<h1><div align="center">
<img alt="pipecat" width="500px" height="auto" src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows/main/pipecat-flows.png">
</div></h1>
[](https://pypi.org/project/pipecat-ai-flows) [](https://docs.pipecat.ai/guides/features/pipecat-flows) [](https://discord.gg/pipecat)
Pipecat Flows is an add-on framework for [Pipecat](https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat/tree/main#readme) that allows you to build structured conversations in your AI applications. It enables you to create both predefined conversation paths and dynamically generated flows while handling the complexities of state management and LLM interactions.
The framework consists of:
- A Python module for building conversation flows with Pipecat
- A [visual editor](#Pipecat-Flows-Editor) for designing and exporting flow configurations
## Dependencies
- Python 3.10 or higher
- [Pipecat](https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat?tab=readme-ov-file#-getting-started)
## Installation
1. Install uv
```bash
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
```
> **Need help?** Refer to the [uv install documentation](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/getting-started/installation/).
2. Install the module
```bash
# For new projects
uv init my-pipecat-flows-app
cd my-pipecat-flows-app
uv add pipecat-ai-flows
# Or for existing projects
uv add pipecat-ai-flows
```
> **Using pip?** You can still use `pip install pipecat-ai-flows` to get set up.
## Quick Start
See [Quick Start README](./examples/quickstart/README.md).
For more detailed examples and guides, visit our [documentation](https://docs.pipecat.ai/guides/features/pipecat-flows).
## Examples
The repository includes several complete example implementations demonstrating various features of Pipecat Flows.
### Available Examples
- **Static Flows**: Pre-defined conversation paths including food ordering, movie exploration, patient intake, and travel planning
- **Dynamic Flows**: Runtime-generated flows including insurance quotes, restaurant reservations, and warm transfers
Each example is available in multiple LLM provider formats (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, AWS Bedrock) to demonstrate cross-platform compatibility.
### Getting Started with Examples
For detailed setup instructions, configuration, and running examples, see the **[Examples README](examples/README.md)**.
Quick start:
```bash
# Install dependencies
uv sync
uv pip install "pipecat-ai[daily,openai,deepgram,cartesia,silero,examples]"
# Configure environment
cp env.example .env # Add your API keys
# Run an example
uv run python examples/static/food_ordering.py -u YOUR_DAILY_ROOM_URL
```
## Contributing to the framework
1. Clone the repository and navigate to it:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows.git
cd pipecat-flows
```
2. Install development dependencies:
```bash
uv sync --group dev
```
3. Install the git pre-commit hooks (these help ensure your code follows project rules):
```bash
uv run pre-commit install
```
> The package is automatically installed in editable mode when you run `uv sync`.
## Tests
The package includes a comprehensive test suite covering the core functionality.
### Setup Test Environment
1. **Install Dependencies**:
```bash
uv sync --group dev
uv add "pipecat-ai[google,aws,openai,anthropic]"
```
### Running Tests
Run all tests:
```bash
uv run pytest tests/
```
Run specific test file:
```bash
uv run pytest tests/test_state.py
```
Run specific test:
```bash
uv run pytest tests/test_state.py -k test_initialization
```
Run with coverage report:
```bash
uv run pytest tests/ --cov=pipecat_flows
```
## Pipecat Flows Editor
> **The Flows Editor is deprecated and will be removed along with Static Flows.**
> We have future plans to introduce a new editor capability that supports dynamic flows, but we don't have a timeline yet.
> We're open to collaborating with any developers or teams who have an interesting in building out this type of UI! Reach out to us on [Discord](https://discord.gg/pipecat) if you're interested.
A visual editor for creating and managing Pipecat conversation flows.
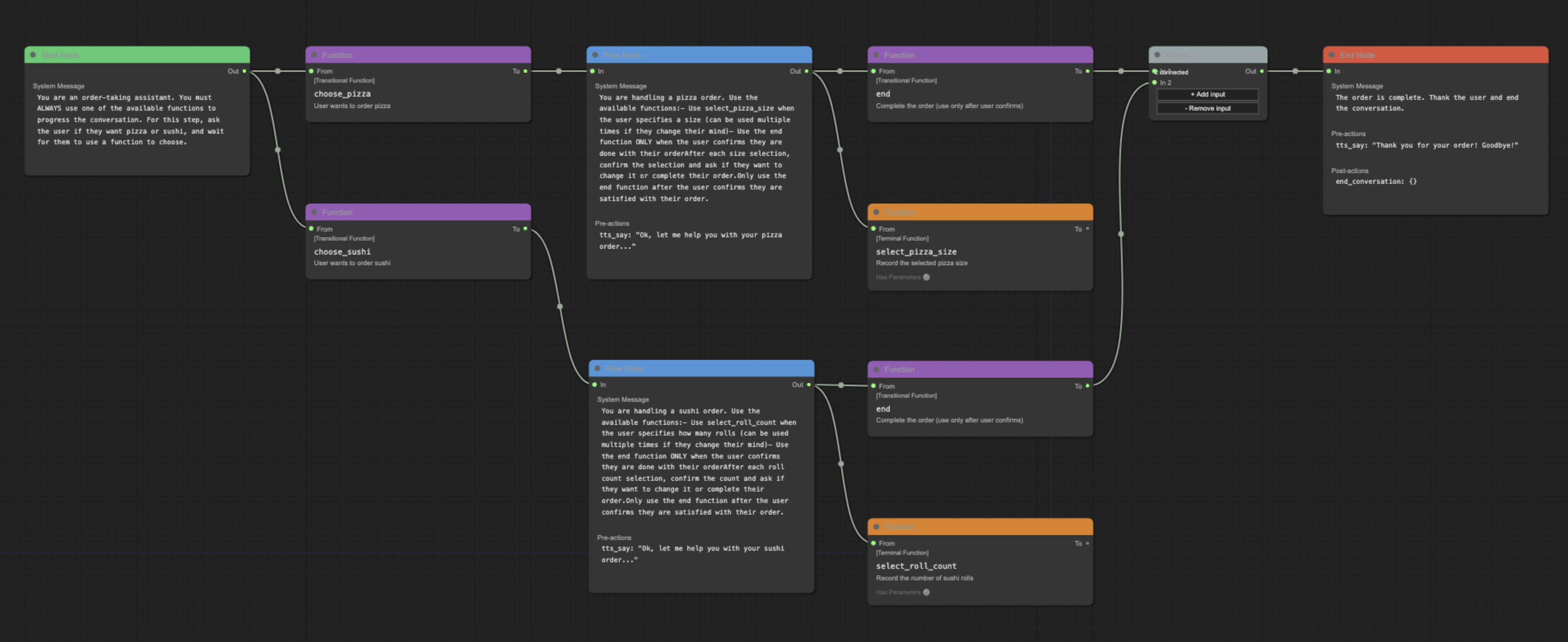
### Features
- Visual flow creation and editing
- Import/export of flow configurations
- Support for node and edge functions
- Merge node support for complex flows
- Real-time validation
### Naming Conventions
While the underlying system is flexible with node naming, the editor follows these conventions for clarity:
- **Start Node**: Named after your initial conversation state (e.g., "greeting", "welcome")
- **End Node**: Conventionally named "end" for clarity, though other names are supported
- **Flow Nodes**: Named to reflect their purpose in the conversation (e.g., "get_time", "confirm_order")
These conventions help maintain readable and maintainable flows while preserving technical flexibility.
### Online Editor
The editor is available online at [flows.pipecat.ai](https://flows.pipecat.ai).
### Local Development
#### Prerequisites
- Node.js (v14 or higher)
- npm (v6 or higher)
#### Installation
Clone the repository
```bash
git clone git@github.com:pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows.git
```
Navigate to project directory
```bash
cd pipecat-flows/editor
```
Install dependencies
```bash
npm install
```
Start development server
```bash
npm run dev
```
Open the page in your browser: http://localhost:5173.
#### Usage
1. Create a new flow using the toolbar buttons
2. Add nodes by right-clicking in the canvas
- Start nodes can have descriptive names (e.g., "greeting")
- End nodes are conventionally named "end"
3. Connect nodes by dragging from outputs to inputs
4. Edit node properties in the side panel
5. Export your flow configuration using the toolbar
#### Examples
The `editor/examples/` directory contains sample flow configurations:
- `food_ordering.json`
- `movie_explorer.py`
- `patient_intake.json`
- `restaurant_reservation.json`
- `travel_planner.json`
To use an example:
1. Open the editor
2. Click "Import Flow"
3. Select an example JSON file
See the [examples directory](editor/examples/) for the complete files and documentation.
### Development
#### Available Scripts
- `npm start` - Start production server
- `npm run dev` - Start development server
- `npm run build` - Build for production
- `npm run preview` - Preview production build locally
- `npm run preview:prod` - Preview production build with base path
- `npm run lint` - Check for linting issues
- `npm run lint:fix` - Fix linting issues
- `npm run format` - Format code with Prettier
- `npm run format:check` - Check code formatting
- `npm run docs` - Generate documentation
- `npm run docs:serve` - Serve documentation locally
#### Documentation
The Pipecat Flows Editor project uses JSDoc for documentation. To generate and view the documentation:
Generate documentation:
```bash
npm run docs
```
Serve documentation locally:
```bash
npm run docs:serve
```
View in browser by opening: http://localhost:8080
## Contributing
We welcome contributions from the community! Whether you're fixing bugs, improving documentation, or adding new features, here's how you can help:
- **Found a bug?** Open an [issue](https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows/issues)
- **Have a feature idea?** Start a [discussion](https://discord.gg/pipecat)
- **Want to contribute code?** Check our [CONTRIBUTING.md](CONTRIBUTING.md) guide
- **Documentation improvements?** [Docs](https://github.com/pipecat-ai/docs) PRs are always welcome
Before submitting a pull request, please check existing issues and PRs to avoid duplicates.
We aim to review all contributions promptly and provide constructive feedback to help get your changes merged.
## Getting help
➡️ [Join our Discord](https://discord.gg/pipecat)
➡️ [Pipecat Flows Guide](https://docs.pipecat.ai/guides/pipecat-flows)
➡️ [Reach us on X](https://x.com/pipecat_ai)
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "pipecat-ai-flows",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "pipecat, conversation, flows, state machine, ai, llm",
"author": null,
"author_email": null,
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/33/ae/c9bb3e5fd7781bfe9b03346cffedb52df630045b7475e6592e1f07c9750d/pipecat_ai_flows-0.0.21.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "<h1><div align=\"center\">\n <img alt=\"pipecat\" width=\"500px\" height=\"auto\" src=\"https://raw.githubusercontent.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows/main/pipecat-flows.png\">\n</div></h1>\n\n[](https://pypi.org/project/pipecat-ai-flows) [](https://docs.pipecat.ai/guides/features/pipecat-flows) [](https://discord.gg/pipecat)\n\nPipecat Flows is an add-on framework for [Pipecat](https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat/tree/main#readme) that allows you to build structured conversations in your AI applications. It enables you to create both predefined conversation paths and dynamically generated flows while handling the complexities of state management and LLM interactions.\n\nThe framework consists of:\n\n- A Python module for building conversation flows with Pipecat\n- A [visual editor](#Pipecat-Flows-Editor) for designing and exporting flow configurations\n\n## Dependencies\n\n- Python 3.10 or higher\n- [Pipecat](https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat?tab=readme-ov-file#-getting-started)\n\n## Installation\n\n1. Install uv\n\n ```bash\n curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh\n ```\n\n > **Need help?** Refer to the [uv install documentation](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/getting-started/installation/).\n\n2. Install the module\n\n ```bash\n # For new projects\n uv init my-pipecat-flows-app\n cd my-pipecat-flows-app\n uv add pipecat-ai-flows\n\n # Or for existing projects\n uv add pipecat-ai-flows\n ```\n\n> **Using pip?** You can still use `pip install pipecat-ai-flows` to get set up.\n\n## Quick Start\n\nSee [Quick Start README](./examples/quickstart/README.md).\n\nFor more detailed examples and guides, visit our [documentation](https://docs.pipecat.ai/guides/features/pipecat-flows).\n\n## Examples\n\nThe repository includes several complete example implementations demonstrating various features of Pipecat Flows.\n\n### Available Examples\n\n- **Static Flows**: Pre-defined conversation paths including food ordering, movie exploration, patient intake, and travel planning\n- **Dynamic Flows**: Runtime-generated flows including insurance quotes, restaurant reservations, and warm transfers\n\nEach example is available in multiple LLM provider formats (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google Gemini, AWS Bedrock) to demonstrate cross-platform compatibility.\n\n### Getting Started with Examples\n\nFor detailed setup instructions, configuration, and running examples, see the **[Examples README](examples/README.md)**.\n\nQuick start:\n\n```bash\n# Install dependencies\nuv sync\nuv pip install \"pipecat-ai[daily,openai,deepgram,cartesia,silero,examples]\"\n\n# Configure environment\ncp env.example .env # Add your API keys\n\n# Run an example\nuv run python examples/static/food_ordering.py -u YOUR_DAILY_ROOM_URL\n```\n\n## Contributing to the framework\n\n1. Clone the repository and navigate to it:\n\n ```bash\n git clone https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows.git\n cd pipecat-flows\n ```\n\n2. Install development dependencies:\n\n ```bash\n uv sync --group dev\n ```\n\n3. Install the git pre-commit hooks (these help ensure your code follows project rules):\n\n ```bash\n uv run pre-commit install\n ```\n\n > The package is automatically installed in editable mode when you run `uv sync`.\n\n## Tests\n\nThe package includes a comprehensive test suite covering the core functionality.\n\n### Setup Test Environment\n\n1. **Install Dependencies**:\n ```bash\n uv sync --group dev\n uv add \"pipecat-ai[google,aws,openai,anthropic]\"\n ```\n\n### Running Tests\n\nRun all tests:\n\n```bash\nuv run pytest tests/\n```\n\nRun specific test file:\n\n```bash\nuv run pytest tests/test_state.py\n```\n\nRun specific test:\n\n```bash\nuv run pytest tests/test_state.py -k test_initialization\n```\n\nRun with coverage report:\n\n```bash\nuv run pytest tests/ --cov=pipecat_flows\n```\n\n## Pipecat Flows Editor\n\n> **The Flows Editor is deprecated and will be removed along with Static Flows.**\n\n> We have future plans to introduce a new editor capability that supports dynamic flows, but we don't have a timeline yet.\n> We're open to collaborating with any developers or teams who have an interesting in building out this type of UI! Reach out to us on [Discord](https://discord.gg/pipecat) if you're interested.\n\nA visual editor for creating and managing Pipecat conversation flows.\n\n\n\n### Features\n\n- Visual flow creation and editing\n- Import/export of flow configurations\n- Support for node and edge functions\n- Merge node support for complex flows\n- Real-time validation\n\n### Naming Conventions\n\nWhile the underlying system is flexible with node naming, the editor follows these conventions for clarity:\n\n- **Start Node**: Named after your initial conversation state (e.g., \"greeting\", \"welcome\")\n- **End Node**: Conventionally named \"end\" for clarity, though other names are supported\n- **Flow Nodes**: Named to reflect their purpose in the conversation (e.g., \"get_time\", \"confirm_order\")\n\nThese conventions help maintain readable and maintainable flows while preserving technical flexibility.\n\n### Online Editor\n\nThe editor is available online at [flows.pipecat.ai](https://flows.pipecat.ai).\n\n### Local Development\n\n#### Prerequisites\n\n- Node.js (v14 or higher)\n- npm (v6 or higher)\n\n#### Installation\n\nClone the repository\n\n```bash\ngit clone git@github.com:pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows.git\n```\n\nNavigate to project directory\n\n```bash\ncd pipecat-flows/editor\n```\n\nInstall dependencies\n\n```bash\nnpm install\n```\n\nStart development server\n\n```bash\nnpm run dev\n```\n\nOpen the page in your browser: http://localhost:5173.\n\n#### Usage\n\n1. Create a new flow using the toolbar buttons\n2. Add nodes by right-clicking in the canvas\n - Start nodes can have descriptive names (e.g., \"greeting\")\n - End nodes are conventionally named \"end\"\n3. Connect nodes by dragging from outputs to inputs\n4. Edit node properties in the side panel\n5. Export your flow configuration using the toolbar\n\n#### Examples\n\nThe `editor/examples/` directory contains sample flow configurations:\n\n- `food_ordering.json`\n- `movie_explorer.py`\n- `patient_intake.json`\n- `restaurant_reservation.json`\n- `travel_planner.json`\n\nTo use an example:\n\n1. Open the editor\n2. Click \"Import Flow\"\n3. Select an example JSON file\n\nSee the [examples directory](editor/examples/) for the complete files and documentation.\n\n### Development\n\n#### Available Scripts\n\n- `npm start` - Start production server\n- `npm run dev` - Start development server\n- `npm run build` - Build for production\n- `npm run preview` - Preview production build locally\n- `npm run preview:prod` - Preview production build with base path\n- `npm run lint` - Check for linting issues\n- `npm run lint:fix` - Fix linting issues\n- `npm run format` - Format code with Prettier\n- `npm run format:check` - Check code formatting\n- `npm run docs` - Generate documentation\n- `npm run docs:serve` - Serve documentation locally\n\n#### Documentation\n\nThe Pipecat Flows Editor project uses JSDoc for documentation. To generate and view the documentation:\n\nGenerate documentation:\n\n```bash\nnpm run docs\n```\n\nServe documentation locally:\n\n```bash\nnpm run docs:serve\n```\n\nView in browser by opening: http://localhost:8080\n\n## Contributing\n\nWe welcome contributions from the community! Whether you're fixing bugs, improving documentation, or adding new features, here's how you can help:\n\n- **Found a bug?** Open an [issue](https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows/issues)\n- **Have a feature idea?** Start a [discussion](https://discord.gg/pipecat)\n- **Want to contribute code?** Check our [CONTRIBUTING.md](CONTRIBUTING.md) guide\n- **Documentation improvements?** [Docs](https://github.com/pipecat-ai/docs) PRs are always welcome\n\nBefore submitting a pull request, please check existing issues and PRs to avoid duplicates.\n\nWe aim to review all contributions promptly and provide constructive feedback to help get your changes merged.\n\n## Getting help\n\n\u27a1\ufe0f [Join our Discord](https://discord.gg/pipecat)\n\n\u27a1\ufe0f [Pipecat Flows Guide](https://docs.pipecat.ai/guides/pipecat-flows)\n\n\u27a1\ufe0f [Reach us on X](https://x.com/pipecat_ai)\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "BSD 2-Clause License",
"summary": "Conversation Flow management for Pipecat AI applications",
"version": "0.0.21",
"project_urls": {
"Source": "https://github.com/pipecat-ai/pipecat-flows",
"Website": "https://www.pipecat.ai"
},
"split_keywords": [
"pipecat",
" conversation",
" flows",
" state machine",
" ai",
" llm"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "16a21fa3773e3bfd89d949924f7103890a35764f0a0e91c9c2d3d65b2b0ee42a",
"md5": "5ef9bf5669a891ed77cb63e077f824b5",
"sha256": "c4e2f6a507912b01174a2b8a2127e90814b81bad43d564ca7496f1b07074366f"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "pipecat_ai_flows-0.0.21-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "5ef9bf5669a891ed77cb63e077f824b5",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"size": 30887,
"upload_time": "2025-09-17T16:03:03",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-09-17T16:03:03.892304Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/16/a2/1fa3773e3bfd89d949924f7103890a35764f0a0e91c9c2d3d65b2b0ee42a/pipecat_ai_flows-0.0.21-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "33aec9bb3e5fd7781bfe9b03346cffedb52df630045b7475e6592e1f07c9750d",
"md5": "37b455b7ee48388c89a2e05f8347ed09",
"sha256": "a27451b96a509fccea2814a89090d4aab8f05b98f8211b17f60dfce0d519c7f7"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "pipecat_ai_flows-0.0.21.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "37b455b7ee48388c89a2e05f8347ed09",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"size": 43382,
"upload_time": "2025-09-17T16:03:05",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-09-17T16:03:05.115082Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/33/ae/c9bb3e5fd7781bfe9b03346cffedb52df630045b7475e6592e1f07c9750d/pipecat_ai_flows-0.0.21.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-09-17 16:03:05",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "pipecat-ai",
"github_project": "pipecat-flows",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"requirements": [
{
"name": "loguru",
"specs": [
[
"~=",
"0.7.2"
]
]
}
],
"lcname": "pipecat-ai-flows"
}
