 'Y', 'N', 'K', 'K']\",LAHYNKK,-0.06637095659971237,IAHYNKR,LAHYNKK,\"L, A, H, Y, N, K, K\",-424.5889587402344,\"[-0.5959059000015259, -0.0059959776699543, -0.01749008148908615, -0.03598890081048012, -0.48958998918533325, -1.5242897272109985, -0.656516432762146]\"\n```\n\nNote that the `--evaluation` flag includes the `targets` column in the output, which contains the\nground truth peptide sequence. Metrics will be calculated and displayed in the console.\n\n### Command line arguments and overriding config values\n\nThe configuration file for inference may be found under [/configs/inference/](./configs/inference/)\nfolder. By default, the [`default.yaml`](configs/inference/default.yaml) file is used.\n\nInstaNovo uses command line arguments for commonly used parameters:\n\n- `--data-path` - Path to the dataset to be evaluated. Allows `.mgf`, `.mzml`, `.mzxml`, `.ipc` or a\n directory. Glob notation is supported: eg.: `./experiment/*.mgf`\n- `--output-path` - Path to output csv file.\n- `--instanovo-model` - Model to use for InstaNovo. Either a model ID (currently supported:\n `instanovo-v1.1.0`) or a path to an Instanovo checkpoint file (.ckpt format).\n- `--instanovo-plus-model` - Model to use for InstaNovo+. Either a model ID (currently supported:\n `instanovoplus-v1.1.0-alpha`) or a path to an Instanovo+ checkpoint file (.ckpt format).\n- `--denovo` - Whether to do _de novo_ predictions. If you want to evaluate the model on annotated\n data, use the flag `--evaluation` flag.\n- `--with-refinement` - Whether to use InstaNovo+ for iterative refinement of InstaNovo predictions.\n Default is `True`. If you don't want to use refinement,use the flag `--no-refinement`.\n\nTo override the configuration values in the config files, you can use command line arguments. For\nexample, by default beam search with one beam is used. If you want to use beam search with 5 beams,\nyou can use the following command:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo predict --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path predictions.csv num_beams=5\n```\n\nNote the lack of prefix `--` before `num_beams` in the command line argument because you are\noverriding the value of key defined in the config file.\n\n**Output description**\n\nWhen `output_path` is specified, a CSV file will be generated containing predictions for all the\ninput spectra. The model will attempt to generate a peptide for every MS2 spectrum regardless of\nconfidence. We recommend filtering the output using the **log_probabilities** and **delta_mass_ppm**\ncolumns.\n\n| Column | Description | Data Type | Notes |\n| ----------------------- | -------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------ | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |\n| scan_number | Scan number of the MS/MS spectrum | Integer | Unique identifier from the input file |\n| precursor_mz | Precursor m/z (mass-to-charge ratio) | Float | The observed m/z of the precursor ion |\n| precursor_charge | Precursor charge state | Integer | Charge state of the precursor ion |\n| experiment_name | Experiment name derived from input filename | String | Based on the input file name (mgf, mzml, or mzxml) |\n| spectrum_id | Unique spectrum identifier | String | Combination of experiment name and scan number (e.g., `yeast:17738`) |\n| targets | Target peptide sequence | String | Ground truth peptide sequence (if available) |\n| predictions | Predicted peptide sequences | String | Model-predicted peptide sequence |\n| predictions_tokenised | Predicted peptide sequence tokenized by amino acids | List[String] | Each amino acid token separated by commas |\n| log_probabilities | Log probability of the entire predicted sequence | Float | Natural logarithm of the sequence confidence, can be converted to probability with np.exp(log_probabilities). |\n| token_log_probabilities | Log probability of each token in the predicted sequence | List[Float] | Natural logarithm of the sequence confidence per amino acid |\n| delta_mass_ppm | Mass difference between precursor and predicted peptide in ppm | Float | Mass deviation in parts per million |\n\n### Models\n\nInstaNovo 1.1.0 includes a new model `instanovo-v1.1.0.ckpt` trained on a larger dataset with more\nPTMs.\n\n> Note: The InstaNovo Extended 1.0.0 training data mis-represented Cysteine as unmodified for the\n> majority of the training data. Please update to the latest version of the model.\n\n**Training Datasets**\n\n- [ProteomeTools](https://www.proteometools.org/) Part\n [I (PXD004732)](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD004732),\n [II (PXD010595)](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD010595), and\n [III (PXD021013)](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD021013) \\\n (referred to as the all-confidence ProteomeTools `AC-PT` dataset in our paper)\n- Additional PRIDE dataset with more modifications: \\\n ([PXD000666](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD000666), [PXD000867](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD000867),\n [PXD001839](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD001839), [PXD003155](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD003155),\n [PXD004364](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD004364), [PXD004612](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD004612),\n [PXD005230](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD005230), [PXD006692](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD006692),\n [PXD011360](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD011360), [PXD011536](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD011536),\n [PXD013543](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD013543), [PXD015928](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD015928),\n [PXD016793](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD016793), [PXD017671](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD017671),\n [PXD019431](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD019431), [PXD019852](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD019852),\n [PXD026910](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD026910), [PXD027772](https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pride/archive/projects/PXD027772))\n- [Massive-KB v1](https://massive.ucsd.edu/ProteoSAFe/static/massive.jsp)\n- Additional phosphorylation dataset \\\n (not yet publicly released)\n\n**Natively Supported Modifications**\n\n| Amino Acid | Single Letter | Modification | Mass Delta (Da) | Unimod ID |\n| --------------------------- | ------------- | ----------------------- | --------------- | --------------------------------------------------------------------------- |\n| Methionine | M | Oxidation | +15.9949 | [\\[UNIMOD:35\\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=35) |\n| Cysteine | C | Carboxyamidomethylation | +57.0215 | [\\[UNIMOD:4\\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=4) |\n| Asparagine, Glutamine | N, Q | Deamidation | +0.9840 | [\\[UNIMOD:7\\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=7) |\n| Serine, Threonine, Tyrosine | S, T, Y | Phosphorylation | +79.9663 | [\\[UNIMOD:21\\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=21) |\n| N-terminal | - | Ammonia Loss | -17.0265 | [\\[UNIMOD:385\\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=385) |\n| N-terminal | - | Carbamylation | +43.0058 | [\\[UNIMOD:5\\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=5) |\n| N-terminal | - | Acetylation | +42.0106 | [\\[UNIMOD:1\\]](https://www.unimod.org/modifications_view.php?editid1=1) |\n\nSee residue configuration under\n[instanovo/configs/residues/extended.yaml](./instanovo/configs/residues/extended.yaml)\n\n### Training\n\nData to train on may be provided in any format supported by the SpectrumDataHandler. See section on\ndata conversion for preferred formatting.\n\n#### Training InstaNovo\n\nTo train the auto-regressive transformer model InstaNovo using the config file\n[instanovo/configs/instanovo.yaml](./instanovo/configs/instanovo.yaml), you can use the following\ncommand:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo transformer train --help\n```\n\n\n\nTo update the InstaNovo model config, modify the config file under\n[instanovo/configs/model/instanovo_base.yaml](instanovo/configs/model/instanovo_base.yaml)\n\n#### Training InstaNovo+\n\nTo train the diffusion model InstaNovo+ using the config file\n[instanovo/configs/instanovoplus.yaml](instanovo/configs/instanovoplus.yaml), you can use the\nfollowing command:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo diffusion train --help\n```\n\n\n\nTo update the InstaNovo+ model config, modify the config file under\n[instanovo/configs/model/instanovoplus_base.yaml](instanovo/configs/model/instanovoplus_base.yaml)\n\n### Advanced prediction options\n\n### Run predictions with only InstaNovo\n\nIf you want to run predictions with only InstaNovo, you can use the following command:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo transformer predict --help\n```\n\n\n\n### Run predictions with only InstaNovo+\n\nIf you want to run predictions with only InstaNovo+, you can use the following command:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo diffusion predict --help\n```\n\n\n\n### Run predictions with InstaNovo and InstaNovo+ in separate steps\n\nYou can first run predictions with InstaNovo\n\n```bash\ninstanovo transformer predict --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path instanovo_predictions.csv\n```\n\nand then use the predictions as input for InstaNovo+:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo diffusion predict --data-path ./sample_data/spectra.mgf --output-path instanovo_plus_predictions.csv instanovo_predictions_path=instanovo_predictions.csv\n```\n\n## Additional features\n\n### Spectrum Data Class\n\nInstaNovo introduces a Spectrum Data Class: [SpectrumDataFrame](./instanovo/utils/data_handler.py).\nThis class acts as an interface between many common formats used for storing mass spectrometry,\nincluding `.mgf`, `.mzml`, `.mzxml`, and `.csv`. This class also supports reading directly from\nHuggingFace, Pandas, and Polars.\n\nWhen using InstaNovo, these formats are natively supported and automatically converted to the\ninternal SpectrumDataFrame supported by InstaNovo for training and inference. Any data path may be\nspecified using [glob notation](<https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Glob_(programming)>). For example you\ncould use the following command to get _de novo_ predictions from all the files in the folder\n`./experiment`:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo predict --data_path=./experiment/*.mgf\n```\n\nAlternatively, a list of files may be specified in the\n[inference config](./configs/inference/default.yaml).\n\nThe SpectrumDataFrame also allows for loading of much larger datasets in a lazy way. To do this, the\ndata is loaded and stored as [`.parquet`](https://docs.pola.rs/user-guide/io/parquet/) files in a\ntemporary directory. Alternatively, the data may be saved permanently natively as `.parquet` for\noptimal loading.\n\n**Example usage:**\n\nConverting mgf files to the native format:\n\n```python\nfrom instanovo.utils import SpectrumDataFrame\n\n# Convert mgf files native parquet:\nsdf = SpectrumDataFrame.load(\"/path/to/data.mgf\", lazy=False, is_annotated=True)\nsdf.save(\"path/to/parquet/folder\", partition=\"train\", chunk_size=1e6)\n```\n\nLoading the native format in shuffle mode:\n\n```python\n# Load a native parquet dataset:\nsdf = SpectrumDataFrame.load(\"path/to/parquet/folder\", partition=\"train\", shuffle=True, lazy=True, is_annotated=True)\n```\n\nUsing the loaded SpectrumDataFrame in a PyTorch DataLoader:\n\n```python\nfrom instanovo.transformer.dataset import SpectrumDataset\nfrom torch.utils.data import DataLoader\n\nds = SpectrumDataset(sdf)\n# Note: Shuffle and workers is handled by the SpectrumDataFrame\ndl = DataLoader(\n ds,\n collate_fn=SpectrumDataset.collate_batch,\n shuffle=False,\n num_workers=0,\n)\n```\n\nSome more examples using the SpectrumDataFrame:\n\n```python\nsdf = SpectrumDataFrame.load(\"/path/to/experiment/*.mzml\", lazy=True)\n\n# Remove rows with a charge value > 3:\nsdf.filter_rows(lambda row: row[\"precursor_charge\"]<=2)\n\n# Sample a subset of the data:\nsdf.sample_subset(fraction=0.5, seed=42)\n\n# Convert to pandas\ndf = sdf.to_pandas() # Returns a pd.DataFrame\n\n# Convert to polars LazyFrame\nlazy_df = sdf.to_polars(return_lazy=True) # Returns a pl.LazyFrame\n\n# Save as an `.mgf` file\nsdf.write_mgf(\"path/to/output.mgf\")\n```\n\n**SpectrumDataFrame Features:**\n\n- The SpectrumDataFrame supports lazy loading with asynchronous prefetching, mitigating wait times\n between files.\n- Filtering and sampling may be performed non-destructively through on file loading\n- A two-fold shuffling strategy is introduced to optimise sampling during training (shuffling files\n and shuffling within files).\n\n### Using your own datasets\n\nTo use your own datasets, you simply need to tabulate your data in either\n[Pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/) or [Polars](https://www.pola.rs/) with the following schema:\n\nThe dataset is tabular, where each row corresponds to a labelled MS2 spectra.\n\n- `sequence (string)` \\\n The target peptide sequence including post-translational modifications\n- `modified_sequence (string) [legacy]` \\\n The target peptide sequence including post-translational modifications\n- `precursor_mz (float64)` \\\n The mass-to-charge of the precursor (from MS1)\n- `charge (int64)` \\\n The charge of the precursor (from MS1)\n- `mz_array (list[float64])` \\\n The mass-to-charge values of the MS2 spectrum\n- `intensity_array (list[float32])` \\\n The intensity values of the MS2 spectrum\n\nFor example, the DataFrame for the\n[nine species benchmark](https://huggingface.co/datasets/InstaDeepAI/ms_ninespecies_benchmark)\ndataset (introduced in [Tran _et al._ 2017](https://www.pnas.org/doi/full/10.1073/pnas.1705691114))\nlooks as follows:\n\n| | sequence | precursor_mz | precursor_charge | mz_array | intensity_array |\n| --: | :----------------------------- | -----------: | ---------------: | :----------------------------------- | :---------------------------------- |\n| 0 | GRVEGMEAR | 335.502 | 3 | [102.05527 104.052956 113.07079 ...] | [ 767.38837 2324.8787 598.8512 ...] |\n| 1 | IGEYK | 305.165 | 2 | [107.07023 110.071236 111.11693 ...] | [ 1055.4957 2251.3171 35508.96 ...] |\n| 2 | GVSREEIQR | 358.528 | 3 | [103.039444 109.59844 112.08704 ...] | [801.19995 460.65268 808.3431 ...] |\n| 3 | SSYHADEQVNEASK | 522.234 | 3 | [101.07095 102.0552 110.07163 ...] | [ 989.45154 2332.653 1170.6191 ...] |\n| 4 | DTFNTSSTSN[UNIMOD:7]STSSSSSNSK | 676.282 | 3 | [119.82458 120.08073 120.2038 ...] | [ 487.86942 4806.1377 516.8846 ...] |\n\nFor _de novo_ prediction, the `sequence` column is not required.\n\nWe also provide a conversion script for converting to native SpectrumDataFrame (sdf) format:\n\n```bash\ninstanovo convert --help\n```\n\n\n\n## Development\n\n### `uv` setup\n\nThis project is set up to use [uv](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/) to manage Python and dependencies.\nFirst, be sure you [have uv installed](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/getting-started/installation/) on\nyour system.\n\nOn Linux and macOS:\n\n```bash\ncurl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh\n```\n\nOn Windows:\n\n```powershell\npowershell -c \"irm https://astral.sh/uv/install.ps1 | iex\"\n```\n\nNote: InstaNovo is built for Python >=3.10, <3.13 and tested on Linux, Windows and macOS.\n\n### Fork and clone the repository\n\nThen [fork](https://github.com/instadeepai/InstaNovo/fork) this repo (having your own fork will make\nit easier to contribute) and\n[clone it](https://docs.github.com/en/repositories/creating-and-managing-repositories/cloning-a-repository).\n\n```bash\ngit clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/InstaNovo.git\ncd InstaNovo\n```\n\nActivate the virtual environment:\n\n```bash\nsource .venv/bin/activate\n```\n\nAnd install the dependencies. If you don't have access to a GPU, you can install the CPU-only\nversion of PyTorch:\n\n```bash\nuv sync --extra cpu\nuv run pre-commit install\n```\n\nIf you do have access to an NVIDIA GPU, you can install the GPU version of PyTorch (recommended):\n\n```bash\nuv sync --extra cu124\nuv run pre-commit install\n```\n\nBoth approaches above also install the development dependencies. If you also want to install the\ndocumentation dependencies, you can do so with:\n\n```bash\nuv sync --extra cu124 --group docs\n```\n\nTo upgrade all packages to the latest versions, you can run:\n\n```bash\nuv lock --upgrade\nuv sync --extra cu124\n```\n\n### Basic development workflows\n\n#### Testing\n\nInstaNovo uses `pytest` for testing. To run the tests, you can use the following command:\n\n```bash\nuv run instanovo/scripts/get_zenodo_record.py # Download the test data\npython -m pytest --cov-report=html --cov --random-order --verbose .\n```\n\nTo see the coverage report, run:\n\n```bash\npython -m coverage report -m\n```\n\nTo view the coverage report in a browser, run:\n\n```bash\npython -m http.server --directory ./coverage\n```\n\nand navigate to `http://0.0.0.0:8000/` in your browser.\n\n#### Linting\n\nInstaNovo uses [pre-commit hooks](https://pre-commit.com/) to ensure code quality. To run the\nlinters, you can use the following command:\n\n```bash\npre-commit run --all-files\n```\n\n#### Building the documentation\n\nTo build the documentation locally, you can use the following commands:\n\n```bash\nuv sync --extra cu124 --group docs\ngit config --global --add safe.directory \"$(dirname \"$(pwd)\")\"\nrm -rf docs/reference\npython ./docs/gen_ref_nav.py\nmkdocs build --verbose --site-dir docs_public\nmkdocs serve\n```\n\n### Generating a requirements.txt file\n\nIf you have a `pip` or `conda` based workflow and want to generate a `requirements.txt` file, you\ncan use the following command:\n\n```bash\nuv export --format requirements-txt > requirements.txt\n```\n\n### Setting Python interpreter in VSCode\n\nTo set the Python interpreter in VSCode, open the Command Palette (`Ctrl+Shift+P`), search for\n`Python: Select Interpreter`, and select `./.venv/bin/python`.\n\n## License\n\nCode is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (see [LICENSE](LICENSE.md))\n\nThe model checkpoints are licensed under Creative Commons Non-Commercial\n([CC BY-NC-SA 4.0](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/))\n\n## BibTeX entry and citation info\n\nIf you use InstaNovo in your research, please cite the following paper:\n\n```bibtex\n@article{eloff_kalogeropoulos_2024_instanovo,\n\ttitle = {De novo peptide sequencing with InstaNovo: Accurate, database-free peptide identification for large scale proteomics experiments},\n\tauthor = {Kevin Eloff and Konstantinos Kalogeropoulos and Oliver Morell and Amandla Mabona and Jakob Berg Jespersen and Wesley Williams and Sam van Beljouw and Marcin Skwark and Andreas Hougaard Laustsen and Stan J. J. Brouns and Anne Ljungars and Erwin Marten Schoof and Jeroen Van Goey and Ulrich auf dem Keller and Karim Beguir and Nicolas Lopez Carranza and Timothy Patrick Jenkins},\n\tyear = {2024},\n\tdoi = {10.1101/2023.08.30.555055},\n\tpublisher = {Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory},\n\tURL = {https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2023.08.30.555055v3},\n\tjournal = {bioRxiv}\n}\n```\n\n## Acknowledgements\n\nBig thanks to Pathmanaban Ramasamy, Tine Claeys, and Lennart Martens of the\n[CompOmics](https://www.compomics.com/) research group for providing us with additional\nphosphorylation training data.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "InstaNovo enables diffusion-powered de novo peptide sequencing in large scale proteomics experiments",
"version": "1.1.0",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/instadeepai/InstaNovo",
"Issues": "https://github.com/instadeepai/InstaNovo/issues",
"documentation": "https://instadeepai.github.io/InstaNovo/"
},
"split_keywords": [
"mass spectrometry",
" bioinformatics",
" machine learning",
" deep learning",
" transformer",
" de novo peptide sequencing"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "bc37046a715581b2d04fafbcaf9466de4b1211798ac82316e79c9c16a18f9544",
"md5": "442c538d27acb21204037122e3dbd819",
"sha256": "6c4b2c1874b0714ba7b3a8541639a4ce521f913245e0938e5f2cd2add9f8f296"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "instanovo-1.1.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "442c538d27acb21204037122e3dbd819",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": "<3.13,>=3.10",
"size": 129669,
"upload_time": "2025-03-28T12:09:50",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-03-28T12:09:50.473416Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bc/37/046a715581b2d04fafbcaf9466de4b1211798ac82316e79c9c16a18f9544/instanovo-1.1.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "8caeabe65cd5cc1dd7d96687e8c57d6beb484c2444b4f9d936c273280d5f880e",
"md5": "7dc43524069b1fce4bac37d237fdf235",
"sha256": "52ca587960820659046ad104b9fe071e91e45a4d011ae4427ec856a770280138"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "instanovo-1.1.0.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "7dc43524069b1fce4bac37d237fdf235",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": "<3.13,>=3.10",
"size": 111064,
"upload_time": "2025-03-28T12:09:51",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-03-28T12:09:51.998567Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/8c/ae/abe65cd5cc1dd7d96687e8c57d6beb484c2444b4f9d936c273280d5f880e/instanovo-1.1.0.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-03-28 12:09:51",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "instadeepai",
"github_project": "InstaNovo",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"lcname": "instanovo"
}
