# nprime
[](https://github.com/sylhare/nprime)
[](https://pypistats.org/packages/nprime)
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/nprime)
[](https://travis-ci.org/sylhare/nprime)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/sylhare/nprime)
## Installation
To install the package use pip:
pip install nprime
## Introduction
Some algorithm on prime numbers. You can find all the functions in the file `nprime/pryprime.py`
Algorithm developed :
- Eratosthenes sieve based
- Fermat's test (based on Fermat's theorem)
- Prime generating functions
- Miller Rabin predictive algorithm
## Specifications
- Language: Python **3.9+** (supports Python 3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12, 3.13)
- Package:
- Basic python packages were preferred
- Matplotlib >=3.5.0 - graph and math
### Integration and pipeline
For the tests coverage, there's [codecov](https://codecov.io/gh/Sylhare/nprime) which is run during the [Travis CI](https://travis-ci.org/Sylhare/nprime) pipeline.
## Math
Here are a bit of information to help understand some of the algorithms
### Congruence
"`≡`" means congruent, `a ≡ b (mod m)` implies that
`m / (a-b), ∃ k ∈ Z` that verifies `a = kn + b`
which implies:
a ≡ 0 (mod n) <-> a = kn <-> "a" is divisible by "n"
### Strong Pseudoprime
A strong [pseudoprime](http://mathworld.wolfram.com/StrongPseudoprime.html) to a base `a` is an odd composite number `n`
with `n-1 = d·2^s` (for d odd) for which either `a^d = 1(mod n)` or `a^(d·2^r) = -1(mod n)` for some `r = 0, 1, ..., s-1` </br>
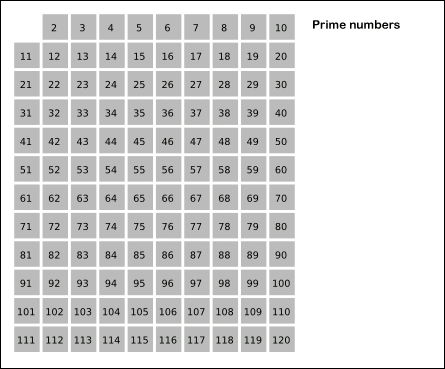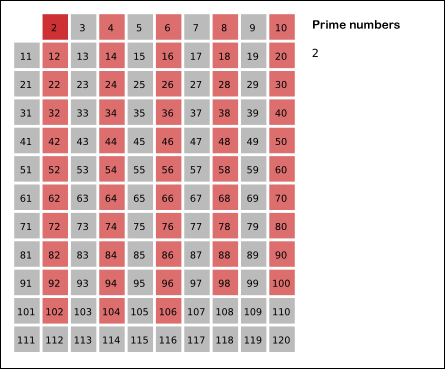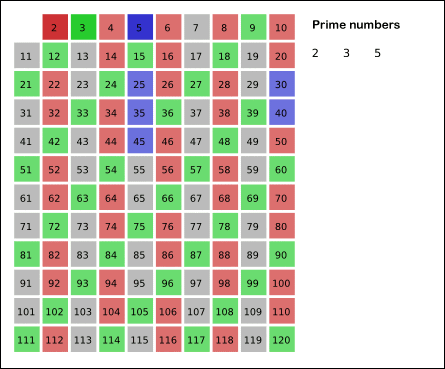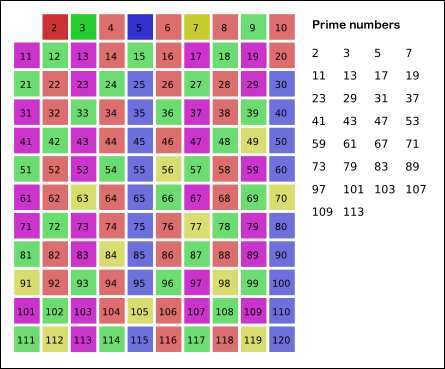
### Erathostene's Sieve
#### How to use
Implementation of the sieve of erathostenes that discover the primes and their composite up to a limit.
It returns a dictionary:
- the key are the primes up to n
- the value is the list of composites of these primes up to n
```python
from nprime import sieve_eratosthenes
# With as a parameter the upper limit
sieve_eratosthenes(10)
>> {2: [4, 6, 8, 10], 3: [9], 5: [], 7: []}
```
The previous behaviour can be called using the `trial_division` which uses the [Trial Division](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trial_division) algorithm
#### Theory
This sieve mark as composite the multiple of each primes. It is an efficient way to find primes.
For `n ∈ N` with `n > 2` and for `∀ a ∈[2, ..., √n]` then `n/a ∉ N` is true.
[](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sieve_of_Eratosthenes)
### Fermat's Theorem
#### How to use
A Probabilistic algorithm taking `t` randoms numbers `a` and testing the Fermat's theorem on number `n > 1`
Prime probability is right is `1 - 1/(2^t)`
Returns a boolean: True if `n` passes the tests.
```python
from nprime import fermat
# With n the number you want to test
fermat(n)
```
#### Theory
If `n` is prime then `∀ a ∈[1, ..., n-1]`
```
a^(n-1) ≡ 1 (mod n) ⇔ a^(n-1) = kn + 1
```
### Miller rabin
#### How to use
A probabilistic algorithm which determines whether a given number (n > 1) is prime or not.
The miller_rabin tests is repeated `t` times to get more accurate results.
Returns a boolean: True if `n` passes the tests.
```python
from nprime import miller_rabin
# With n the number you want to test
miller_rabin(n)
```
#### Theory
For `n ∈ N` and `n > 2`, </br>
Take a random `a ∈ {1,...,n−1}` </br>
Find `d` and `s` such as with `n - 1 = 2^s * d` (with d odd) </br>
if `(a^d)^2^r ≡ 1 mod n` for all `r` in `0` to `s-1` </br>
Then `n` is prime.
The test output is false of 1/4 of the "a values" possible in `n`,
so the test is repeated t times.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/Sylhare/nprime",
"name": "nprime",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "prime, fermat, miller rabin, math",
"author": "sylhare",
"author_email": "sylhare <sylhare@outlook.com>",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/a0/8e/34a0f95a21dbe242066615d7233aae82e23ad8011cbbd0999ec008ecbf61/nprime-1.3.1.tar.gz",
"platform": "any",
"description": "# nprime \n\n [](https://github.com/sylhare/nprime) \n [](https://pypistats.org/packages/nprime)\n [](https://badge.fury.io/py/nprime) \n [](https://travis-ci.org/sylhare/nprime) \n [](https://codecov.io/gh/sylhare/nprime) \n\n## Installation\n\nTo install the package use pip:\n\n pip install nprime\n\n\n## Introduction\n\nSome algorithm on prime numbers. You can find all the functions in the file `nprime/pryprime.py`\n\nAlgorithm developed : \n\n- Eratosthenes sieve based\n- Fermat's test (based on Fermat's theorem)\n- Prime generating functions\n- Miller Rabin predictive algorithm\n\n## Specifications\n\n- Language: Python **3.9+** (supports Python 3.9, 3.10, 3.11, 3.12, 3.13)\n- Package:\n\t- Basic python packages were preferred\n\t- Matplotlib >=3.5.0 - graph and math\n\n### Integration and pipeline\n\nFor the tests coverage, there's [codecov](https://codecov.io/gh/Sylhare/nprime) which is run during the [Travis CI](https://travis-ci.org/Sylhare/nprime) pipeline.\n\n## Math\n\nHere are a bit of information to help understand some of the algorithms\n\n### Congruence\n\n \"`\u2261`\" means congruent, `a \u2261 b (mod m)` implies that \n`m / (a-b), \u2203 k \u2208 Z` that verifies `a = kn + b`\n \n which implies:\n\n a \u2261 0 (mod n) <-> a = kn <-> \"a\" is divisible by \"n\" \n \n### Strong Pseudoprime\n\nA strong [pseudoprime](http://mathworld.wolfram.com/StrongPseudoprime.html) to a base `a` is an odd composite number `n` \nwith `n-1 = d\u00b72^s` (for d odd) for which either `a^d = 1(mod n)` or `a^(d\u00b72^r) = -1(mod n)` for some `r = 0, 1, ..., s-1` </br>\n \n### Erathostene's Sieve\n\n#### How to use\n\nImplementation of the sieve of erathostenes that discover the primes and their composite up to a limit.\nIt returns a dictionary:\n - the key are the primes up to n\n - the value is the list of composites of these primes up to n\n\n```python\nfrom nprime import sieve_eratosthenes\n\n# With as a parameter the upper limit\nsieve_eratosthenes(10)\n>> {2: [4, 6, 8, 10], 3: [9], 5: [], 7: []}\n```\n\nThe previous behaviour can be called using the `trial_division` which uses the [Trial Division](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Trial_division) algorithm\n\n#### Theory\n\nThis sieve mark as composite the multiple of each primes. It is an efficient way to find primes.\nFor `n \u2208 N` with `n > 2` and for `\u2200 a \u2208[2, ..., \u221an]` then `n/a \u2209 N` is true.\n\n[](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sieve_of_Eratosthenes)\n\n\n### Fermat's Theorem\n\n#### How to use\n\nA Probabilistic algorithm taking `t` randoms numbers `a` and testing the Fermat's theorem on number `n > 1`\nPrime probability is right is `1 - 1/(2^t)`\nReturns a boolean: True if `n` passes the tests.\n\n```python\nfrom nprime import fermat\n\n# With n the number you want to test\nfermat(n)\n```\n\n#### Theory\n\nIf `n` is prime then `\u2200 a \u2208[1, ..., n-1]`\n\n```\n a^(n-1) \u2261 1 (mod n) \u21d4 a^(n-1) = kn + 1\n```\n \n### Miller rabin\n\n#### How to use\n\nA probabilistic algorithm which determines whether a given number (n > 1) is prime or not.\nThe miller_rabin tests is repeated `t` times to get more accurate results.\nReturns a boolean: True if `n` passes the tests.\n\n```python\nfrom nprime import miller_rabin\n\n# With n the number you want to test\nmiller_rabin(n)\n```\n\n#### Theory\nFor `n \u2208 N` and `n > 2`, </br>\nTake a random `a \u2208 {1,...,n\u22121}` </br>\nFind `d` and `s` such as with `n - 1 = 2^s * d` (with d odd) </br>\nif `(a^d)^2^r \u2261 1 mod n` for all `r` in `0` to `s-1` </br>\nThen `n` is prime.\n\nThe test output is false of 1/4 of the \"a values\" possible in `n`, \nso the test is repeated t times.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "GNU General Public License v3.0",
"summary": "Python library for primes algorithms",
"version": "1.3.1",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/Sylhare/nprime",
"Issues": "https://github.com/Sylhare/nprime/issues",
"Repository": "https://github.com/Sylhare/nprime"
},
"split_keywords": [
"prime",
" fermat",
" miller rabin",
" math"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "16093738d8dff1e6943bddfb23bd8dbb1aa13bf38cd4bd2f22d842356bf22af1",
"md5": "de053f9b9a863cd4966b4161e54f9a9e",
"sha256": "55a65ce6c832e8893d4f6efb73f04d81a20f63af53e1881e89c30e687ff7039c"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "nprime-1.3.1-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "de053f9b9a863cd4966b4161e54f9a9e",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"size": 20677,
"upload_time": "2025-08-18T12:50:16",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-08-18T12:50:16.477597Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/16/09/3738d8dff1e6943bddfb23bd8dbb1aa13bf38cd4bd2f22d842356bf22af1/nprime-1.3.1-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "a08e34a0f95a21dbe242066615d7233aae82e23ad8011cbbd0999ec008ecbf61",
"md5": "5306e2b8a9f1b0f27b613483e91b0202",
"sha256": "2375c4e94ede934e4a8ce06f8e1f57024d925c7559d3e89e902247c7275464c5"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "nprime-1.3.1.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "5306e2b8a9f1b0f27b613483e91b0202",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.9",
"size": 148976,
"upload_time": "2025-08-18T12:50:18",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-08-18T12:50:18.248708Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/a0/8e/34a0f95a21dbe242066615d7233aae82e23ad8011cbbd0999ec008ecbf61/nprime-1.3.1.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-08-18 12:50:18",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "Sylhare",
"github_project": "nprime",
"travis_ci": true,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"requirements": [
{
"name": "matplotlib",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"3.5.0"
]
]
},
{
"name": "setuptools",
"specs": []
},
{
"name": "pypandoc",
"specs": []
},
{
"name": "pytest",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"7.0.0"
]
]
},
{
"name": "coverage",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"6.0"
]
]
},
{
"name": "pytest-cov",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"4.0.0"
]
]
},
{
"name": "codecov",
"specs": []
},
{
"name": "codacy-coverage",
"specs": []
},
{
"name": "xdoctest",
"specs": []
}
],
"lcname": "nprime"
}

