# NVIDIA Nsight Tools JupyterLab Extension
A JupyterLab extension for profiling cells execution using NVIDIA Nsight tools.
## Demo
Click on the image to launch the video
[](https://www.youtube.com/embed/e_km8B3v_qI)
## Requirements
- JupyterLab >= 4.0.0
- Docker (optional, for GUI support)
- [nvtx](https://pypi.org/project/nvtx/) (For Nsight Compute support, required to be installed on the profiled Python)
Nsight tools are not bundled with this extension. The required tool(s) should be installed separately on the JupyterLab server machine.
## Install and setup
- To install the extension, execute:
```bash
pip install jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight
```
- Install [Nsight Systems](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-systems) and/or [Nsight Compute](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-compute) (these tools are not shipped with this extension).
- Set Nsight Systems and/or Nsight Compute installation location in the extension settings.
- Example: If Nsight Systems installation location is set to `/opt/nvidia/nsight-systems/<version>`,
then the extension will look for nsys executable in `/opt/nvidia/nsight-systems/<version>/target-linux-x64`
- If not set, `PATH` environment variable should contain the locations of the tool's executables.
## Profile JupyterLab cells
1. Enable Nsight tool by using the _Profiling with Nsight Systems/Compute..._ command
under the _NVIDIA Nsight_ menu, or by using the command palette.
- **Note**: This restarts the JupyterLab kernel.
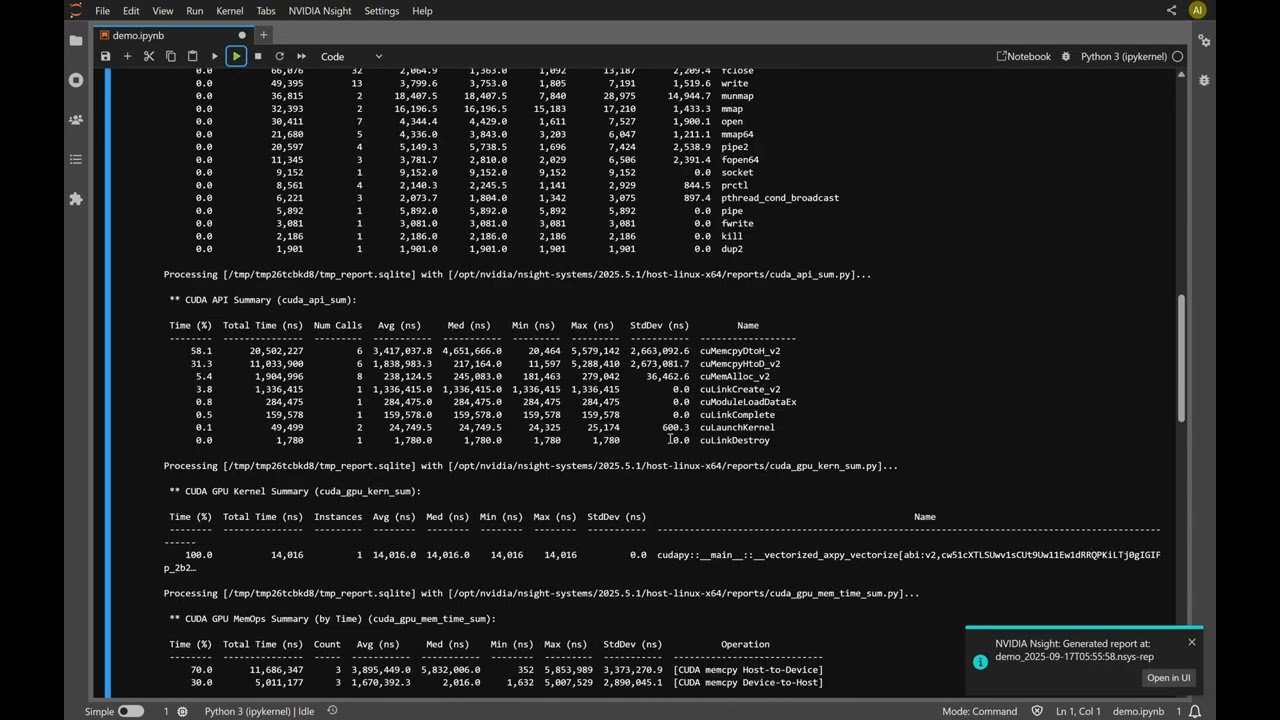
2. Profile cells execution by using the _Run and profile selected cells..._ command.
3. The cell's profiling info is displayed in the cell output area.
## Analyzing the profile session in Nsight tools GUI
- Open Nsight tools report files in a tab inside JupyterLab.
- Display of Nsight tools GUI requires [NVIDIA Nsight Streamer](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/devtools/resources/nsight-streamer-resources).
- When JupyterLab is running inside a Docker container, displaying Nsight tools UI requires to have
the Docker daemon socket mounted
(i.e., `docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock ...`).
- **SECURITY ALERT:** The Docker daemon socket should not be mounted when using untrusted sources because it may provide root access to the host system.
- See also the Docker Example section below.
- Nsight Streamer requires two communication ports for HTTP and media.
By default, the extension picks two random free ports per each open report.
Use "Allowed HTTP ports" and "Allowed media ports" to restrict the pool of the ports used for this purpose.
- For systems where the Jupyter server is not directly reachable from the client,
and Jupyter is behind nginx, the following is typically required:
- Expose the HTTP port with nginx.
- Use a TURN server for the media communication channel.
- See "NGINX Example" and "TURN Server Example" sections below.
## Supported Tools
### Nsight Systems
- Supports Nsight Systems release 2024.1.1 or later. It is recommended to use the [latest release](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-systems).
- Use `--stats=true` when profiling cells execution to see textual output of `nsys stats`.
<details>
<summary>NSYS CLI flags that can't be used within the extension</summary>
- `--help`, `-h`
- `--hotkey-capture`
- `--output`, `-o`
- `--session-new`
- `--session`
- `--stop-on-exit`, `-x`
</details>
### Nsight Compute
- Supports Nsight Compute release 2024.3 or later. It is recommended to use the [latest release](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-compute).
- Requires [nvtx](https://pypi.org/project/nvtx/) to be installed on the profiled Python.
<details>
<summary>NCU CLI flags that can't be used within the extension</summary>
- `--app-replay-buffer`
- `--app-replay-match`
- `--app-replay-mode`
- `--check-exit-code`
- `--chips`
- `--config-file-path`
- `--config-file`
- `--export`, `-o`
- `--force-overwrite`, `-f`
- `--help`, `-h`
- `--hostname`
- `--import`, `-i`
- `--kill`
- `--list-chips`
- `--list-metrics`
- `--list-rules`
- `--list-sections`
- `--list-sets`
- `--log-file`
- `--mode`
- `--null-stdin`
- `--open-in-ui`
- `--profile-from-start`
- `--query-metrics-collection`
- `--query-metrics-mode`
- `--query-metrics`
- `--quiet`
- `--range-filter`
- `--range-replay-options`
- `--rename-kernels-export`
- `--replay-mode`
- `--section-folder-restore`
- `--version`, `-v`
</details>
<details>
<summary>NCU CLI flags that can be used only when enabling NCU</summary>
- `--apply-rules`
- `--cache-control`
- `--call-stack-type`
- `--call-stack`
- `--clock-control`
- `--disable-profiler-start-stop`
- `--graph-profiling`
- `--import-source`
- `--injection-path-32`
- `--injection-path-64`
- `--max-connections`
- `--metrics`
- `--pm-sampling-buffer-size`
- `--pm-sampling-interval`
- `--pm-sampling-max-passes`
- `--port`, `-p`
- `--preload-library`
- `--rule`
- `--section-folder-recursive`
- `--section-folder`
- `--section`
- `--set`
- `--source-folders`
- `--support-32bit`
- `--target-processes-filter`
- `--target-processes`
- `--verbose`
- `--warp-sampling-buffer-size`
- `--warp-sampling-interval`
- `--warp-sampling-max-passes`
</details>
<details>
<summary>NCU CLI flags that can be used only when profiling cells</summary>
- `--csv`
- `--devices`
- `--disable-extra-suffixes`
- `--filter-mode`
- `--kernel-id`
- `--kernel-name-base`
- `--kernel-name`, `-k`
- `--launch-count`, `-c`
- `--launch-skip-before-match`
- `--launch-skip`, `-s`
- `--nvtx-exclude`
- `--nvtx-include`
- `--page`
- `--print-details`
- `--print-fp`
- `--print-kernel-base`
- `--print-metric-attribution`
- `--print-metric-instances`
- `--print-metric-name`
- `--print-nvtx-rename`
- `--print-rule-details`
- `--print-source`
- `--print-summary`
- `--print-units`
- `--rename-kernels-path`
- `--rename-kernels`
- `--resolve-source-file`
</details>
## Docker Example
This example demonstrates how to use the extension in a [Jupyter Docker Stacks](https://jupyter-docker-stacks.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) image.
The following Dockerfile defines a Docker image based on `pytorch-notebook` with CUDA 12,
and includes the extension and cuda-toolkit.\
**It is recommended to use the latest cuda-toolkit** - https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads
<details>
<summary>Dockerfile</summary>
```dockerfile
FROM quay.io/jupyter/pytorch-notebook:cuda12-python-3.11.8
# Install cuda-toolkit
ADD https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu2404/x86_64/cuda-keyring_1.1-1_all.deb /tmp/
USER root
RUN dpkg -i /tmp/cuda-keyring_1.1-1_all.deb && apt-get -y update && \
apt-get -y install cuda-toolkit-12-9
USER ${NB_UID}
# Install jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight and set the default settings
ARG HOST_IP
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight nvtx && \
fix-permissions "${CONDA_DIR}" && fix-permissions "/home/${NB_USER}" && \
mkdir -p /home/${NB_USER}/.jupyter/lab/user-settings/jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight && echo ' \
{ \
"ui": { \
"enabled": true, \
"suppressServerAddressWarning": true, \
"dockerHost": "'"$HOST_IP"'" \
}, \
"nsys": { \
"installationPath": "/opt/nvidia/nsight-systems/2025.1.3", \
"args": "--trace=cuda,nvtx,osrt --python-sampling=true --python-backtrace=cuda --cudabacktrace=all" \
}, \
"ncu": { \
"installationPath": "/opt/nvidia/nsight-compute/2025.2.1" \
} \
}' > /home/${NB_USER}/.jupyter/lab/user-settings/jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight/plugin.jupyterlab-settings
```
</details>
### Build the image:
```bash
docker build --rm --tag <your-image-name> --build-arg HOST_IP="$(hostname -i | cut -d' ' -f1)" .
```
### Run the container:
```bash
# SECURITY ALERT: Remove `-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock` when using untrusted sources
docker run -it --rm --group-add $(getent group docker | cut -d: -f3) --runtime=nvidia -p 8888:8888 -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock <your-image-name>
```
Note: Using `--runtime=nvidia` requires [NVIDIA Container Toolkit](https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/latest/).
## NGINX Example
`jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight` uses [NVIDIA Nsight Streamer](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/devtools/resources/nsight-streamer-resources)
for displaying Nsight tools UI inside JupyterLab. Hence, when JupyterLab is proxied via nginx,
in order to properly display the UI, the HTTP port that is used for the streamer must be properly
exposed by nginx. This example demonstrates a minimal nginx configuration for proxying JupyterLab,
and the modifications required for properly displaying Nsight tools UI.
JupyterLab is started with the following command, allowing remote access:
```bash
jupyter lab --no-browser --ServerApp.allow_remote_access=True
```
Below is a basic nginx configuration file for exposing only the JupyterLab server over HTTPS.
Commonly saved at `/etc/nginx/sites-available/` and soft linked to `/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/`.
<details>
<summary>nginx configuration file without Nsight extension settings (/etc/nginx/sites-available/jupyter)</summary>
```nginx
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name my-server-hostname;
ssl_certificate /path/to/mycert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /path/to/mykey.key;
# The location path should match the JupyterLab `ServerApp.base_url` ('/' by default).
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8888/; # Replace with the actual JupyterLab server address
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
}
```
</details>
<br>
After reloading nginx with `sudo systemctl reload nginx`, it is possible to open JupyterLab
from a browser via `https://my-server-hostname/`,
(assuming the used SSL certificate is valid, and trusted by the browser).
But displaying Nsight tools UI inside JupyterLab doesn't work because
the ports used by Nsight Streamer are not exposed by nginx.
Change the `jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight` settings as follows:
1. Set "Proxy domain".
- This example uses "NsightStreamer", any name can be chosen.
- The location path for exposing Nsight Streamer in nginx should match this setting.
See inline comment in the configuration example snippet below.
2. Set "Allowed HTTP ports".
- This example arbitrarily uses "9001-9003", any set of free ports can be chosen.
- The number of ports sets the maximum number of report files that can be opened simultaneously
in the extension.
Add a "location" block inside the nginx conf for properly exposing the Nsight Streamer.
Here is the updated configuration file.
<details>
<summary>nginx configuration file with Nsight extension settings (/etc/nginx/sites-available/jupyter)</summary>
```nginx
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name my-server-hostname;
ssl_certificate /path/to/mycert.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /path/to/mykey.key;
# The location path should match the JupyterLab `ServerApp.base_url` ('/' by default).
location / {
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8888/; # Replace with the actual JupyterLab server address
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
# The location path should contain the JupyterLab `ServerApp.base_url`, and the Proxy domain
# defined in the extension settings.
# For example, if `ServerApp.base_url == 'my_base_url'`, then the location path would be:
# ^/my_base_url/NsightStreamer/(\d+)/(.*)
location ~ ^/NsightStreamer/(\d+)/(.*) {
set $port $1;
set $rest $2;
if ($is_nsight_streamer_port = INVALID) {
return 403 "Port not allowed";
}
# Replace "0.0.0.0" with the Jupyter server address
set $target "http://0.0.0.0:$port/$rest$is_args$args";
proxy_pass $target;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}
map $port $is_nsight_streamer_port {
default INVALID;
9001 OK;
9002 OK;
9003 OK;
}
```
</details>
<br>
After reloading nginx, displaying Nsight UI inside JupyterLab works.
If the display is stuck on "Waiting for stream", it indicates that the media communication
channel is broken. First, make sure that the media port that is used by Nsight streamer is not
blocked by Firewall or NAT. If a direct peer-to-peer communication is not possible,
see next section "TURN server Example" for a possible solution.
## TURN Server Example
This section provide a solution for when a direct peer-to-peer communication is not possible between
the client and the Jupyter server via the media port
(use "Allowed media ports" setting to control which media ports are used by the extension).
In such case, the Nsight UI display is stuck on "Waiting for stream".
This is commonly needed in corporate environments or when the Jupyter server is behind strict
network policies.
The solution is to run and use a TURN server that is reachable from both the client (browser)
and the Jupyter server, typically the TURN server runs on the same host that runs nginx.
The following example demonstrates how to set up a TURN server using
[coturn](https://github.com/coturn/coturn), and how to configure the extension appropriately.
### Save a coturn configuration file
**Note**: The coturn configuration requirements may vary on different environments.
See this [example](https://github.com/coturn/coturn/blob/master/examples/etc/turnserver.conf)
for more information about coturn configuration.
<details>
<summary>turnserver.conf</summary>
```ini
# Should be set as the "Turn port" extension setting
listening-port=3478
# This port range should be set as the "Allowed media ports" setting
# One media port is required per each opened report (in addition to the http port)
min-port=49152
max-port=49154
# Should match the "JupyterLab server address" setting
allowed-peer-ip=<jupyter-server-ip>
# Must be set, the value is usually arbitrary.
realm=nsightstreamer
# Default is username=nvidia, password=nvidia
# For non-default, set the "TURN username" and "TURN password" accordingly
lt-cred-mech
fingerprint
user=nvidia:nvidia
```
</details>
### Run coturn
```bash
docker run -d --rm --network=host -v /path/to/turnserver.conf:/etc/turnserver.conf coturn/coturn -c /etc/turnserver.conf
```
### Set the extension settings
- "Turn server address" - The IP address (or hostname) of the TURN server.
- "Turn port" - The `listening-port` as set in the coturn configuration above.
- "Allowed media ports" - The `<min-port>:<max-port>` range as set in the coturn configuration above.
- "TURN username" and "TURN password" - The user credentials as set in the coturn configuration above.
If Nsight UI display still doesn't work,
adding `verbose` and `log-file=stdout` to `turnserver.conf` and inspecting
coturn logs (using `docker logs` command) are a good starting point to understand what went wrong.
## Uninstall
To remove the extension, execute:
```bash
pip uninstall jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight
```
## Troubleshooting
If you are seeing the frontend extension, but it is not working, check
that the server extension is enabled:
```bash
jupyter server extension list
```
If the server extension is installed and enabled, but you are not seeing
the frontend extension, check the frontend extension is installed:
```bash
jupyter labextension list
```
## Known Issues
- While Nsight Compute is enabled, interrupting the JupyterLab kernel with the "Interrupt Kernel" command (by using the command palette, kernel menu or the stop-button) causes the kernel to terminate and restart.
## Release Notes
### 0.8.0
- New setting for configuring the allowed media ports to be used for displaying Nsight UI.
- Support displaying Nsight UI when JupyterLab is running on a private network
using an external TURN server.
- Introduces new settings for configuring the TURN server that is used -
Turn server address, Turn port, and Turn username and password.
### 0.7.1
- Support Linux SBSA.
- Support displaying Nsight UI when JupyterLab is running over HTTPS.
- Support displaying Nsight UI when JupyterLab is proxied via nginx.
- Support displaying Nsight UI when JupyterLab is using a remote file system.
- New setting for configuring the allowed HTTP ports to be used for displaying Nsight UI.
- New setting for configuring the maximum resolution of Nsight Streamer.
- New command for refreshing a Nsight UI display tab.
- By right-clicking a tab and selecting "Refresh Tab".
- Register report files in Jupyter DocumentRegistry with Nsight UI display as the default file
opener (e.g., double-clicking a report file will display it with Nsight UI).
### 0.7.0
- New setting for configuring the location of the generated reports.
- Support displaying Nsight UI when running inside a docker container.
- Use (and pull if required) the latest NVIDIA Nsight Streamer for displaying Nsight UI.
- See [Nsight Streamer for Nsight Systems](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/devtools/containers/nsight-streamer-nsys) and [Nsight Streamer for Nsight Compute](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/devtools/containers/nsight-streamer-ncu).
- Support displaying an external WebRTC streamer.
### 0.6.0
- Support displaying Nsight Compute UI inside JupyterLab.
- Fix keyboard interaction with Nsight tools UI.
### 0.5.2
- Added Nsight Compute section in the project description.
- Verify server connection on extension load.
### 0.5.1
- Initial release.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "jupyter, jupyterlab, jupyterlab-extension",
"author": null,
"author_email": "NVIDIA Corporation <devtools-support@nvidia.com>",
"download_url": null,
"platform": null,
"description": "# NVIDIA Nsight Tools JupyterLab Extension\n\nA JupyterLab extension for profiling cells execution using NVIDIA Nsight tools.\n\n## Demo\n\nClick on the image to launch the video\n\n[](https://www.youtube.com/embed/e_km8B3v_qI)\n\n## Requirements\n\n- JupyterLab >= 4.0.0\n- Docker (optional, for GUI support)\n- [nvtx](https://pypi.org/project/nvtx/) (For Nsight Compute support, required to be installed on the profiled Python)\n\nNsight tools are not bundled with this extension. The required tool(s) should be installed separately on the JupyterLab server machine.\n\n## Install and setup\n\n- To install the extension, execute:\n\n```bash\npip install jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight\n```\n\n- Install [Nsight Systems](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-systems) and/or [Nsight Compute](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-compute) (these tools are not shipped with this extension).\n\n- Set Nsight Systems and/or Nsight Compute installation location in the extension settings.\n - Example: If Nsight Systems installation location is set to `/opt/nvidia/nsight-systems/<version>`,\n then the extension will look for nsys executable in `/opt/nvidia/nsight-systems/<version>/target-linux-x64`\n - If not set, `PATH` environment variable should contain the locations of the tool's executables.\n\n## Profile JupyterLab cells\n\n1. Enable Nsight tool by using the _Profiling with Nsight Systems/Compute..._ command\n under the _NVIDIA Nsight_ menu, or by using the command palette.\n - **Note**: This restarts the JupyterLab kernel.\n2. Profile cells execution by using the _Run and profile selected cells..._ command.\n3. The cell's profiling info is displayed in the cell output area.\n\n## Analyzing the profile session in Nsight tools GUI\n\n- Open Nsight tools report files in a tab inside JupyterLab.\n- Display of Nsight tools GUI requires [NVIDIA Nsight Streamer](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/devtools/resources/nsight-streamer-resources).\n- When JupyterLab is running inside a Docker container, displaying Nsight tools UI requires to have\n the Docker daemon socket mounted\n (i.e., `docker run -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock ...`).\n - **SECURITY ALERT:** The Docker daemon socket should not be mounted when using untrusted sources because it may provide root access to the host system.\n - See also the Docker Example section below.\n\n- Nsight Streamer requires two communication ports for HTTP and media.\n By default, the extension picks two random free ports per each open report.\n Use \"Allowed HTTP ports\" and \"Allowed media ports\" to restrict the pool of the ports used for this purpose.\n- For systems where the Jupyter server is not directly reachable from the client,\n and Jupyter is behind nginx, the following is typically required:\n - Expose the HTTP port with nginx.\n - Use a TURN server for the media communication channel.\n - See \"NGINX Example\" and \"TURN Server Example\" sections below.\n\n## Supported Tools\n\n### Nsight Systems\n\n- Supports Nsight Systems release 2024.1.1 or later. It is recommended to use the [latest release](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-systems).\n- Use `--stats=true` when profiling cells execution to see textual output of `nsys stats`.\n\n<details>\n<summary>NSYS CLI flags that can't be used within the extension</summary>\n\n- `--help`, `-h`\n- `--hotkey-capture`\n- `--output`, `-o`\n- `--session-new`\n- `--session`\n- `--stop-on-exit`, `-x`\n\n</details>\n\n### Nsight Compute\n\n- Supports Nsight Compute release 2024.3 or later. It is recommended to use the [latest release](https://developer.nvidia.com/nsight-compute).\n- Requires [nvtx](https://pypi.org/project/nvtx/) to be installed on the profiled Python.\n\n<details>\n<summary>NCU CLI flags that can't be used within the extension</summary>\n\n- `--app-replay-buffer`\n- `--app-replay-match`\n- `--app-replay-mode`\n- `--check-exit-code`\n- `--chips`\n- `--config-file-path`\n- `--config-file`\n- `--export`, `-o`\n- `--force-overwrite`, `-f`\n- `--help`, `-h`\n- `--hostname`\n- `--import`, `-i`\n- `--kill`\n- `--list-chips`\n- `--list-metrics`\n- `--list-rules`\n- `--list-sections`\n- `--list-sets`\n- `--log-file`\n- `--mode`\n- `--null-stdin`\n- `--open-in-ui`\n- `--profile-from-start`\n- `--query-metrics-collection`\n- `--query-metrics-mode`\n- `--query-metrics`\n- `--quiet`\n- `--range-filter`\n- `--range-replay-options`\n- `--rename-kernels-export`\n- `--replay-mode`\n- `--section-folder-restore`\n- `--version`, `-v`\n\n</details>\n\n<details>\n<summary>NCU CLI flags that can be used only when enabling NCU</summary>\n\n- `--apply-rules`\n- `--cache-control`\n- `--call-stack-type`\n- `--call-stack`\n- `--clock-control`\n- `--disable-profiler-start-stop`\n- `--graph-profiling`\n- `--import-source`\n- `--injection-path-32`\n- `--injection-path-64`\n- `--max-connections`\n- `--metrics`\n- `--pm-sampling-buffer-size`\n- `--pm-sampling-interval`\n- `--pm-sampling-max-passes`\n- `--port`, `-p`\n- `--preload-library`\n- `--rule`\n- `--section-folder-recursive`\n- `--section-folder`\n- `--section`\n- `--set`\n- `--source-folders`\n- `--support-32bit`\n- `--target-processes-filter`\n- `--target-processes`\n- `--verbose`\n- `--warp-sampling-buffer-size`\n- `--warp-sampling-interval`\n- `--warp-sampling-max-passes`\n\n</details>\n\n<details>\n<summary>NCU CLI flags that can be used only when profiling cells</summary>\n\n- `--csv`\n- `--devices`\n- `--disable-extra-suffixes`\n- `--filter-mode`\n- `--kernel-id`\n- `--kernel-name-base`\n- `--kernel-name`, `-k`\n- `--launch-count`, `-c`\n- `--launch-skip-before-match`\n- `--launch-skip`, `-s`\n- `--nvtx-exclude`\n- `--nvtx-include`\n- `--page`\n- `--print-details`\n- `--print-fp`\n- `--print-kernel-base`\n- `--print-metric-attribution`\n- `--print-metric-instances`\n- `--print-metric-name`\n- `--print-nvtx-rename`\n- `--print-rule-details`\n- `--print-source`\n- `--print-summary`\n- `--print-units`\n- `--rename-kernels-path`\n- `--rename-kernels`\n- `--resolve-source-file`\n\n</details>\n\n## Docker Example\n\nThis example demonstrates how to use the extension in a [Jupyter Docker Stacks](https://jupyter-docker-stacks.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) image.\n\nThe following Dockerfile defines a Docker image based on `pytorch-notebook` with CUDA 12,\nand includes the extension and cuda-toolkit.\\\n**It is recommended to use the latest cuda-toolkit** - https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads\n\n<details>\n<summary>Dockerfile</summary>\n\n```dockerfile\nFROM quay.io/jupyter/pytorch-notebook:cuda12-python-3.11.8\n\n# Install cuda-toolkit\nADD https://developer.download.nvidia.com/compute/cuda/repos/ubuntu2404/x86_64/cuda-keyring_1.1-1_all.deb /tmp/\nUSER root\nRUN dpkg -i /tmp/cuda-keyring_1.1-1_all.deb && apt-get -y update && \\\n apt-get -y install cuda-toolkit-12-9\nUSER ${NB_UID}\n\n# Install jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight and set the default settings\nARG HOST_IP\nRUN pip install --no-cache-dir jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight nvtx && \\\n fix-permissions \"${CONDA_DIR}\" && fix-permissions \"/home/${NB_USER}\" && \\\n mkdir -p /home/${NB_USER}/.jupyter/lab/user-settings/jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight && echo ' \\\n{ \\\n \"ui\": { \\\n \"enabled\": true, \\\n \"suppressServerAddressWarning\": true, \\\n \"dockerHost\": \"'\"$HOST_IP\"'\" \\\n }, \\\n \"nsys\": { \\\n \"installationPath\": \"/opt/nvidia/nsight-systems/2025.1.3\", \\\n \"args\": \"--trace=cuda,nvtx,osrt --python-sampling=true --python-backtrace=cuda --cudabacktrace=all\" \\\n }, \\\n \"ncu\": { \\\n \"installationPath\": \"/opt/nvidia/nsight-compute/2025.2.1\" \\\n } \\\n}' > /home/${NB_USER}/.jupyter/lab/user-settings/jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight/plugin.jupyterlab-settings\n```\n\n</details>\n\n### Build the image:\n\n```bash\ndocker build --rm --tag <your-image-name> --build-arg HOST_IP=\"$(hostname -i | cut -d' ' -f1)\" .\n```\n\n### Run the container:\n\n```bash\n# SECURITY ALERT: Remove `-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock` when using untrusted sources\ndocker run -it --rm --group-add $(getent group docker | cut -d: -f3) --runtime=nvidia -p 8888:8888 -v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock <your-image-name>\n```\n\nNote: Using `--runtime=nvidia` requires [NVIDIA Container Toolkit](https://docs.nvidia.com/datacenter/cloud-native/container-toolkit/latest/).\n\n## NGINX Example\n\n`jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight` uses [NVIDIA Nsight Streamer](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/devtools/resources/nsight-streamer-resources)\nfor displaying Nsight tools UI inside JupyterLab. Hence, when JupyterLab is proxied via nginx,\nin order to properly display the UI, the HTTP port that is used for the streamer must be properly\nexposed by nginx. This example demonstrates a minimal nginx configuration for proxying JupyterLab,\nand the modifications required for properly displaying Nsight tools UI.\n\nJupyterLab is started with the following command, allowing remote access:\n\n```bash\njupyter lab --no-browser --ServerApp.allow_remote_access=True\n```\n\nBelow is a basic nginx configuration file for exposing only the JupyterLab server over HTTPS.\nCommonly saved at `/etc/nginx/sites-available/` and soft linked to `/etc/nginx/sites-enabled/`.\n\n<details>\n<summary>nginx configuration file without Nsight extension settings (/etc/nginx/sites-available/jupyter)</summary>\n\n```nginx\nserver {\n listen 443 ssl;\n server_name my-server-hostname;\n\n ssl_certificate /path/to/mycert.pem;\n ssl_certificate_key /path/to/mykey.key;\n\n # The location path should match the JupyterLab `ServerApp.base_url` ('/' by default).\n location / {\n proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8888/; # Replace with the actual JupyterLab server address\n proxy_set_header Host $host;\n proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;\n proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;\n proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;\n\n proxy_http_version 1.1;\n proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;\n proxy_set_header Connection \"upgrade\";\n }\n}\n```\n\n</details>\n\n<br>\n\nAfter reloading nginx with `sudo systemctl reload nginx`, it is possible to open JupyterLab\nfrom a browser via `https://my-server-hostname/`,\n(assuming the used SSL certificate is valid, and trusted by the browser).\nBut displaying Nsight tools UI inside JupyterLab doesn't work because\nthe ports used by Nsight Streamer are not exposed by nginx.\n\nChange the `jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight` settings as follows:\n\n1. Set \"Proxy domain\".\n - This example uses \"NsightStreamer\", any name can be chosen.\n - The location path for exposing Nsight Streamer in nginx should match this setting.\n See inline comment in the configuration example snippet below.\n2. Set \"Allowed HTTP ports\".\n - This example arbitrarily uses \"9001-9003\", any set of free ports can be chosen.\n - The number of ports sets the maximum number of report files that can be opened simultaneously\n in the extension.\n\nAdd a \"location\" block inside the nginx conf for properly exposing the Nsight Streamer.\nHere is the updated configuration file.\n\n<details>\n<summary>nginx configuration file with Nsight extension settings (/etc/nginx/sites-available/jupyter)</summary>\n\n```nginx\nserver {\n listen 443 ssl;\n server_name my-server-hostname;\n\n ssl_certificate /path/to/mycert.pem;\n ssl_certificate_key /path/to/mykey.key;\n\n # The location path should match the JupyterLab `ServerApp.base_url` ('/' by default).\n location / {\n proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:8888/; # Replace with the actual JupyterLab server address\n proxy_set_header Host $host;\n proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;\n proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;\n proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;\n\n proxy_http_version 1.1;\n proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;\n proxy_set_header Connection \"upgrade\";\n }\n\n # The location path should contain the JupyterLab `ServerApp.base_url`, and the Proxy domain\n # defined in the extension settings.\n # For example, if `ServerApp.base_url == 'my_base_url'`, then the location path would be:\n # ^/my_base_url/NsightStreamer/(\\d+)/(.*)\n location ~ ^/NsightStreamer/(\\d+)/(.*) {\n set $port $1;\n set $rest $2;\n\n if ($is_nsight_streamer_port = INVALID) {\n return 403 \"Port not allowed\";\n }\n\n # Replace \"0.0.0.0\" with the Jupyter server address\n set $target \"http://0.0.0.0:$port/$rest$is_args$args\";\n\n proxy_pass $target;\n proxy_set_header Host $host;\n proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;\n proxy_http_version 1.1;\n proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;\n proxy_set_header Connection \"upgrade\";\n proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;\n }\n}\n\nmap $port $is_nsight_streamer_port {\n default INVALID;\n 9001 OK;\n 9002 OK;\n 9003 OK;\n}\n```\n\n</details>\n\n<br>\n\nAfter reloading nginx, displaying Nsight UI inside JupyterLab works.\nIf the display is stuck on \"Waiting for stream\", it indicates that the media communication\nchannel is broken. First, make sure that the media port that is used by Nsight streamer is not\nblocked by Firewall or NAT. If a direct peer-to-peer communication is not possible,\nsee next section \"TURN server Example\" for a possible solution.\n\n## TURN Server Example\n\nThis section provide a solution for when a direct peer-to-peer communication is not possible between\nthe client and the Jupyter server via the media port\n(use \"Allowed media ports\" setting to control which media ports are used by the extension).\nIn such case, the Nsight UI display is stuck on \"Waiting for stream\".\nThis is commonly needed in corporate environments or when the Jupyter server is behind strict\nnetwork policies.\n\nThe solution is to run and use a TURN server that is reachable from both the client (browser)\nand the Jupyter server, typically the TURN server runs on the same host that runs nginx.\n\nThe following example demonstrates how to set up a TURN server using\n[coturn](https://github.com/coturn/coturn), and how to configure the extension appropriately.\n\n### Save a coturn configuration file\n\n**Note**: The coturn configuration requirements may vary on different environments.\nSee this [example](https://github.com/coturn/coturn/blob/master/examples/etc/turnserver.conf)\nfor more information about coturn configuration.\n\n<details>\n<summary>turnserver.conf</summary>\n\n```ini\n# Should be set as the \"Turn port\" extension setting\nlistening-port=3478\n\n# This port range should be set as the \"Allowed media ports\" setting\n# One media port is required per each opened report (in addition to the http port)\nmin-port=49152\nmax-port=49154\n\n# Should match the \"JupyterLab server address\" setting\nallowed-peer-ip=<jupyter-server-ip>\n\n# Must be set, the value is usually arbitrary.\nrealm=nsightstreamer\n\n# Default is username=nvidia, password=nvidia\n# For non-default, set the \"TURN username\" and \"TURN password\" accordingly\nlt-cred-mech\nfingerprint\nuser=nvidia:nvidia\n```\n\n</details>\n\n### Run coturn\n\n```bash\ndocker run -d --rm --network=host -v /path/to/turnserver.conf:/etc/turnserver.conf coturn/coturn -c /etc/turnserver.conf\n```\n\n### Set the extension settings\n\n- \"Turn server address\" - The IP address (or hostname) of the TURN server.\n- \"Turn port\" - The `listening-port` as set in the coturn configuration above.\n- \"Allowed media ports\" - The `<min-port>:<max-port>` range as set in the coturn configuration above.\n- \"TURN username\" and \"TURN password\" - The user credentials as set in the coturn configuration above.\n\nIf Nsight UI display still doesn't work,\nadding `verbose` and `log-file=stdout` to `turnserver.conf` and inspecting\ncoturn logs (using `docker logs` command) are a good starting point to understand what went wrong.\n\n## Uninstall\n\nTo remove the extension, execute:\n\n```bash\npip uninstall jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight\n```\n\n## Troubleshooting\n\nIf you are seeing the frontend extension, but it is not working, check\nthat the server extension is enabled:\n\n```bash\njupyter server extension list\n```\n\nIf the server extension is installed and enabled, but you are not seeing\nthe frontend extension, check the frontend extension is installed:\n\n```bash\njupyter labextension list\n```\n\n## Known Issues\n\n- While Nsight Compute is enabled, interrupting the JupyterLab kernel with the \"Interrupt Kernel\" command (by using the command palette, kernel menu or the stop-button) causes the kernel to terminate and restart.\n\n## Release Notes\n\n### 0.8.0\n\n- New setting for configuring the allowed media ports to be used for displaying Nsight UI.\n- Support displaying Nsight UI when JupyterLab is running on a private network\n using an external TURN server.\n - Introduces new settings for configuring the TURN server that is used -\n Turn server address, Turn port, and Turn username and password.\n\n### 0.7.1\n\n- Support Linux SBSA.\n- Support displaying Nsight UI when JupyterLab is running over HTTPS.\n- Support displaying Nsight UI when JupyterLab is proxied via nginx.\n- Support displaying Nsight UI when JupyterLab is using a remote file system.\n- New setting for configuring the allowed HTTP ports to be used for displaying Nsight UI.\n- New setting for configuring the maximum resolution of Nsight Streamer.\n- New command for refreshing a Nsight UI display tab.\n - By right-clicking a tab and selecting \"Refresh Tab\".\n- Register report files in Jupyter DocumentRegistry with Nsight UI display as the default file\n opener (e.g., double-clicking a report file will display it with Nsight UI).\n\n### 0.7.0\n\n- New setting for configuring the location of the generated reports.\n- Support displaying Nsight UI when running inside a docker container.\n- Use (and pull if required) the latest NVIDIA Nsight Streamer for displaying Nsight UI.\n - See [Nsight Streamer for Nsight Systems](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/devtools/containers/nsight-streamer-nsys) and [Nsight Streamer for Nsight Compute](https://catalog.ngc.nvidia.com/orgs/nvidia/teams/devtools/containers/nsight-streamer-ncu).\n- Support displaying an external WebRTC streamer.\n\n### 0.6.0\n\n- Support displaying Nsight Compute UI inside JupyterLab.\n- Fix keyboard interaction with Nsight tools UI.\n\n### 0.5.2\n\n- Added Nsight Compute section in the project description.\n- Verify server connection on extension load.\n\n### 0.5.1\n\n- Initial release.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "NVIDIA Proprietary Software",
"summary": "A JupyterLab extension for profiling cells execution using NVIDIA Nsight tools.",
"version": "0.8.0",
"project_urls": {
"Bug Tracker": "https://forums.developer.nvidia.com/c/developer-tools/nsight-systems/profiling-linux-targets",
"Homepage": "https://pypi.org/project/jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight"
},
"split_keywords": [
"jupyter",
" jupyterlab",
" jupyterlab-extension"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "8e1ebe4ff450283117827ef53b3fc8bc5f300d2cb7dc0294439f87c032cd5511",
"md5": "9a4fd16e73cb6ab7ed61390555b1f81f",
"sha256": "6394205b09199bddf9c7956df47185f3df81d0a0472c98dd08e1436545341d2b"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "jupyterlab_nvidia_nsight-0.8.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "9a4fd16e73cb6ab7ed61390555b1f81f",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"size": 69796,
"upload_time": "2025-10-09T12:17:26",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-10-09T12:17:26.787412Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/8e/1e/be4ff450283117827ef53b3fc8bc5f300d2cb7dc0294439f87c032cd5511/jupyterlab_nvidia_nsight-0.8.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-10-09 12:17:26",
"github": false,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"lcname": "jupyterlab-nvidia-nsight"
}