# Neuromorphic Constrained Optimization Library
**A library of solvers that leverage neuromorphic hardware for constrained optimization.**
<details>
<summary>Table of Contents</summary>
<ol>
<li>
<a href="#about-the-project">About The Project</a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#taxonomy-of-optimization-problems">Taxonomy of Optimization Problems</a></li>
<li><a href="#optimizationsolver-and-optimizationproblem-classes">OptimizationSolver and OptimizationProblem Classes</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#tutorials">Tutorials</a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#quadratic-programming">Quadratic Programming</a></li>
<li><a href="#quadratic-unconstrained-binary-optimization">Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#examples">Examples</a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#solving-qp-problems">Solving QP</a></li>
<li><a href="#solving-qubo">Solving QUBO</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
<li>
<a href="#getting-started">Getting Started</a>
<ul>
<li><a href="#requirements">Requirements</a></li>
<li><a href="#installation">Installation</a></li>
</ul>
</li>
</ol>
</details>
## About the Project
Constrained optimization searches for the values of input variables that minimize or maximize a given objective function, while the variables are subject to constraints. This kind of problem is ubiquitous throughout scientific domains and industries.
Constrained optimization is a promising application for neuromorphic computing as
it [naturally aligns with the dynamics of spiking neural networks](https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2021.3067593). When individual neurons represent states of variables, the neuronal connections can directly encode constraints between the variables: in its simplest form, recurrent inhibitory synapses connect neurons that represent mutually exclusive variable states, while recurrent excitatory synapses link neurons representing reinforcing states. Implemented on massively parallel neuromorphic hardware, such a spiking neural network can simultaneously evaluate conflicts and cost functions involving many variables, and update all variables accordingly. This allows a quick convergence towards an optimal state. In addition, the fine-scale timing dynamics of SNNs allow them to readily escape from local minima.
This Lava repository currently supports solvers for the following constrained optimization problems:
- Quadratic Programming (QP)
- Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO)
As we continue development, the library will support more constrained optimization problems that are relevant for robotics and operations research.
We currently plan the following development order in such a way that new solvers build on the capabilities of existing ones:
- Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) [problem interface already available]
- Integer Linear Programming (ILP)
- Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP)
- Mixed-Integer Quadratic Programming (MIQP)
- Linear Programming (LP)
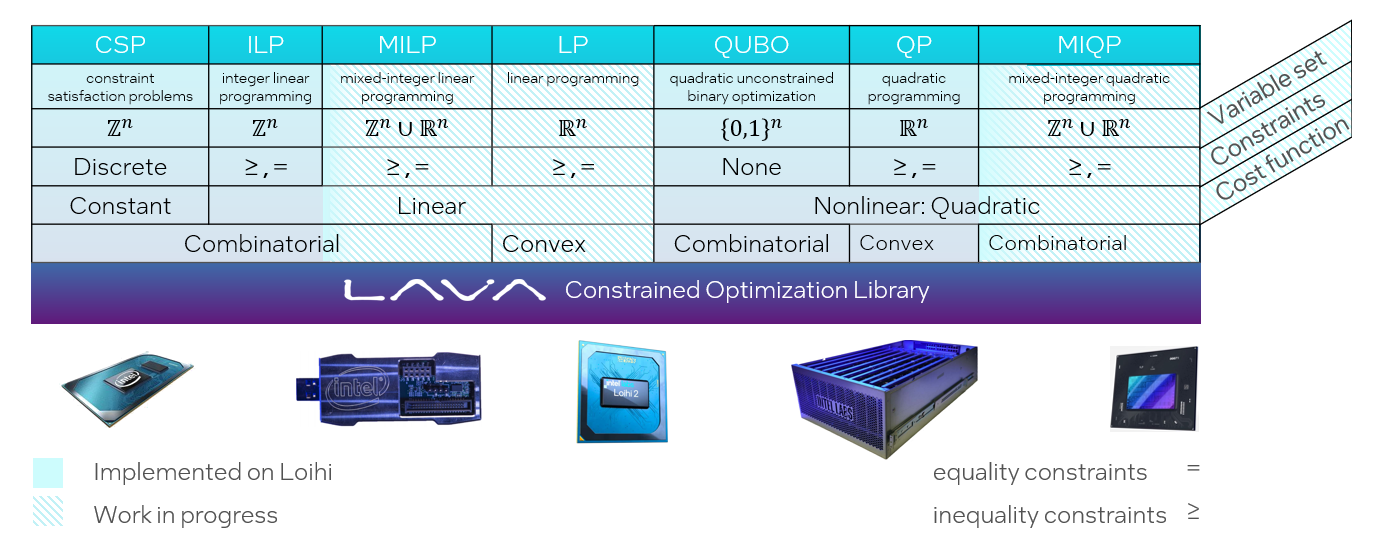
### Taxonomy of Optimization Problems
More formally, the general form of a constrained optimization problem is:
$$
\displaystyle{\min_{x} \lbrace f(x) | g_i(x) \leq b, h_i(x) = c.\rbrace}
$$
Where $f(x)$ is the objective function to be optimized while $g(x)$ and $h(x)$
constrain the validity of $f(x)$ to regions in the state space satisfying the
respective equality and inequality constraints. The vector $x$ can be
continuous, discrete or a mixture of both. We can then construct the following
taxonomy of optimization problems according to the characteristics of the
variable domain and of $f$, $g$, and $h$:

In the long run, lava-optimization aims to offer support to solve all of the problems in the figure with a neuromorphic backend.
### OptimizationSolver and OptimizationProblem Classes
The figure below shows the general architecture of the library. We harness the general definition of constraint optimization problems to create ``OptimizationProblem`` instances by composing ``Constraints``, ``Variables``, and ``Cost`` classes which describe the characteristics of every subproblem class. Note that while a quadratic problem (QP) will be described by linear equality and inequality constraints with variables on the continuous domain and a quadratic function. A constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) will be described by discrete constraints, defined by variable subsets and a binary relation describing the mutually allowed values for such discrete variables and will have a constant cost function with the pure goal of satisfying constraints.
An API for every problem class can be created by inheriting from ``OptimizationSolver`` and composing particular flavors of ``Constraints``, ``Variables``, and ``Cost``.

The instance of an ``Optimization problem`` is the valid input for instantiating the generic ``OptimizationSolver`` class. In this way, the ``OptimizationSolver`` interface is left fixed and the ``OptimizationProblem`` allows the greatest flexibility for creating new APIs. Under the hood, the ``OptimizationSolver`` understands the composite structure of the ``OptimizationProblem`` and will in turn compose the required solver components and Lava processes.
## Tutorials
### Quadratic Programming
- [Solving LASSO.](https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization/blob/release/v0.2.0/tutorials/tutorial_01_solving_lasso.ipynb)
### Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization
- [Solving Maximum Independent Set.](https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization/blob/release/v0.2.0/tutorials/tutorial_02_solving_qubos.ipynb)
## Examples
### Solving QP problems
```python
import numpy as np
from lava.lib.optimization.problems.problems import QP
from lava.lib.optimization.solvers.generic.solver import (
SolverConfig,
OptimizationSolver,
)
# Define QP problem
Q = np.array([[100, 0, 0], [0, 15, 0], [0, 0, 5]])
p = np.array([[1, 2, 1]]).T
A = -np.array([[1, 2, 2], [2, 100, 3]])
k = -np.array([[-50, 50]]).T
qp = QP(Q, p, A, k)
# Define hyper-parameters
hyperparameters = {
"neuron_model": "qp-lp_pipg",
"alpha_mantissa": 160,
"alpha_exponent": -8,
"beta_mantissa": 7,
"beta_exponent": -10,
"decay_schedule_parameters": (100, 100, 0),
"growth_schedule_parameters": (3, 2),
}
# Solve using QPSolver
solver = OptimizationSolver(problem=qp)
config = SolverConfig(timeout=400, hyperparameters=hyperparameters, backend="Loihi2")
solver.solve(config=config)
```
### Solving QUBO
```python
import numpy as np
from lava.lib.optimization.problems.problems import QUBO
from lava.lib.optimization.solvers.generic.solver import (
SolverConfig,
OptimizationSolver,
)
# Define QUBO problem
q = np.array([[-5, 2, 4, 0],
[ 2,-3, 1, 0],
[ 4, 1,-8, 5],
[ 0, 0, 5,-6]]))
qubo = QUBO(q)
# Solve using generic OptimizationSolver
solver = OptimizationSolver(problem=qubo)
config = SolverConfig(timeout=3000, target_cost=-50, backend="Loihi2")
solution = solver.solve(config=config)
```
## Getting Started
### Requirements
- Working installation of Lava, installed automatically with poetry below. [ For custom installs see Lava installation
tutorial.](https://github.com/lava-nc/lava/blob/main/tutorials/in_depth/tutorial01_installing_lava.ipynb)
### Installation
#### [Linux/MacOS]
```bash
cd $HOME
git clone git@github.com:lava-nc/lava-optimization.git
cd lava-optimization
curl -sSL https://install.python-poetry.org | python3 -
poetry config virtualenvs.in-project true
poetry install
source .venv/bin/activate
pytest
```
#### [Windows]
```powershell
# Commands using PowerShell
cd $HOME
git clone git@github.com:lava-nc/lava-optimization.git
cd lava-optimization
python3 -m venv .venv
.venv\Scripts\activate
pip install -U pip
curl -sSL https://install.python-poetry.org | python3 -
poetry config virtualenvs.in-project true
poetry install
pytest
```
### [Alternative] Installing Lava via Conda
If you use the Conda package manager, you can simply install the Lava package
via:
```bash
conda install lava-optimization -c conda-forge
```
Alternatively with intel numpy and scipy:
```bash
conda create -n lava-optimization python=3.9 -c intel
conda activate lava-optimization
conda install -n lava-optimization -c intel numpy scipy
conda install -n lava-optimization -c conda-forge lava-optimization --freeze-installed
```
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://lava-nc.org/",
"name": "lava-optimization",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": "<3.11,>=3.10",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "neuromorphic, ai, artificial intelligence, neural models, spiking neural networks, deep learning, optimization",
"author": "Intel's Neuromorphic Computing Lab and the open source community",
"author_email": "lava@intel.com",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/f9/ba/958def4f6f152563d28350b446d812cb2778304348652b174b6244ba0352/lava_optimization-0.5.0.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "# Neuromorphic Constrained Optimization Library\n\n**A library of solvers that leverage neuromorphic hardware for constrained optimization.**\n\n<details>\n <summary>Table of Contents</summary>\n <ol>\n <li>\n <a href=\"#about-the-project\">About The Project</a>\n <ul>\n <li><a href=\"#taxonomy-of-optimization-problems\">Taxonomy of Optimization Problems</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#optimizationsolver-and-optimizationproblem-classes\">OptimizationSolver and OptimizationProblem Classes</a></li>\n </ul>\n </li>\n <li>\n <a href=\"#tutorials\">Tutorials</a>\n <ul>\n <li><a href=\"#quadratic-programming\">Quadratic Programming</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#quadratic-unconstrained-binary-optimization\">Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization</a></li>\n </ul>\n </li>\n <li>\n <a href=\"#examples\">Examples</a>\n <ul>\n <li><a href=\"#solving-qp-problems\">Solving QP</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#solving-qubo\">Solving QUBO</a></li>\n </ul>\n </li>\n <li>\n <a href=\"#getting-started\">Getting Started</a>\n <ul>\n <li><a href=\"#requirements\">Requirements</a></li>\n <li><a href=\"#installation\">Installation</a></li>\n </ul>\n </li>\n </ol>\n</details>\n\n## About the Project \n\nConstrained optimization searches for the values of input variables that minimize or maximize a given objective function, while the variables are subject to constraints. This kind of problem is ubiquitous throughout scientific domains and industries.\nConstrained optimization is a promising application for neuromorphic computing as\nit [naturally aligns with the dynamics of spiking neural networks](https://doi.org/10.1109/JPROC.2021.3067593). When individual neurons represent states of variables, the neuronal connections can directly encode constraints between the variables: in its simplest form, recurrent inhibitory synapses connect neurons that represent mutually exclusive variable states, while recurrent excitatory synapses link neurons representing reinforcing states. Implemented on massively parallel neuromorphic hardware, such a spiking neural network can simultaneously evaluate conflicts and cost functions involving many variables, and update all variables accordingly. This allows a quick convergence towards an optimal state. In addition, the fine-scale timing dynamics of SNNs allow them to readily escape from local minima.\n\nThis Lava repository currently supports solvers for the following constrained optimization problems:\n\n- Quadratic Programming (QP)\n- Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization (QUBO)\n\nAs we continue development, the library will support more constrained optimization problems that are relevant for robotics and operations research.\nWe currently plan the following development order in such a way that new solvers build on the capabilities of existing ones:\n\n- Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP) [problem interface already available]\n- Integer Linear Programming (ILP)\n- Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP)\n- Mixed-Integer Quadratic Programming (MIQP)\n- Linear Programming (LP)\n\n \n\n\n### Taxonomy of Optimization Problems\nMore formally, the general form of a constrained optimization problem is:\n\n$$\n\\displaystyle{\\min_{x} \\lbrace f(x) | g_i(x)\t\\leq b,\th_i(x)\t= c.\\rbrace}\n$$\n\nWhere $f(x)$ is the objective function to be optimized while $g(x)$ and $h(x)$ \nconstrain the validity of $f(x)$ to regions in the state space satisfying the \nrespective equality and inequality constraints. The vector $x$ can be\n continuous, discrete or a mixture of both. We can then construct the following \n taxonomy of optimization problems according to the characteristics of the \n variable domain and of $f$, $g$, and $h$:\n\n\n\nIn the long run, lava-optimization aims to offer support to solve all of the problems in the figure with a neuromorphic backend. \n\n### OptimizationSolver and OptimizationProblem Classes\n\nThe figure below shows the general architecture of the library. We harness the general definition of constraint optimization problems to create ``OptimizationProblem`` instances by composing ``Constraints``, ``Variables``, and ``Cost`` classes which describe the characteristics of every subproblem class. Note that while a quadratic problem (QP) will be described by linear equality and inequality constraints with variables on the continuous domain and a quadratic function. A constraint satisfaction problem (CSP) will be described by discrete constraints, defined by variable subsets and a binary relation describing the mutually allowed values for such discrete variables and will have a constant cost function with the pure goal of satisfying constraints.\n\nAn API for every problem class can be created by inheriting from ``OptimizationSolver`` and composing particular flavors of ``Constraints``, ``Variables``, and ``Cost``. \n\n\n\nThe instance of an ``Optimization problem`` is the valid input for instantiating the generic ``OptimizationSolver`` class. In this way, the ``OptimizationSolver`` interface is left fixed and the ``OptimizationProblem`` allows the greatest flexibility for creating new APIs. Under the hood, the ``OptimizationSolver`` understands the composite structure of the ``OptimizationProblem`` and will in turn compose the required solver components and Lava processes. \n\n## Tutorials\n\n### Quadratic Programming\n- [Solving LASSO.](https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization/blob/release/v0.2.0/tutorials/tutorial_01_solving_lasso.ipynb)\n\n### Quadratic Unconstrained Binary Optimization\n- [Solving Maximum Independent Set.](https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization/blob/release/v0.2.0/tutorials/tutorial_02_solving_qubos.ipynb)\n\n## Examples\n\n### Solving QP problems \n\n```python\nimport numpy as np\nfrom lava.lib.optimization.problems.problems import QP\nfrom lava.lib.optimization.solvers.generic.solver import (\n SolverConfig,\n OptimizationSolver,\n)\n\n# Define QP problem\nQ = np.array([[100, 0, 0], [0, 15, 0], [0, 0, 5]])\np = np.array([[1, 2, 1]]).T\nA = -np.array([[1, 2, 2], [2, 100, 3]])\nk = -np.array([[-50, 50]]).T\n\nqp = QP(Q, p, A, k)\n\n# Define hyper-parameters\nhyperparameters = {\n \"neuron_model\": \"qp-lp_pipg\",\n \"alpha_mantissa\": 160,\n \"alpha_exponent\": -8,\n \"beta_mantissa\": 7,\n \"beta_exponent\": -10,\n \"decay_schedule_parameters\": (100, 100, 0),\n \"growth_schedule_parameters\": (3, 2),\n}\n\n# Solve using QPSolver\nsolver = OptimizationSolver(problem=qp)\nconfig = SolverConfig(timeout=400, hyperparameters=hyperparameters, backend=\"Loihi2\")\nsolver.solve(config=config)\n```\n\n### Solving QUBO\n```python\nimport numpy as np\nfrom lava.lib.optimization.problems.problems import QUBO\nfrom lava.lib.optimization.solvers.generic.solver import (\n SolverConfig,\n OptimizationSolver,\n)\n\n# Define QUBO problem\nq = np.array([[-5, 2, 4, 0],\n [ 2,-3, 1, 0],\n [ 4, 1,-8, 5],\n [ 0, 0, 5,-6]]))\n\nqubo = QUBO(q)\n\n# Solve using generic OptimizationSolver\nsolver = OptimizationSolver(problem=qubo)\nconfig = SolverConfig(timeout=3000, target_cost=-50, backend=\"Loihi2\")\nsolution = solver.solve(config=config)\n```\n\n## Getting Started\n\n### Requirements\n- Working installation of Lava, installed automatically with poetry below. [ For custom installs see Lava installation\ntutorial.](https://github.com/lava-nc/lava/blob/main/tutorials/in_depth/tutorial01_installing_lava.ipynb)\n\n### Installation\n\n#### [Linux/MacOS]\n```bash\ncd $HOME\ngit clone git@github.com:lava-nc/lava-optimization.git\ncd lava-optimization\ncurl -sSL https://install.python-poetry.org | python3 -\npoetry config virtualenvs.in-project true\npoetry install\nsource .venv/bin/activate\npytest\n```\n#### [Windows]\n```powershell\n# Commands using PowerShell\ncd $HOME\ngit clone git@github.com:lava-nc/lava-optimization.git\ncd lava-optimization\npython3 -m venv .venv\n.venv\\Scripts\\activate\npip install -U pip\ncurl -sSL https://install.python-poetry.org | python3 -\npoetry config virtualenvs.in-project true\npoetry install\npytest\n```\n\n### [Alternative] Installing Lava via Conda\nIf you use the Conda package manager, you can simply install the Lava package\nvia:\n```bash\nconda install lava-optimization -c conda-forge\n```\n\nAlternatively with intel numpy and scipy:\n\n```bash\nconda create -n lava-optimization python=3.9 -c intel\nconda activate lava-optimization\nconda install -n lava-optimization -c intel numpy scipy\nconda install -n lava-optimization -c conda-forge lava-optimization --freeze-installed\n```\n\n\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "(BSD-3-Clause)",
"summary": "A library of solvers that leverage neuromorphic hardware for constrained optimization. Lava-Optimization is part of Lava Framework. Lava-optimization is part of Lava Framework",
"version": "0.5.0",
"project_urls": {
"Discussions": "https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization/discussions",
"Frequently Asked Questions": "https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization/wiki/Frequently-Asked-Questions-(FAQ)",
"Homepage": "https://lava-nc.org/",
"Issue and Bug Tracker": "https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization/issues",
"Questions and Answers": "https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization/discussions/categories/q-a",
"Repository": "https://github.com/lava-nc/lava-optimization"
},
"split_keywords": [
"neuromorphic",
" ai",
" artificial intelligence",
" neural models",
" spiking neural networks",
" deep learning",
" optimization"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "d8eaf1c32c40ca6d5e79fa487cded1342bc41a032f5117dc06c260dd96322066",
"md5": "60f3cd8a3ac92c1296c2ea9e1e5c8698",
"sha256": "af10f3f22b976597d2269548e7a40527b62e916c45df69742518f479571a7613"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "lava_optimization-0.5.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "60f3cd8a3ac92c1296c2ea9e1e5c8698",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": "<3.11,>=3.10",
"size": 189058,
"upload_time": "2024-08-08T05:24:20",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-08-08T05:24:20.423086Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d8/ea/f1c32c40ca6d5e79fa487cded1342bc41a032f5117dc06c260dd96322066/lava_optimization-0.5.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "f9ba958def4f6f152563d28350b446d812cb2778304348652b174b6244ba0352",
"md5": "b7de54093e23cfe5b468782d3074d16f",
"sha256": "3aecfff7a86e86a32a4da7676b271477d03967ecd0fdabd1121f48de31475315"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "lava_optimization-0.5.0.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "b7de54093e23cfe5b468782d3074d16f",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": "<3.11,>=3.10",
"size": 4006421,
"upload_time": "2024-08-08T05:24:22",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-08-08T05:24:22.359597Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/f9/ba/958def4f6f152563d28350b446d812cb2778304348652b174b6244ba0352/lava_optimization-0.5.0.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-08-08 05:24:22",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "lava-nc",
"github_project": "lava-optimization",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"lcname": "lava-optimization"
}
