[](https://pypi.org/project/lbl2vec/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/lbl2vec/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/lbl2vec/)
[](https://github.com/sebischair/Lbl2Vec/blob/main/LICENSE)
[](https://lbl2vec.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://doi.org/10.5220/0010710300003058)
[](https://paperswithcode.com/sota/unsupervised-text-classification-on-1?p=lbl2vec-an-embedding-based-approach-for)
[](https://paperswithcode.com/sota/unsupervised-text-classification-on-ag-news?p=lbl2vec-an-embedding-based-approach-for)
Lbl2Vec
=======
Lbl2Vec is an algorithm for **unsupervised document classification** and **unsupervised document retrieval.** It
automatically generates jointly embedded label, document and word vectors and returns documents of topics modeled by
manually predefined keywords. This package includes **two different model types**. The plain **[Lbl2Vec](#lbl2vec-model)
model
uses
Doc2Vec**, whereas **[Lbl2TransformerVec](#lbl2transformervec-model) uses transformer-based language models** to create
the
embeddings. Once you
train a model you can:
* Classify documents as related to one of the predefined topics.
* Get similarity scores for documents to each predefined topic.
* Get most similar predefined topic of documents.
See the papers introducing [Lbl2Vec](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.06023)
and [Lbl2TransformerVec](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16285) for more details on how it
works.
Corresponding Medium post describing the use of Lbl2Vec for unsupervised text classification can be
found [here](https://towardsdatascience.com/unsupervised-text-classification-with-lbl2vec-6c5e040354de).
# Benefits
1. No need to label the whole document dataset for classification.
2. No stop word lists required.
3. No need for stemming/lemmatization.
4. Works on short text.
5. Creates jointly embedded label, document, and word vectors.
<a name="toc"/></a>
# Table of Contents
<!--ts-->
1. [How does it work?](#how-does-it-work)
2. [Installation](#installation)
3. [Usage](#usage)
1. [Model Training](#model-training)
1. [Lbl2Vec](#lbl2vec-model)
2. [Lbl2TransformerVec](#lbl2transformervec-model)
2. [Document prediction](#document-prediction)
3. [Save and load models](#save-and-load-models)
4. [Citation information](#citation-information)
<!--te-->
<a name="#how-does-it-work"/></a>
# How does it work?
[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)
The key idea of the algorithm is that many semantically similar keywords can represent a topic. In the first step, the
algorithm creates a joint embedding of document and word vectors. Once documents and words are embedded in a vector
space, the goal of the algorithm is to learn label vectors from previously manually defined keywords representing a
topic. Finally, the algorithm can predict the affiliation of documents to topics from *document vector <-> label vector*
similarities.
## The Algorithm
**0. Use the manually defined keywords for each topic of interest.**
> Domain knowledge is needed to define keywords that describe topics and are semantically similar to each other within
> the topics.
| Basketball | Soccer | Baseball |
|:----------:|:------:|:--------:|
| NBA | FIFA | MLB |
| Basketball | Soccer | Baseball |
| LeBron | Messi | Ruth |
| ... | ... | ... |
**1. Create jointly embedded document and word vectors
using [Doc2Vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html "Gensim Doc2Vec")
, [Sentence-Transformers](https://www.sbert.net/ "SBERT Documentation"),
or [SimCSE](https://github.com/princeton-nlp/SimCSE "SimCSE GitHub").**
> Documents will be placed close to other similar documents and close to the most distinguishing words.
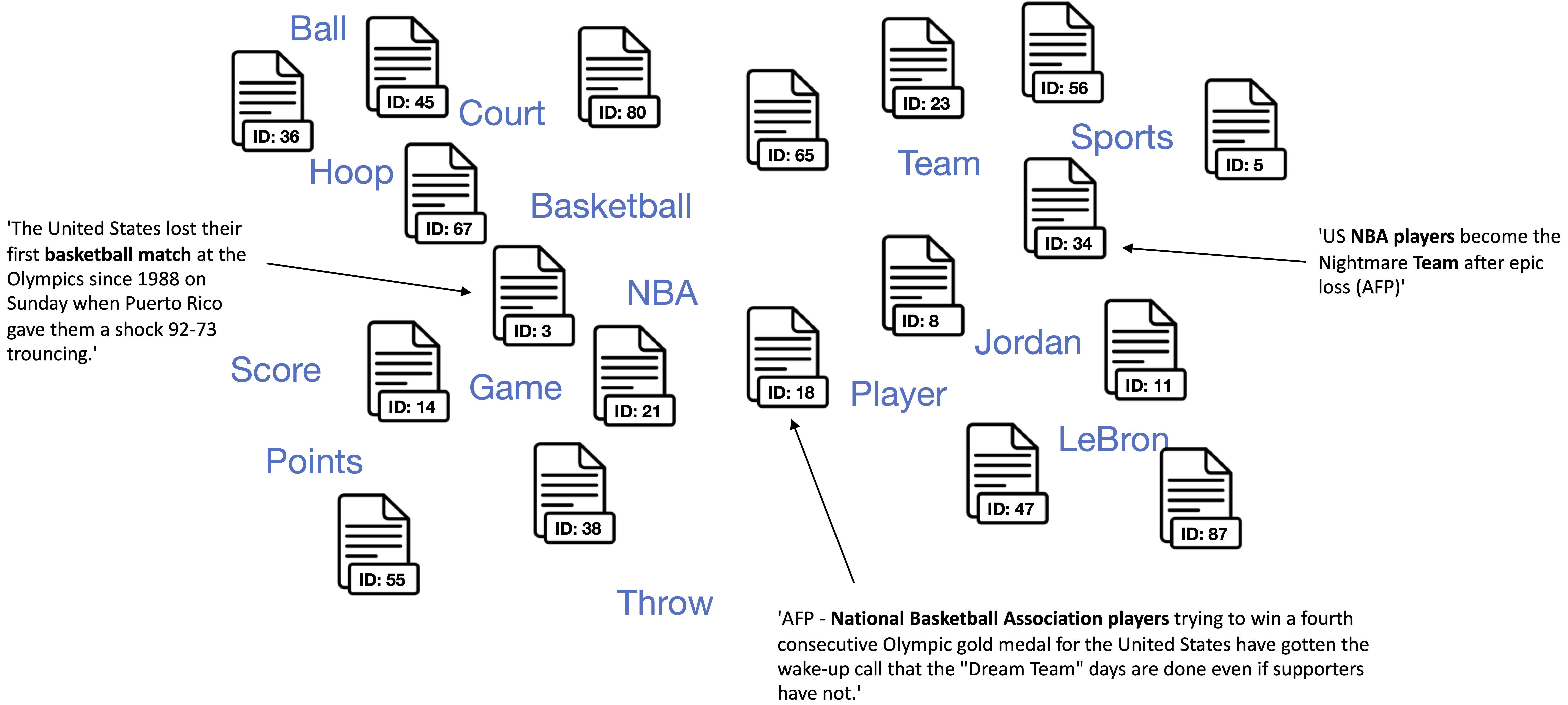
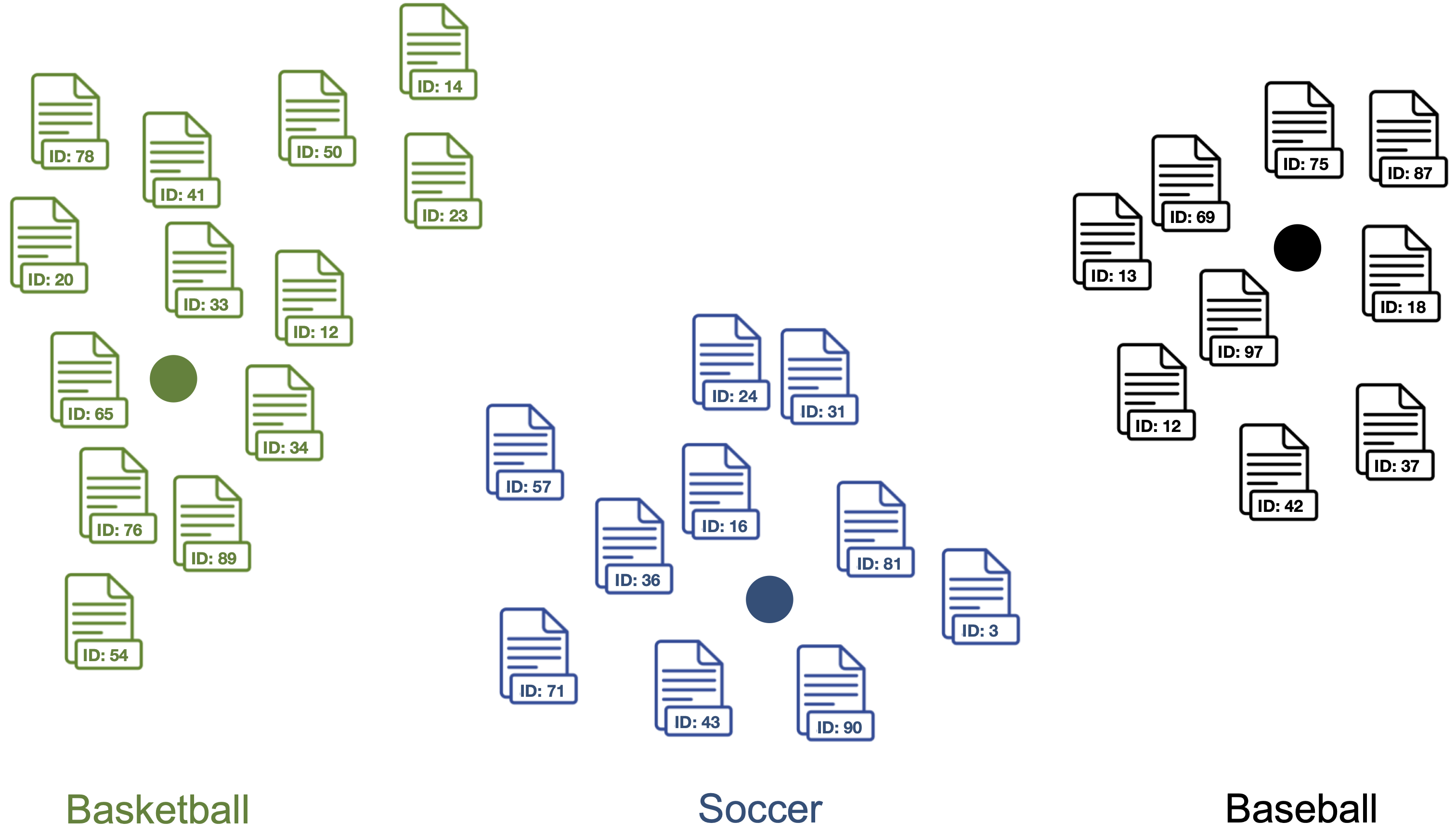
**2. Find document vectors that are similar to the keyword vectors of each topic.**
> Each color represents a different topic described by the respective keywords.
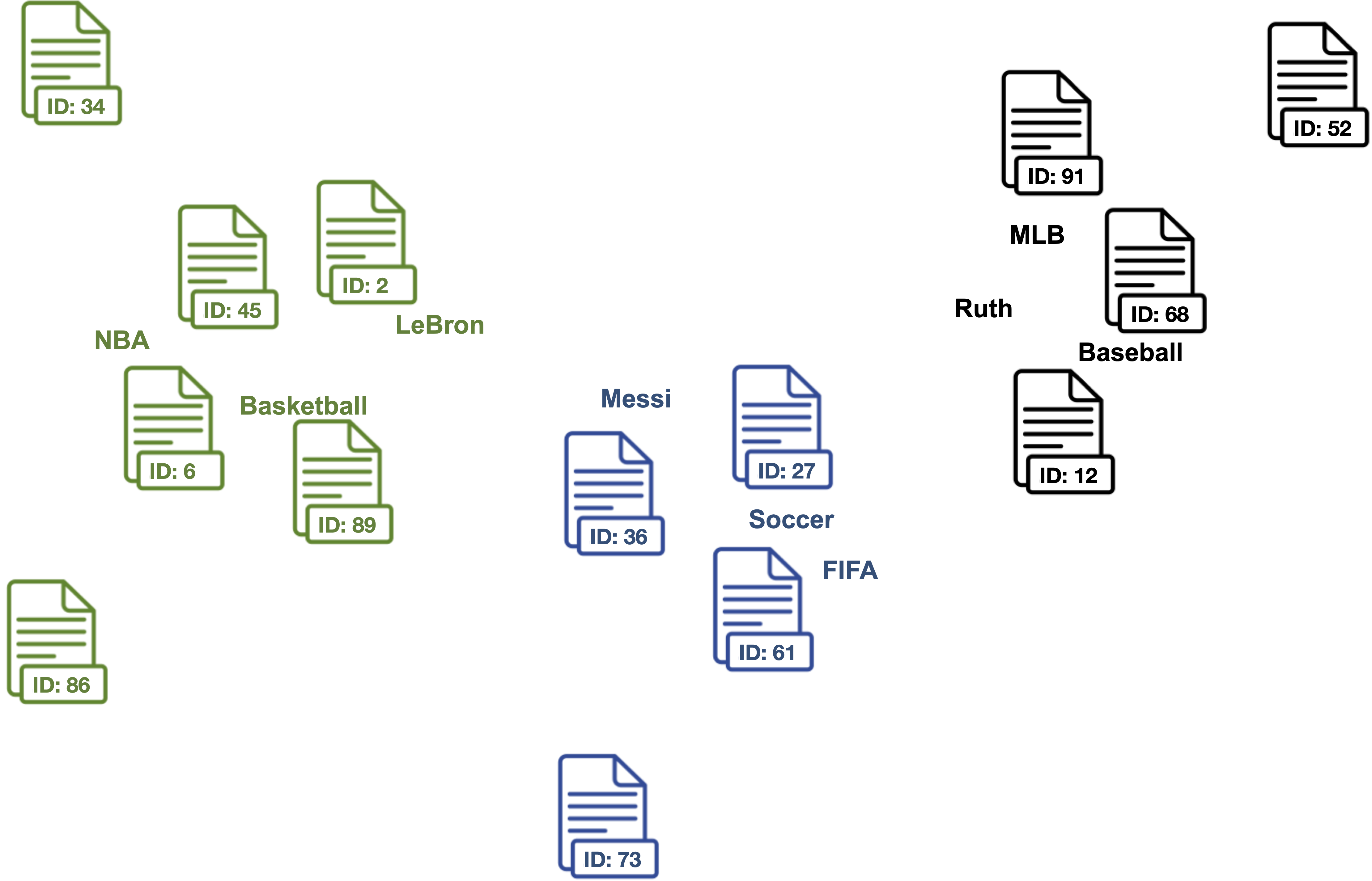
**3. Clean outlier document vectors for each topic.**
> Red documents are outlier vectors that are removed and do not get used for calculating the label vector.
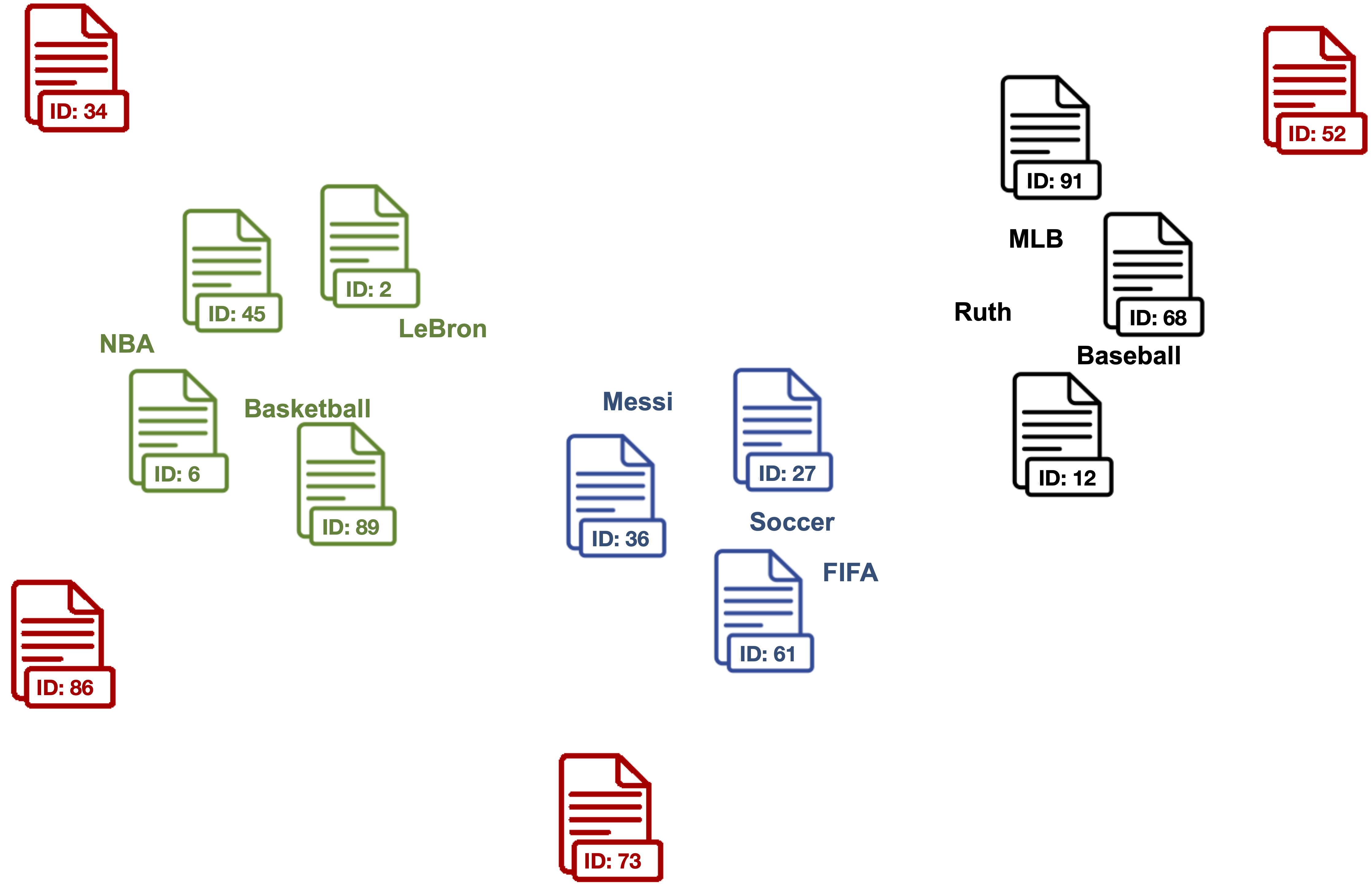
**4. Compute the centroid of the outlier cleaned document vectors as label vector for each topic.**
> Points represent the label vectors of the respective topics.
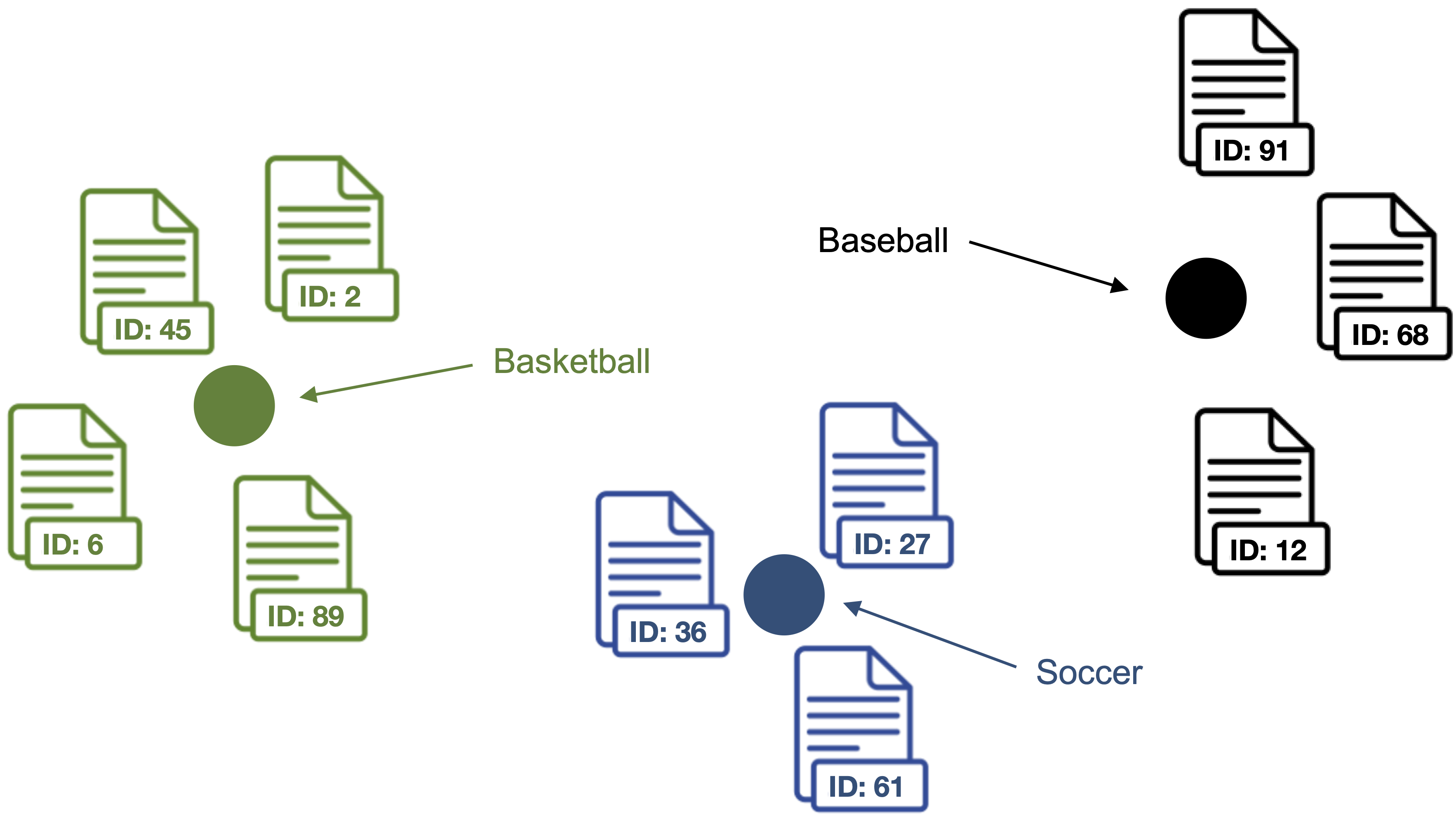
**5. Compute *label vector <-> document vector* similarities for each label vector and document vector in the dataset.**
> Documents are classified as topic with the highest *label vector <-> document vector* similarity.
<a name="#installation"/></a>
# Installation
[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)
```
pip install lbl2vec
```
<a name="#usage"/></a>
# Usage
[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)
For detailed information visit the [API Guide](https://lbl2vec.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api.html#) and
the [examples](https://github.com/sebischair/Lbl2Vec/tree/main/examples).
<a name="#model-training"/></a>
## Model Training
<a name="#lbl2vec-model"/></a>
### Lbl2Vec model
[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)
> Lbl2Vec learns word vectors, document vectors and label vectors using Doc2Vec during training.
#### Train new Lbl2Vec model from scratch using [Doc2Vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html "Gensim Doc2Vec")
```python
from lbl2vec import Lbl2Vec
# init model
model = Lbl2Vec(keywords_list=descriptive_keywords, tagged_documents=tagged_docs)
# train model
model.fit()
```
**Important parameters:**
* `keywords_list`: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive
keyword has to be added as list of str.
* `tagged_documents`: iterable list
of [gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html#gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument)
elements. If you wish to train a new Doc2Vec model this parameter can not be None, whereas the `doc2vec_model`
parameter must be None. If you use a pretrained Doc2Vec model this parameter has to be None. Input corpus, can be
simply a list of elements, but for larger corpora, consider an iterable that streams the documents directly from
disk/network.
#### Use word and document vectors from pretrained [Doc2Vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html "Gensim Doc2Vec") model
> Uses word vectors and document vectors from a pretrained Doc2Vec model to learn label vectors during Lbl2Vec model
> training.
```python
from lbl2vec import Lbl2Vec
# init model
model = Lbl2Vec(keywords_list=descriptive_keywords, doc2vec_model=pretrained_d2v_model)
# train model
model.fit()
```
**Important parameters:**
* `keywords_list`: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive
keyword has to be added as list of str.
* `doc2vec_model`:
pretrained [gensim.models.doc2vec.Doc2Vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html#gensim.models.doc2vec.Doc2Vec)
model. If given a pretrained Doc2Vec model, Lbl2Vec uses the pre-trained Doc2Vec model from this parameter. If this
parameter is defined, `tagged_documents` parameter has to be None. In order to get optimal Lbl2Vec results the given
Doc2Vec model should be trained with the parameters "dbow_words=1" and "dm=0".
<a name="#lbl2transformervec-model"/></a>
### Lbl2TransformerVec model
[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)
> Lbl2TransformerVec learns word vectors, document vectors and label vectors using transformer-based language models
> during training. Using state-of-the-art transformer embeddings may not only yield to better predictions but also
> eliminates the issue of unknown keywords during model training. While the Doc2Vec-based model can only use keywords
> that
> Lbl2Vec has seen during training, the transformer-based Lbl2TransformerVec model can learn label vectors from any set
> of
> keywords. That is because transformer vocabularies consist of individual characters, subwords, and words, allowing
> transformers to effectively represent every word in a sentence. This eliminates the out-of-vocabulary scenario.
> However,
> using transformers instead of Doc2Vec is much more computationally expensive, especially if no GPU is available.
#### Train new Lbl2TransformerVec model from scratch using the default transformer-embedding model
```python
from lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec
# init model using the default transformer-embedding model ("sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2")
model = Lbl2TransformerVec(keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords, documents=document_list)
# train model
model.fit()
```
#### Train Lbl2TransformerVec model using an arbitrary [Sentence-Transformers](https://www.sbert.net/ "SBERT Documentation") embedding model
```python
from lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec
from sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer
# select sentence-tranformers model
transformer_model = SentenceTransformer("all-mpnet-base-v2")
# init model
model = Lbl2TransformerVec(transformer_model=transformer_model, keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords,
documents=document_list)
# train model
model.fit()
```
#### Train Lbl2TransformerVec model using an arbitrary [SimCSE](https://github.com/princeton-nlp/SimCSE "SimCSE GitHub") embedding model
```python
from lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec
from transformers import AutoModel
# select SimCSE model
transformer_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("princeton-nlp/sup-simcse-roberta-base")
# init model
model = Lbl2TransformerVec(transformer_model=transformer_model, keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords,
documents=document_list)
# train model
model.fit()
```
**Important parameters:**
* `keywords_list`: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive
keyword has to be added as list of str.
* `documents`: iterable list of text document elements (strings).
* `transformer_model`: Transformer model used to embed the labels, documents and keywords. The embedding models must be
either of
type [sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer](https://www.sbert.net/docs/package_reference/SentenceTransformer.html#sentencetransformer)
or [transformers.AutoModel](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/auto#transformers.AutoModel)
### Document prediction
[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)
> The prediction API calls are the same for Lbl2Vec and Lbl2TransformerVec.
#### Predict label similarities for documents used for training
> Computes the similarity scores for each document vector stored in the model to each of the label vectors.
```python
# get similarity scores from trained model
model.predict_model_docs()
```
**Important parameters:**
* `doc_keys`: list of document keys (optional). If None: return the similarity scores for all documents that are used to
train the Lbl2Vec model. Else: only return the similarity scores of training documents with the given keys.
#### Predict label similarities for new documents that are not used for training
> Computes the similarity scores for each given and previously unknown document vector to each of the label vectors from
> the model.
```python
# get similarity scores for each new document from trained model
model.predict_new_docs(tagged_docs=tagged_docs)
```
**Important parameters:**
* `tagged_docs`: iterable list
of [gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html#gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument)
elements
<a name="#save-and-load-models"/></a>
### Save and load models
[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)
> The save and load API calls are the same for Lbl2Vec and Lbl2TransformerVec.
#### Save model to disk
```python
model.save('model_name')
```
#### Load model from disk
```python
model = Lbl2Vec.load('model_name')
```
<a name="#citation-information"/></a>
# Citation information
[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)
When citing [Lbl2Vec](https://www.scitepress.org/Link.aspx?doi=10.5220/0010710300003058)
or [Lbl2TransformerVec](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16285) in academic papers and
theses, please use the following BibTeX entries:
```
@conference{schopf_etal_webist21,
author={Tim Schopf and Daniel Braun and Florian Matthes},
title={Lbl2Vec: An Embedding-based Approach for Unsupervised Document Retrieval on Predefined Topics},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - WEBIST,},
year={2021},
pages={124-132},
publisher={SciTePress},
organization={INSTICC},
doi={10.5220/0010710300003058},
isbn={978-989-758-536-4},
issn={2184-3252},
}
```
```
@inproceedings{schopf_etal_nlpir22,
author = {Schopf, Tim and Braun, Daniel and Matthes, Florian},
title = {Evaluating Unsupervised Text Classification: Zero-shot and Similarity-based Approaches},
year = {2023},
publisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
booktitle = {2022 6th International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval (NLPIR)},
keywords = {Natural Language Processing, Unsupervised Text Classification, Zero-shot Text Classification},
location = {Bangkok, Thailand},
series = {NLPIR 2022}
}
```
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/sebischair/Lbl2Vec",
"name": "lbl2vec",
"maintainer": "",
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.8",
"maintainer_email": "",
"keywords": "",
"author": "Tim Schopf",
"author_email": "tim.schopf@tum.de",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/e1/c7/56e5e9e8002e1a6ae8aafb51149c8b637f95237578f348342ea5aa3af08e/lbl2vec-1.0.2.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "[](https://pypi.org/project/lbl2vec/)\n[](https://pypi.org/project/lbl2vec/)\n[](https://pypi.org/project/lbl2vec/)\n[](https://github.com/sebischair/Lbl2Vec/blob/main/LICENSE)\n[](https://lbl2vec.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)\n[](https://doi.org/10.5220/0010710300003058)\n[](https://paperswithcode.com/sota/unsupervised-text-classification-on-1?p=lbl2vec-an-embedding-based-approach-for)\n[](https://paperswithcode.com/sota/unsupervised-text-classification-on-ag-news?p=lbl2vec-an-embedding-based-approach-for)\n\nLbl2Vec\n======= \n\nLbl2Vec is an algorithm for **unsupervised document classification** and **unsupervised document retrieval.** It\nautomatically generates jointly embedded label, document and word vectors and returns documents of topics modeled by\nmanually predefined keywords. This package includes **two different model types**. The plain **[Lbl2Vec](#lbl2vec-model)\nmodel\nuses\nDoc2Vec**, whereas **[Lbl2TransformerVec](#lbl2transformervec-model) uses transformer-based language models** to create\nthe\nembeddings. Once you\ntrain a model you can:\n\n* Classify documents as related to one of the predefined topics.\n* Get similarity scores for documents to each predefined topic.\n* Get most similar predefined topic of documents.\n\nSee the papers introducing [Lbl2Vec](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.06023)\nand [Lbl2TransformerVec](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16285) for more details on how it\nworks.\n\nCorresponding Medium post describing the use of Lbl2Vec for unsupervised text classification can be\nfound [here](https://towardsdatascience.com/unsupervised-text-classification-with-lbl2vec-6c5e040354de).\n\n# Benefits\n\n1. No need to label the whole document dataset for classification.\n2. No stop word lists required.\n3. No need for stemming/lemmatization.\n4. Works on short text.\n5. Creates jointly embedded label, document, and word vectors.\n\n<a name=\"toc\"/></a>\n\n# Table of Contents\n\n<!--ts-->\n\n1. [How does it work?](#how-does-it-work)\n2. [Installation](#installation)\n3. [Usage](#usage)\n 1. [Model Training](#model-training)\n 1. [Lbl2Vec](#lbl2vec-model)\n 2. [Lbl2TransformerVec](#lbl2transformervec-model)\n 2. [Document prediction](#document-prediction)\n 3. [Save and load models](#save-and-load-models)\n4. [Citation information](#citation-information)\n\n<!--te-->\n\n<a name=\"#how-does-it-work\"/></a>\n\n# How does it work?\n\n[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)\n\nThe key idea of the algorithm is that many semantically similar keywords can represent a topic. In the first step, the\nalgorithm creates a joint embedding of document and word vectors. Once documents and words are embedded in a vector\nspace, the goal of the algorithm is to learn label vectors from previously manually defined keywords representing a\ntopic. Finally, the algorithm can predict the affiliation of documents to topics from *document vector <-> label vector*\nsimilarities.\n\n## The Algorithm\n\n**0. Use the manually defined keywords for each topic of interest.**\n> Domain knowledge is needed to define keywords that describe topics and are semantically similar to each other within\n> the topics.\n\n| Basketball | Soccer | Baseball |\n|:----------:|:------:|:--------:|\n| NBA | FIFA | MLB |\n| Basketball | Soccer | Baseball |\n| LeBron | Messi | Ruth |\n| ... | ... | ... |\n\n**1. Create jointly embedded document and word vectors\nusing [Doc2Vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html \"Gensim Doc2Vec\")\n, [Sentence-Transformers](https://www.sbert.net/ \"SBERT Documentation\"),\nor [SimCSE](https://github.com/princeton-nlp/SimCSE \"SimCSE GitHub\").**\n> Documents will be placed close to other similar documents and close to the most distinguishing words.\n\n\n\n**2. Find document vectors that are similar to the keyword vectors of each topic.**\n> Each color represents a different topic described by the respective keywords.\n\n\n\n**3. Clean outlier document vectors for each topic.**\n> Red documents are outlier vectors that are removed and do not get used for calculating the label vector.\n\n\n\n**4. Compute the centroid of the outlier cleaned document vectors as label vector for each topic.**\n> Points represent the label vectors of the respective topics.\n\n\n\n**5. Compute *label vector <-> document vector* similarities for each label vector and document vector in the dataset.**\n> Documents are classified as topic with the highest *label vector <-> document vector* similarity.\n\n\n\n<a name=\"#installation\"/></a>\n\n# Installation\n\n[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)\n\n```\npip install lbl2vec\n```\n\n<a name=\"#usage\"/></a>\n\n# Usage\n\n[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)\n\nFor detailed information visit the [API Guide](https://lbl2vec.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api.html#) and\nthe [examples](https://github.com/sebischair/Lbl2Vec/tree/main/examples).\n\n<a name=\"#model-training\"/></a>\n\n## Model Training\n\n<a name=\"#lbl2vec-model\"/></a>\n\n### Lbl2Vec model\n\n[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)\n\n> Lbl2Vec learns word vectors, document vectors and label vectors using Doc2Vec during training.\n\n#### Train new Lbl2Vec model from scratch using [Doc2Vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html \"Gensim Doc2Vec\")\n\n```python\nfrom lbl2vec import Lbl2Vec\n\n# init model\nmodel = Lbl2Vec(keywords_list=descriptive_keywords, tagged_documents=tagged_docs)\n\n# train model\nmodel.fit()\n```\n\n**Important parameters:**\n\n* `keywords_list`: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive\n keyword has to be added as list of str.\n* `tagged_documents`: iterable list\n of [gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html#gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument)\n elements. If you wish to train a new Doc2Vec model this parameter can not be None, whereas the `doc2vec_model`\n parameter must be None. If you use a pretrained Doc2Vec model this parameter has to be None. Input corpus, can be\n simply a list of elements, but for larger corpora, consider an iterable that streams the documents directly from\n disk/network.\n\n#### Use word and document vectors from pretrained [Doc2Vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html \"Gensim Doc2Vec\") model\n\n> Uses word vectors and document vectors from a pretrained Doc2Vec model to learn label vectors during Lbl2Vec model\n> training.\n\n```python\nfrom lbl2vec import Lbl2Vec\n\n# init model\nmodel = Lbl2Vec(keywords_list=descriptive_keywords, doc2vec_model=pretrained_d2v_model)\n\n# train model\nmodel.fit()\n```\n\n**Important parameters:**\n\n* `keywords_list`: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive\n keyword has to be added as list of str.\n* `doc2vec_model`:\n pretrained [gensim.models.doc2vec.Doc2Vec](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html#gensim.models.doc2vec.Doc2Vec)\n model. If given a pretrained Doc2Vec model, Lbl2Vec uses the pre-trained Doc2Vec model from this parameter. If this\n parameter is defined, `tagged_documents` parameter has to be None. In order to get optimal Lbl2Vec results the given\n Doc2Vec model should be trained with the parameters \"dbow_words=1\" and \"dm=0\".\n\n<a name=\"#lbl2transformervec-model\"/></a>\n\n### Lbl2TransformerVec model\n\n[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)\n\n> Lbl2TransformerVec learns word vectors, document vectors and label vectors using transformer-based language models\n> during training. Using state-of-the-art transformer embeddings may not only yield to better predictions but also\n> eliminates the issue of unknown keywords during model training. While the Doc2Vec-based model can only use keywords\n> that\n> Lbl2Vec has seen during training, the transformer-based Lbl2TransformerVec model can learn label vectors from any set\n> of\n> keywords. That is because transformer vocabularies consist of individual characters, subwords, and words, allowing\n> transformers to effectively represent every word in a sentence. This eliminates the out-of-vocabulary scenario.\n> However,\n> using transformers instead of Doc2Vec is much more computationally expensive, especially if no GPU is available.\n\n#### Train new Lbl2TransformerVec model from scratch using the default transformer-embedding model\n\n```python\nfrom lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec\n\n# init model using the default transformer-embedding model (\"sentence-transformers/all-MiniLM-L6-v2\")\nmodel = Lbl2TransformerVec(keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords, documents=document_list)\n\n# train model\nmodel.fit()\n```\n\n#### Train Lbl2TransformerVec model using an arbitrary [Sentence-Transformers](https://www.sbert.net/ \"SBERT Documentation\") embedding model\n\n```python\nfrom lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec\nfrom sentence_transformers import SentenceTransformer\n\n# select sentence-tranformers model\ntransformer_model = SentenceTransformer(\"all-mpnet-base-v2\")\n\n# init model\nmodel = Lbl2TransformerVec(transformer_model=transformer_model, keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords,\n documents=document_list)\n\n# train model\nmodel.fit()\n```\n\n#### Train Lbl2TransformerVec model using an arbitrary [SimCSE](https://github.com/princeton-nlp/SimCSE \"SimCSE GitHub\") embedding model\n\n```python\nfrom lbl2vec import Lbl2TransformerVec\nfrom transformers import AutoModel\n\n# select SimCSE model\ntransformer_model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(\"princeton-nlp/sup-simcse-roberta-base\")\n\n# init model\nmodel = Lbl2TransformerVec(transformer_model=transformer_model, keywords_list=listdescriptive_keywords,\n documents=document_list)\n\n# train model\nmodel.fit()\n```\n\n**Important parameters:**\n\n* `keywords_list`: iterable list of lists with descriptive keywords of type str. For each label at least one descriptive\n keyword has to be added as list of str.\n* `documents`: iterable list of text document elements (strings).\n* `transformer_model`: Transformer model used to embed the labels, documents and keywords. The embedding models must be\n either of\n type [sentence_transformers.SentenceTransformer](https://www.sbert.net/docs/package_reference/SentenceTransformer.html#sentencetransformer)\n or [transformers.AutoModel](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/model_doc/auto#transformers.AutoModel)\n\n### Document prediction\n\n[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)\n> The prediction API calls are the same for Lbl2Vec and Lbl2TransformerVec.\n\n#### Predict label similarities for documents used for training\n\n> Computes the similarity scores for each document vector stored in the model to each of the label vectors.\n\n```python\n# get similarity scores from trained model\nmodel.predict_model_docs()\n```\n\n**Important parameters:**\n\n* `doc_keys`: list of document keys (optional). If None: return the similarity scores for all documents that are used to\n train the Lbl2Vec model. Else: only return the similarity scores of training documents with the given keys.\n\n#### Predict label similarities for new documents that are not used for training\n\n> Computes the similarity scores for each given and previously unknown document vector to each of the label vectors from\n> the model.\n\n```python\n# get similarity scores for each new document from trained model\nmodel.predict_new_docs(tagged_docs=tagged_docs)\n```\n\n**Important parameters:**\n\n* `tagged_docs`: iterable list\n of [gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument](https://radimrehurek.com/gensim/models/doc2vec.html#gensim.models.doc2vec.TaggedDocument)\n elements\n\n<a name=\"#save-and-load-models\"/></a>\n\n### Save and load models\n\n[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)\n> The save and load API calls are the same for Lbl2Vec and Lbl2TransformerVec.\n\n#### Save model to disk\n\n```python\nmodel.save('model_name')\n``` \n\n#### Load model from disk\n\n```python\nmodel = Lbl2Vec.load('model_name')\n```\n\n<a name=\"#citation-information\"/></a>\n\n# Citation information\n\n[Back to Table of Contents](#toc)\n\nWhen citing [Lbl2Vec](https://www.scitepress.org/Link.aspx?doi=10.5220/0010710300003058)\nor [Lbl2TransformerVec](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16285) in academic papers and\ntheses, please use the following BibTeX entries:\n\n``` \n@conference{schopf_etal_webist21,\nauthor={Tim Schopf and Daniel Braun and Florian Matthes},\ntitle={Lbl2Vec: An Embedding-based Approach for Unsupervised Document Retrieval on Predefined Topics},\nbooktitle={Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies - WEBIST,},\nyear={2021},\npages={124-132},\npublisher={SciTePress},\norganization={INSTICC},\ndoi={10.5220/0010710300003058},\nisbn={978-989-758-536-4},\nissn={2184-3252},\n}\n``` \n\n``` \n@inproceedings{schopf_etal_nlpir22,\nauthor = {Schopf, Tim and Braun, Daniel and Matthes, Florian},\ntitle = {Evaluating Unsupervised Text Classification: Zero-shot and Similarity-based Approaches},\nyear = {2023},\npublisher = {Association for Computing Machinery},\naddress = {New York, NY, USA},\nbooktitle = {2022 6th International Conference on Natural Language Processing and Information Retrieval (NLPIR)},\nkeywords = {Natural Language Processing, Unsupervised Text Classification, Zero-shot Text Classification},\nlocation = {Bangkok, Thailand},\nseries = {NLPIR 2022}\n}\n``` \n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "BSD 3-Clause \"New\" or \"Revised\" License",
"summary": "Lbl2Vec learns jointly embedded label, document and word vectors to retrieve documents with predefined topics from an unlabeled document corpus.",
"version": "1.0.2",
"split_keywords": [],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"md5": "1c36665f8061c40d18f1fd9c76a591bc",
"sha256": "fb55033ac1c0b483db49edffc2096867ef6ef2edaf6ed5bd0f565da85a32d30a"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "lbl2vec-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "1c36665f8061c40d18f1fd9c76a591bc",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.8",
"size": 24742,
"upload_time": "2022-12-29T12:55:04",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2022-12-29T12:55:04.737321Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/81/3a/c66ba40541823641036a4195c0d1f139fe0da22700026549ca646110b2cc/lbl2vec-1.0.2-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"md5": "05b0f43a9fc496c4dd07e977fead85f9",
"sha256": "c0d0fe87963eff10d9a31964ad665dbc1c11db40e751be54c9c346186866327e"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "lbl2vec-1.0.2.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "05b0f43a9fc496c4dd07e977fead85f9",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.8",
"size": 25195,
"upload_time": "2022-12-29T12:55:06",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2022-12-29T12:55:06.738751Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/e1/c7/56e5e9e8002e1a6ae8aafb51149c8b637f95237578f348342ea5aa3af08e/lbl2vec-1.0.2.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2022-12-29 12:55:06",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"github_user": "sebischair",
"github_project": "Lbl2Vec",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"requirements": [],
"lcname": "lbl2vec"
}
