
[](https://ci-cd.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush)
[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/issues)
[](https://github.com/blacklight/platypush)
[](https://github.com/blacklight/platypush)
[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/commits/branch/master)
[](https://lemmy.platypush.tech/c/platypush)
[](https://matrix.to/#/#platypush:matrix.platypush.tech)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/platypush/)
[](https://www.codefactor.io/repository/github/blacklight/platypush)
[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)
[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/LICENSE.txt)
[](https://github.com/sponsors/blacklight)
[](https://blog.platypush.tech)
[](https://docs.platypush.tech)
[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/wiki)
[](irc://platypush@irc.platypush.tech:6697)
[](https://paypal.me/fabiomanganiello)
<!-- toc -->
- [Introduction](#introduction)
* [What it can do](#what-it-can-do)
- [Core concepts](#core-concepts)
- [A few examples](#a-few-examples)
* [Turn on the lights when I say so](#turn-on-the-lights-when-i-say-so)
* [Play the music when I say so](#play-the-music-when-i-say-so)
* [Turn on the lights when the sun goes down](#turn-on-the-lights-when-the-sun-goes-down)
* [Event matching and token extraction through hook templates](#event-matching-and-token-extraction-through-hook-templates)
* [Complex hook conditions](#complex-hook-conditions)
* [Turn off the lights at 1 AM](#turn-off-the-lights-at-1-am)
* [Greet me with lights and music when I come home](#greet-me-with-lights-and-music-when-i-come-home)
- [Core Installation](#core-installation)
* [System package manager installation](#system-package-manager-installation)
+ [Arch Linux](#arch-linux)
+ [Debian/Ubuntu](#debianubuntu)
+ [Fedora](#fedora)
* [`pip`](#pip)
* [Docker](#docker)
+ [Base image installation](#base-image-installation)
+ [The docker-compose way](#the-docker-compose-way)
+ [Exposing host devices](#exposing-host-devices)
* [Manual installation](#manual-installation)
- [Plugins installation](#plugins-installation)
* [`pip`](#pip-1)
* [Web interface](#web-interface)
* [Docker (`platydock`)](#docker-platydock)
* [Virtual environment (`platyvenv`)](#virtual-environment-platyvenv)
* [Manual installation](#manual-installation-1)
- [HTTP API](#http-api)
* [The _Execute_ tab](#the-_execute_-tab)
- [Websocket API](#websocket-api)
* [Events](#events)
* [Actions](#actions)
- [Web hooks](#web-hooks)
- [Entities](#entities)
- [Configuration](#configuration)
* [Configuration file](#configuration-file)
+ [Scripts directory](#scripts-directory)
+ [Splitting configuration on multiple files](#splitting-configuration-on-multiple-files)
* [Working directory](#working-directory)
* [Database](#database)
* [Device ID](#device-id)
* [systemd service](#systemd-service)
* [Redis](#redis)
* [nginx](#nginx)
- [The Web interface](#the-web-interface)
* [Other Web panels](#other-web-panels)
* [Dashboards](#dashboards)
* [PWA support](#pwa-support)
- [Two-factor authentication](#two-factor-authentication)
- [Mobile app](#mobile-app)
- [Browser extension](#browser-extension)
- [Tests](#tests)
<!-- tocstop -->
## Introduction
Platypush is a general-purpose and extensible platform for automation across
multiple services and devices with [hundreds of supported
integrations](https://docs.platypush.tech/plugins.html).
It enables users to create their own self-hosted pieces of automation based on
events (*if this happens then do that*)
and it provides a comprehensive and customizable user interface that collects
everything you need to visualize and control under one roof.
It borrows concepts from [IFTTT](https://ifttt.com),
[Tasker](https://tasker.joaoapps.com/) and [Home
Assistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/) to provide an environment where the
user can easily connect things together. It focuses on an automation-as-code
and API-first approach, offering power users great flexibility in customizing
their routines.
It's built with compatibility and flexibility in mind, and it can easily run on
any device that can run a Python interpreter - from a Raspberry Pi, to an old
smartphone, to a beefy server.
### What it can do
You can use Platypush to do things like:
- [Control your smart
lights](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Ultimate-self-hosted-automation-with-Platypush)
- [Control your music across multiple
devices](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Build-your-open-source-multi-room-and-multi-provider-sound-server-with-Platypush-Mopidy-and-Snapcast)
- [Create custom and privacy-secure voice assistants that run custom hooks on
your
phrases](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Build-custom-voice-assistants)
- Build integrations between sensors,
[cameras](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/camera.pi.html),
[microphones](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/sound.html)
and [machine learning
models](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/tensorflow.html)
to create smart pieces of automation for e.g. [people
detection](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Detect-people-with-a-RaspberryPi-a-thermal-camera-Platypush-and-a-pinch-of-machine-learning)
or [sound
detection](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Create-your-smart-baby-monitor-with-Platypush-and-Tensorflow)
- [Display events from your calendars and build automation on
them](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/calendar.html)
- [Build automation routines and visualizations from your sensors
data](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/How-to-build-your-personal-infrastructure-for-data-collection-and-visualization)
- [Control and automate a self-built
robot](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/gpio.zeroborg.html)
- [Deliver automated newsletters from custom RSS
digests](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Deliver-customized-newsletters-from-RSS-feeds-with-Platypush)
- [Synchronize the clipboards on your
devices](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/clipboard.html)
- [Implement custom text-to-speech
logic](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/tts.html)
- [Build any kind of automation routines with your Android device using
Tasker](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/How-to-build-your-personal-infrastructure-for-data-collection-and-visualization)
- Play local
videos,
YouTube videos and torrent media from any device and service, to any device, with support for [Kodi](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.kodi.html), [Chromecast](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.chromecast.html), [VLC](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.vlc.html), [Jellyfin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.jellyfin.html), [Plex](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.plex.html) and more
- [Get weather forecast events for your location and build automation routines on them](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/weather.darksky.html)
- [Create a custom single hub for Zigbee and Z-Wave smart devices](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Transform-a-RaspberryPi-into-a-universal-Zigbee-and-Z-Wave-bridge)
- Build your own web dashboard with calendar, weather, news and music controls
(basically, anything that has a Platypush web widget)
- ...and much more (basically, anything that comes with a [Platypush plugin](https://docs.platypush.tech)).
The full list of available integrations is available at
[docs.platypush.tech](https://docs.platypush.tech), which also contains a more
in-depth wiki on the features supported by the platform.
The wiki is also mirrored on
[git.platypush.tech](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/wiki).
[The blog](https://blog.platypush.tech) regularly publishes content with
step-by-step tutorials and recipes.
## Core concepts
The foundations of Platypush rest on a few simple building blocks that offer
great versatility to build arbitrarily complex automation routines:
- 🧩 **Plugins**. Plugins are the bread-and-butter of the platform. Each plugin
exposes an API to interact with an integration - there are plugins for media
players and devices, calendars, sensors, voice assistants, smart devices,
cloud services, and so on.
- ⏻ **Actions**. These are the methods of a plugin transparently exposed to the
user over a simple JSON RPC API, and they are always expressed in the
format `<plugin_name>.<action_name>`. For instance,
[`light.hue.on`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/light.hue.html#platypush.plugins.light.hue.LightHuePlugin.on)
can be used to turn on Philips Hue-compatible lights,
[`media.vlc.play`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.vlc.html#platypush.plugins.media.vlc.MediaVlcPlugin.play)
to play some media on a VLC player, etc.
- ⚙️ **Backends**. These are special integrations whose main purpose is to
deliver messages to the main application. The principal one is the
[`http` backend](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/http.html),
which exposes the HTTP and WebSocket APIs, serves the main UI and is used
by several integrations to provide additional services. A [`nodered`
backend](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/nodered.html) is
also available to expose a Platypush action component to a Node-RED
instance, as well as an internal [`redis`
backend](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/redis.html) and an
(insecure) [`tcp`
backend](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/tcp.html) to receive
raw messages.
- 📧 **Events**. Plugins emit _events_ whenever some particular conditions happen
for example, a [new media track is
played](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/media.html#platypush.message.event.media.MediaPlayEvent),
a [voice assistant conversation has
started](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/assistant.html#platypush.message.event.assistant.ConversationStartEvent),
and so on.
- 🪝 **Hooks**. Users can define custom callbacks on events in the form of
*hooks*. Hooks can contain lists of actions to execute when a certain event
matches the hook *condition*, or any kind of custom logic - for example,
*send a notification on my phone when the presence sensor in my garage goes
on*, or *use a TTS plugin to process the digest of the latest RSS feeds if
I tell the voice assistant "play the news"*. Event hooks can be expressed
either in YAML format or as Python runtime scripts.
- 📜 **Procedures**. Procedures are custom snippets of logic that can be invoked
using the Platypush API. For example, you can define an `at_home` procedure
that will be executed when you arrive home, which turns on the lights, plays
the music, sets the thermostat temperature etc., and then call it using the
Platypush API from any device. Like event hooks, procedures can be defined
both in YAML format (good if you just want to execute lists of actions
without much added logic), or as Python scripts.
- 🕗 **Cronjobs**. Cronjobs are special procedures that can be executed either
at regular intervals (the [UNIX cron
syntax](https://linuxhandbook.com/crontab/) is supported), or at a specific
time (one-shot). Just like procedures, they can be defined either in YAML or
as Python scripts.
- 💡 **Entities**. Some plugins expose generic _entities_ - such a lights,
sensors, media players, switches, voice assistants etc. These entities can be
controlled through [the same generic
APIs](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/entities.html), emit [the
same types of
events](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/entities.html), can
be controlled from the same Web view or dashboard, and their state is
persisted across runs.
## A few examples
The bulk of the configuration of Platypush lives under the `config.yaml` file.
An extensive [`config.yaml`
example](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/platypush/config/config.yaml)
is provided in the repo. All the sections are optional - the only one enabled by
default is the HTTP server, `backend.http`, but that is optional too.
Let's take an example where we want to control the following entities:
- A Philips Hue bridge and its connected smart lights.
- An on-device voice assistant (we'll consider the Google Assistant in this
example as it's the easiest to configure, although Google deprecated the
Assistant libraries long ago).
- A compatible music player - we'll consider MPD/Mopidy in this example as they
are the ones best supported in Platypush, and Mopidy also offers plugins with
basically any audio backend out there.
We'll need the following plugins enabled in the `config.yaml`:
- [`light.hue`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/light.hue.html)
- [`assistant.google`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/assistant.google.html)
- [`music.mopidy`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/music.mopidy.html)
or
[`music.mpd`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/music.mpd.html)
(they expose the same API)
The documentation pages of these plugins already provide some comprehensive
configuration snippets that you can use.
The most basic configuration would be something like this:
```yaml
# Enable it if you want the enable the HTTP API and the Web interface
backend.http:
light.hue:
# IP/hostname of the Hue bridge
bridge: 192.168.1.10
# Default groups that should be targeted by actions if none is specified
# (default: all lights/groups)
groups:
- Living Room
# Check the plugin documentation on how to get the credentials
assistant.google:
music.mopidy: # Or music.mpd
# IP/hostname of the MPD/Mopidy server
host: 192.168.1.2
```
Now that we have our integrations configured, let's build some automation routines.
### Turn on the lights when I say so
In this case we will have to create a hook that listens to a
[`SpeechRecognizedEvent`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/assistant.html#platypush.message.event.assistant.SpeechRecognizedEvent)
triggered by the assistant - for example, when we say "_OK, Google_" followed
by "_turn on the lights_".
We can declare the hook in YAML format directly in the `config.yaml`, or in one
of the files included in it through the `include:` directive:
```yaml
event.hook.turn_lights_on_voice_command:
if:
type: platypush.message.event.assistant.SpeechRecognizedEvent
# Note that a minimal regex-like syntax is supported here.
# This condition matches both a phrase that contains
# "turn on the lights" and one that contains "turn on lights"
phrase: "turn on (the)? lights"
then:
- action: light.hue.on
args:
groups:
- Living Room
```
Or we can declare the hook in a Python script - you just have to create a `.py`
file (e.g. `lights.py`) under a `scripts` directory located under the same
folder as your `config.yaml`:
```python
from platypush import run, when
from platypush.events.assistant import SpeechRecognizedEvent
@when(SpeechRecognizedEvent, phrase="turn on (the)? lights")
def lights_on_voice_command(): # Also accepts an optional `event` argument
run('light.hue.on', groups=['Living Room'])
```
Or, using the `get_plugin` API:
```python
from platypush import get_plugin, when
from platypush.events.assistant import SpeechRecognizedEvent
@when(SpeechRecognizedEvent, phrase="turn on (the)? lights")
def lights_on_voice_command():
get_plugin('light.hue').on(groups=['Living Room'])
```
### Play the music when I say so
The approach is similar for a "_play the music_" voice command. YAML:
```yaml
event.hook.play_music_voice_command:
if:
type: platypush.message.event.assistant.SpeechRecognizedEvent
phrase: "play (the)? music"
then:
- action: music.mopidy.play
```
Python:
```python
from platypush import run, when
from platypush.events.assistant import SpeechRecognizedEvent
@when(SpeechRecognizedEvent, phrase="play (the)? music")
def lights_on_voice_command():
run('music.mopidy.play')
```
### Turn on the lights when the sun goes down
This example requires the [`sun`
plugin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/sun.html) configured:
```yaml
sun:
latitude: LAT
longitude: LONG
```
You can then simply subscribe to
[`SunsetEvent`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/sun.html#platypush.message.event.sun.SunsetEvent).
YAML:
```yaml
event.hook.sunset_lights_on:
if:
type: platypush.message.event.sun.SunsetEvent
then:
- action: light.hue.on
```
Python:
```python
from platypush import run, when
from platypush.events.sun import SunsetEvent
@when(SunsetEvent)
def sunset_lights_on():
run('light.hue.on')
```
### Event matching and token extraction through hook templates
You can also operate token extraction from event arguments if the values are
strings.
For example, you can use advanced pattern matching and token extraction to
create voice assistant hooks that will match a template with parametrized field
which will be passed as arguments to your event hook:
```python
from platypush import run, when
from platypush.events.assistant import SpeechRecognizedEvent
@when(SpeechRecognizedEvent, phrase='play ${title} by ${artist}')
def on_music_play_command(event, title, artist):
results = run(
'music.mpd.search',
filter={
'artist': artist,
'title': title,
}
)
if results:
run('music.mpd.play', results[0]['file'])
```
### Complex hook conditions
Your event hooks can include more complex filters too. Structured filters
against partial event arguments are also possible, and relational operators are
supported as well. For example:
```python
from platypush import when
from platypush.events.sensor import SensorDataChangeEvent
@when(SensorDataChangeEvent, data=1):
def hook_1(event):
"""
Triggered when event.data == 1
"""
@when(SensorDataChangeEvent, data={'state': 1}):
def hook_2(event):
"""
Triggered when event.data['state'] == 1
"""
@when(SensorDataChangeEvent, data={
'temperature': {'$gt': 25},
'humidity': {'$le': 15}
}):
def hook_3(event):
"""
Triggered when event.data['temperature'] > 25 and
event.data['humidity'] <= 15.
"""
```
The supported relational fields are the same supported by ElasticSearch - `$gt`
for greater than, `$lt` for lesser than, `$ge` for greater or equal, `$ne` for
not equal, etc.
### Turn off the lights at 1 AM
We can use a `cron` for this case. YAML:
```yaml
cron.lights_off_night:
# Run this every day at 1 AM
cron_expression: '0 1 * * *'
actions:
- action: light.hue.off
```
Python:
```python
from platypush import cron, run
@cron('0 1 * * *')
def lights_off_night():
run('light.hue.off')
```
### Greet me with lights and music when I come home
Let's create an `at_home` procedure for this purpose. We can also use a
text-to-speech plugin like the [`tts`
plugin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/tts.html) (it requires no
configuration as it relies on the Google Translate frontend API, but other,
more sophisticated plugins are also available) to have a warm voice to welcome
us home. YAML:
```yaml
# Make sure that the sound plugin is also enabled, for audio processing
sound:
procedure.at_home:
- action: tts.say
args:
text: "Welcome home!"
# Get luminosity data from a sensor - e.g. LTR559
- action: gpio.sensor.ltr559.get_data
# If it's lower than a certain threshold, turn on the lights.
# Note that we can directly access attributes returned by the
# previous request(s) as local context variables within the
# procedure/hook/cron. In this case, `light` is an attribute returned
# on the response of the previous command.
# Otherwise, you can also use the special `output` variable to get only
# the response of the latest action, e.g. `output['light']`
# Also note the use of the special `if ${}` construct. It accepts
# a snippet of Python code and it can access variables within the
# current context.
- if ${light is not None and light < 110}:
- action: light.hue.on
- action: music.mopidy.play
args:
resource: "uri:to:my:favourite:playlist"
```
Python:
```python
from platypush import procedure, run
@procedure("at_home")
def at_home_proc():
run('tts.say', text='Welcome home!')
luminosity = run('gpio.sensor.ltr559.get_data').get('light', 0)
if luminosity < 110:
run('light.hue.on')
run('music.mopidy.play', resource='uri:to:my:favourite:playlist')
```
You can then call the procedure from a hook or another script:
```python
from platypush import run
run('procedure.at_home')
```
Or, from YAML:
```yaml
procedure.some_other_procedure:
- action: procedure.at_home
```
Or using the [available APIs](#http-api).
## Core Installation
### System package manager installation
#### Arch Linux
You can either install the
[`platypush`](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/platypush) package (for the
latest stable version) or the
[`platypush-git`](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/platypush-git) package
(for the latest git version) through your favourite AUR package manager. For
example, using `yay`:
```bash
$ yay platypush
# Or
$ yay platypush-git
```
The Arch Linux packages on AUR are automatically updated upon new git commits
or tags.
#### Debian/Ubuntu
1. Add the Platypush APT key to your trusted keyring:
```
# wget -q -O \
/etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/platypush.asc \
https://apt.platypush.tech/pubkey.txt
```
2. Add the Platypush repository to your APT sources:
```
# wget -q -O \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/platypush.list \
https://apt.platypush.tech/lists/platypush-<deb_version>-<branch>.list
```
Where:
- `deb_version` can be either:
- `stable`: current Debian stable
- `oldstable`: previous Debian stable
- `ubuntu`: latest Ubuntu release
- `branch` can be either:
- `main`: latest stable release
- `dev`: a package always in sync with the latest git version
For example, to install the latest stable tags on Debian stable:
```
# wget -q -O \
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/platypush.list \
https://apt.platypush.tech/lists/platypush-stable-main.list
```
3. Update your repos and install Platypush:
```
# apt update
# apt install platypush
```
#### Fedora
RPM builds targeting the latest Fedora release are automatically built on every
push pipeline.
To install Platypush via RPM on Fedora:
- Add the Platypush RPM repository configuration to the package manager:
```
# yum config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.platypush.tech/platypush.repo
```
- Install Platypush, either the latest stable release or the rolling release
updated on every commit to the main branch:
```
# yum install platypush
# Or
# yum install platypush-git
```
### `pip`
```bash
$ pip install platypush
```
Or, for the latest git version:
```bash
# Official repo
$ pip install git+https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush
# Github mirror
$ pip install git+https://github.com/blacklight/platypush
```
### Docker
#### Base image installation
```bash
$ docker run -it --name platypush \
-p 8008:8008 \
-e "PLATYPUSH_DEVICE_ID=my-device" \
-v /path/to/your/platypush/config:/etc/platypush \
-v /path/to/your/platypush/share:/var/lib/platypush \
quay.io/platypush/platypush
```
The following architectures are currently supported:
- `amd64`/`x86_64` (standard Intel-based architectures)
- `arm64`/`aarch64` (ARM64, such as modern ARM-based MacBooks, most of the
Android devices or RaspberryPi 4 and 5)
- `armv7l` (older ARM-based devices, such as RaspberryPi 2 and 3 or older
Android devices)
The Web service will be available on `http://localhost:8008`, and a default
configuration file will be initialized under
`/path/to/your/platypush/config/config.yaml` if not available. The next
executions of the service can be triggered via `docker start platypush`.
Note that this will install an Alpine-based image. For other base images (e.g.
Debian, Ubuntu or Fedora) please consult the [custom docker-compose
way](#the-docker-compose-way).
Also note that any extra plugin dependencies installed in the container will be
lost if the container is removed.
In order to preserve the state of the container after installing and configuring
your plugins, you can leverage the `docker commit` command:
```bash
❯ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
f00546d3bd35 quay.io/platypush/platypush "/bin/sh -c 'platypu…" 38 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 0.0.0.0:8008->8008/tcp, :::8008->8008/tcp platypush
❯ docker commit f00546d3bd35 my-custom-platypush-image
sha256:13d4a4cae4e7eedee924a8a79deae9a9978aa70b46699c1f2abfd16bf5ed910b
# You can now use the my-custom-platypush-image even if the container is destroyed
```
Alternatively, you can use [the `platydock` command](#docker-(platydock)) to
directly create a Docker image or a `Dockerfile` from a configuration, with all
the required plugins and dependencies pre-installed.
#### The docker-compose way
```bash
$ git clone https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush.git
$ cd platypush
# Copy .env.example to .env and edit docker-compose.yml if required.
# In particular, you may want /etc/platypush and /var/lib/platypush
# to point to directories on your hosts
$ docker compose up
```
Note that the default `Dockerfile` uses Alpine, but in `docker-compose.yml` you
can also specify an alternative `Dockerfile` - Debian, Ubuntu and Fedora are
supported.
#### Exposing host devices
Note that some plugins may require access to the host hardware - such as USB
devices, Bluetooth adapters etc.
In order to make these devices visible to the Docker container you may need to
explicitly mount them as volumes.
For example, the [`serial`
plugin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/serial.html) may need to
access an Arduino/ESP device over USB. You can export only that device to the
Docker container:
```bash
$ docker run --device=/dev/ttyUSB0 ...
# Or, if you set up static naming via udev rules
$ docker run --device=/dev/arduino ...
```
Or, through `docker-compose.yml`:
```yaml
services:
platypush:
# ...
devices:
- /dev/ttyUSB0
```
Otherwise, for privileged access to the USB bus on a Linux host:
```bash
$ docker run --priviliged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb ...
```
Or, through `docker-compose.yml`:
```yaml
services:
platypush:
# ...
volumes:
- /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb
```
### Manual installation
```shell
$ git clone https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush.git
$ cd platypush
$ pip install .
```
## Plugins installation
All the plugins included in the main repo will be available once you have
installed the core platform.
However, some plugins may require extra (optional) dependencies. You have
several ways of installing those dependencies:
### `pip`
You can install extra dependencies via pip extras:
```shell
pip install 'platypush[plugin1,plugin2,...]'
```
For example:
```shell
pip install 'platypush[light.hue,music.mpd,rss]'
```
Will install Platypush with the dependencies for the `light.hue`, `music.mpd`
and `rss` plugins.
### Web interface
Plugins can be installed from the Web interface too. Navigate to the
_Extensions_ entry in the sidebar, select the extension that you want to install,
select the _Install_ tab and click _Install_.
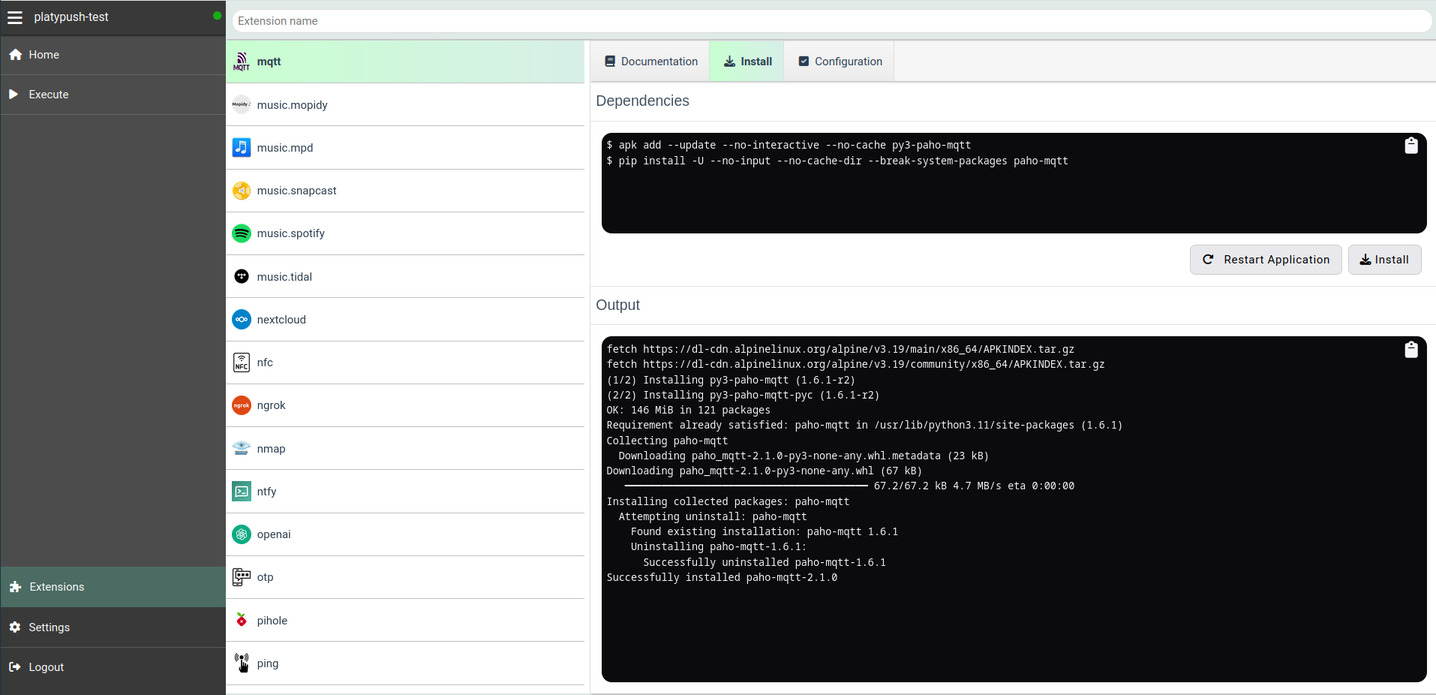
This section also includes the _Configuration_ tab, with a ready-to-paste
configuration snippet template for that plugin, as well as a documentation page
that includes all the actions supported by a given plugin and the events it
triggers.
### Docker (`platydock`)
If you already have the base installation of Platypush on your machine, and you
have a configuration file with a custom set of integrations, then you may opt
to generate a custom Docker image from your configuration file, with all the
extra dependencies configured, using the `platydock` command.
The following command:
```shell
❯ platydock -c /path/to/your/config.yaml -d platypush-test
```
Will create a Platypush Docker image for a device with ID `platypush-test`,
with all the requirements for the additional integrations listed in
`config.yaml`.
You can pass the `--print` option if you just want to print the content of the
output `Dockerfile` instead of generating the image.
By default the image will use Alpine Linux as a base. You can use the
`-i`/`--image` to specify another supported base image - `ubuntu`, `debian` or
`fedora`.
### Virtual environment (`platyvenv`)
If you already have the base installation of Platypush on your machine, and you
have a configuration file with a custom set of integrations, then you may opt
to generate a custom virtual environment from your configuration file, with all
the extra dependencies configured, using the `platyvenv` command.
The following command:
```bash
❯ platyvenv -c /path/to/your/config.yaml -o /path/to/your/venv
```
Will create a new virtual environment under `/path/to/your/venv` using the
specified `config.yaml` to determine which optional dependencies should be installed.
You can then run Platypush after activating your new environment:
```bash
❯ source /path/to/your/venv/bin/activate
❯ platypush -c /path/to/your/config.yaml
```
### Manual installation
The [plugin/backend documentation](https://docs.platypush.tech) reports all the
dependencies required by each plugin, as well as the commands to install them
on multiple platforms.
If you want to customize your installation, or if you need to install
dependencies for a plugin that requires some manual steps, you can check out
any plugin-specific installation steps from its documentation.
## HTTP API
Actions and procedures can also be called using the JSON-RPC API exposed by
Platypush.
Your configuration requires the [`backend.http`
section](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/http.html) enabled if
you want to use the HTTP API - default listen port: `8008`.
After ensuring that the HTTP backend is enabled, head to
`http://localhost:8008` and register a new user.
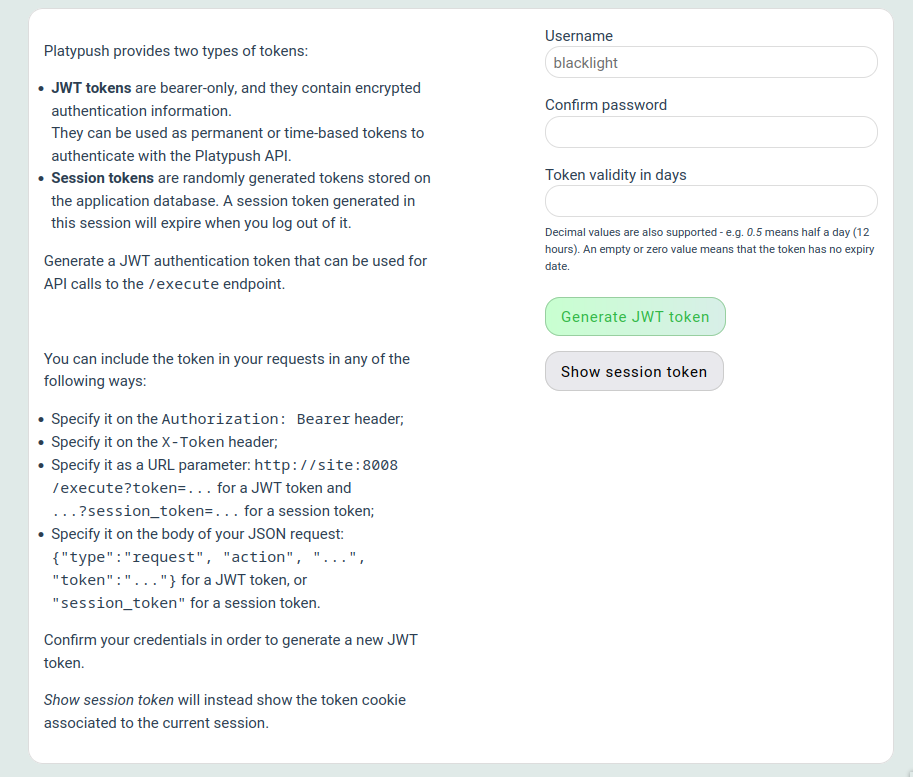
From the Web UI, head to _Settings_ → _Tokens_, insert your password again and
click _Generate JWT token_.
Alternatively, you can retrieve a token via HTTP request:
```shell
❯ curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '
{
"username": "$YOUR_USER",
"password": "$YOUR_PASSWORD"
}' http://localhost:8008/auth
```
You can then send requests to Platypush using a simple RPC API:
```bash
❯ curl -XPOST \
-d '{"type":"request", "action":"procedure.at_home"}' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN" \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
http://localhost:8008/execute
❮
{
"id": "724754df98968247a284557ce32f74bb",
"type": "response",
"target": "http",
"origin": "myhost",
"_timestamp": 1716575901.046127,
"response": {
"output": {
"success": true
},
"errors": []
}
}
```
If your procedure returned something, then that will be returned on the API
response too, so downstream consumers can use it.
The `POST /execute` endpoint accepts a payload in the format:
```javascript
{
"type": "request", // Constant
"action": "<plugin-name>.<action-name>", // Or procedure.<name>
"args": {
"arg1": "arg2",
// ...
}
}
```
In our `procedure.at_home` example, you can for instance create an automation
snippet paired with your phone that runs the routine whenever you arrive home
(or your phone does):
1. Install an app like [Tasker](https://tasker.joaoapps.com/) to create
automation tasks on your Android device.
2. Install a plugin like [AutoLocation](https://joaoapps.com/autolocation/) to
create automation tasks based on your phone's location.
3. Create a profile that triggers whenever you enter your home location (and/or
exit it).
4. Leverage the [HTTP
Request](https://tasker.joaoapps.com/userguide/en/help/ah_http_request.html)
Tasker action to send a request to your Platypush API to trigger the routine.
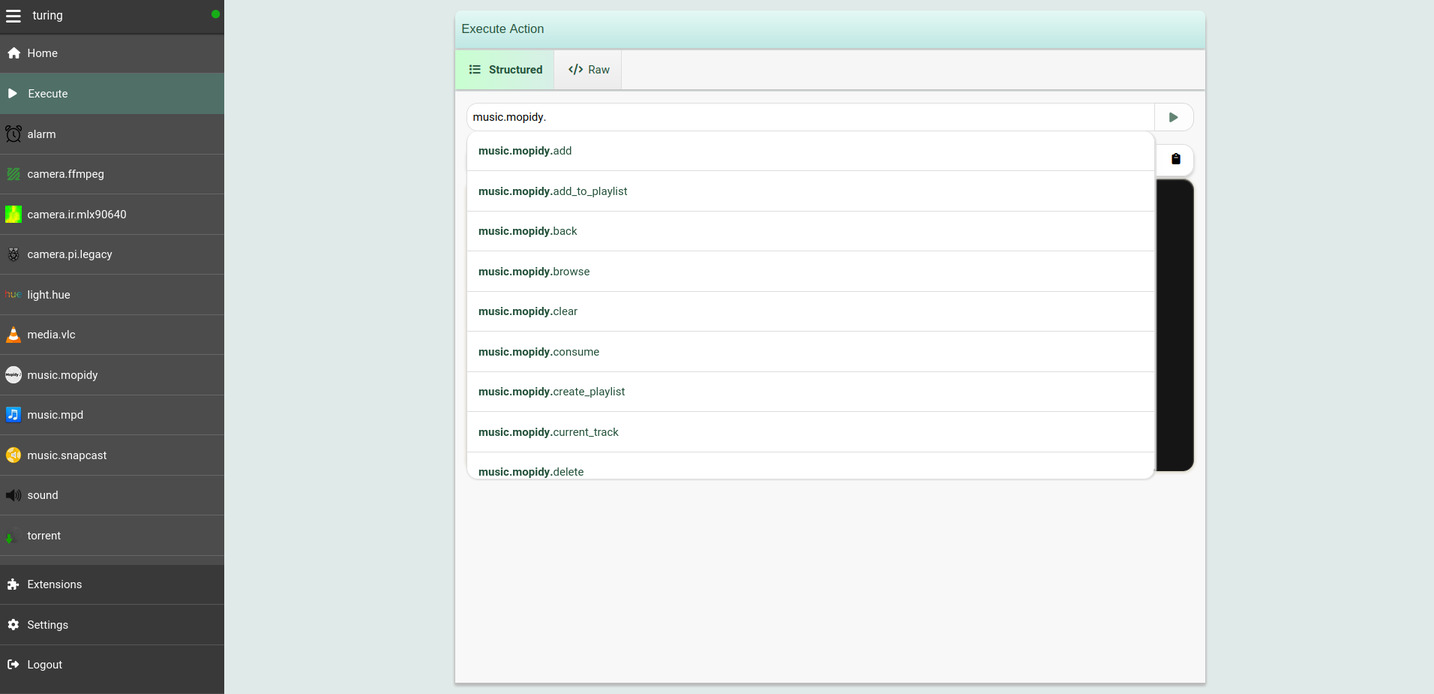
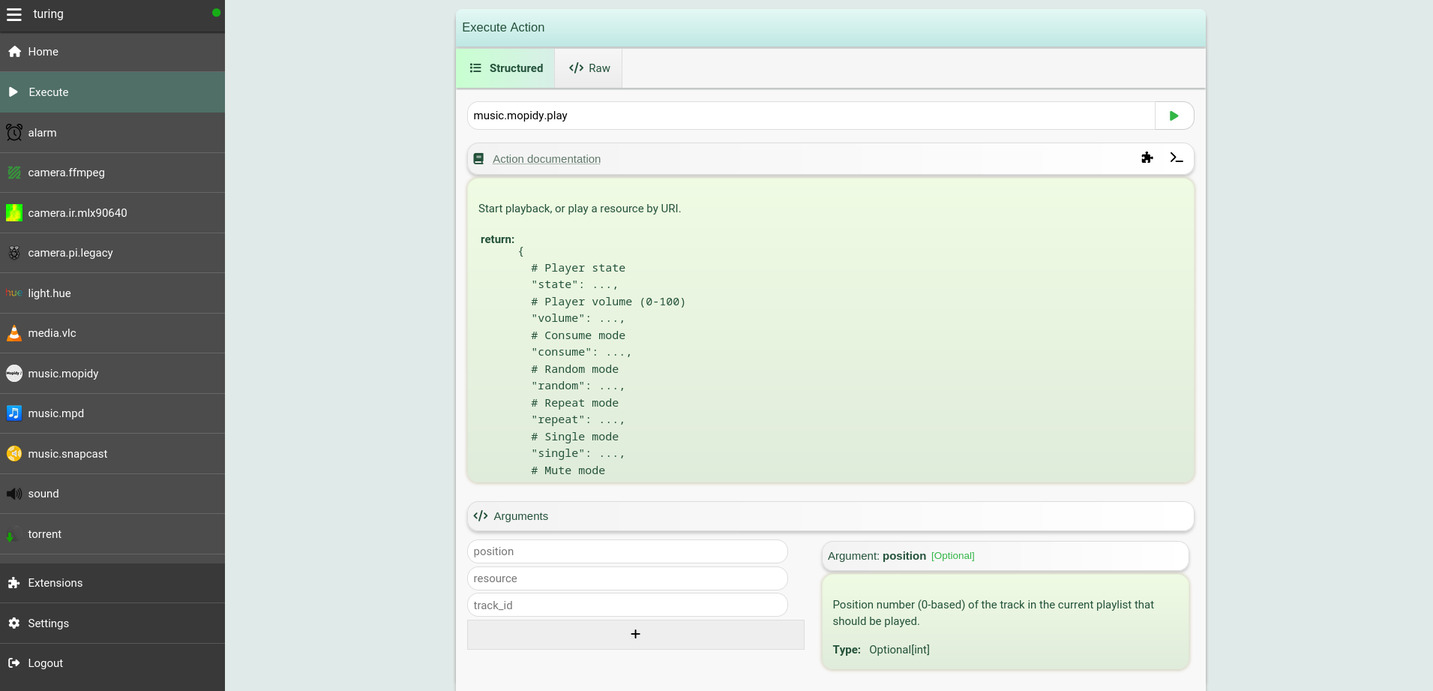
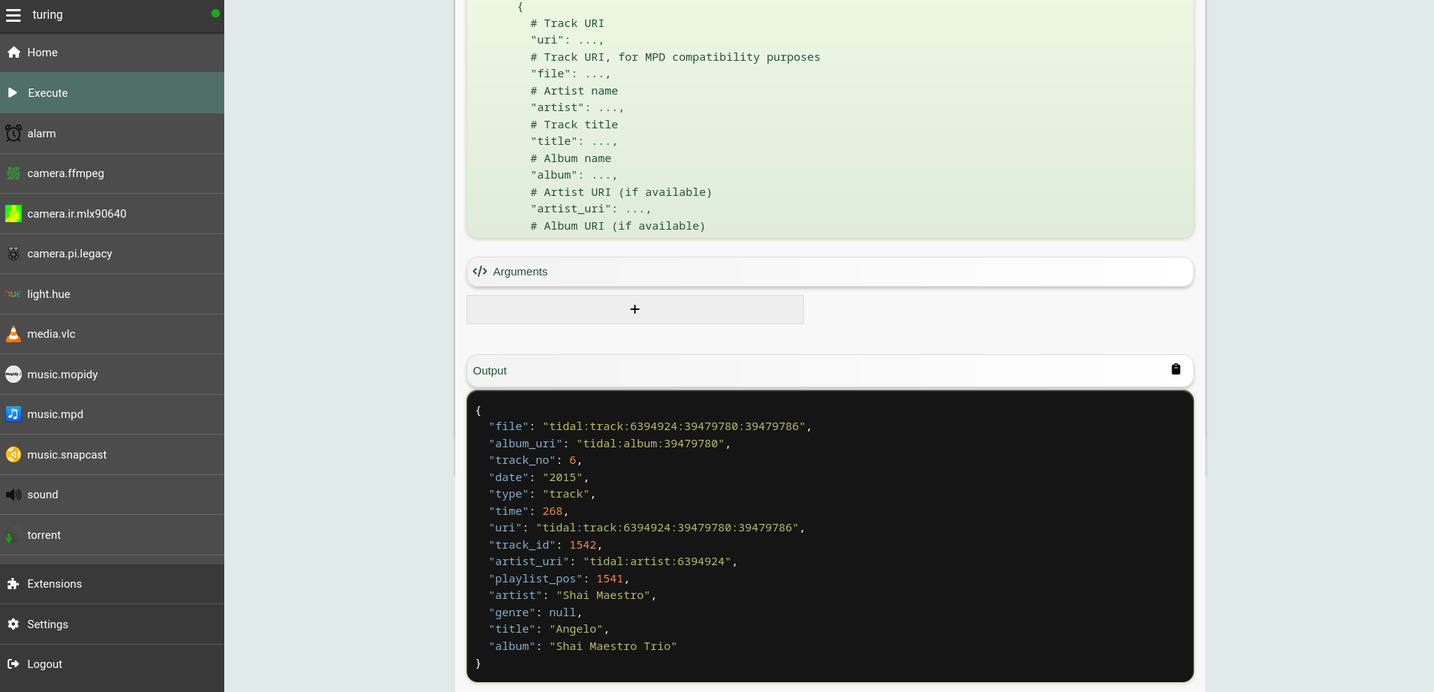
### The _Execute_ tab
The Web interface also provides an _Execute_ tab under the menu sidebar. You
can use this tab to dynamically discover the actions exposed by various plugins
(and also your own procedures):
## Websocket API
### Events
You can subscribe to events generated by the application over the `/ws/events`
Websocket endpoint, and send events to this endpoint too.
This is useful if you want to synchronize Platypush events with another client,
or send custom events outside of those native to the application and build
custom automation hooks on them.
Sending events:
```bash
❯ wscat -H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN" \
-c "ws://localhost:8008/ws/events" \
-w 1 \
-x '
{
"type": "event",
"args": {
"type": "platypush.message.event.custom.CustomEvent",
"subtype": "foo",
"args": {
"bar": "baz"
}
}
}'
```
Receiving events:
```bash
❯ wscat -H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN" -c "ws://localhost:8008/ws/events"
```
### Actions
You can also send requests to the `/ws/requests` Websocket endpoint, and get
responses asynchronously on the same channel:
```bash
❯ wscat -H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN" \
-c "ws://localhost:8008/ws/requests" \
-w 1 \
-x '{"type": "requests", "action": "procedure.foo.bar"}'
```
## Web hooks
You can use Platypush to expose your custom routines as dynamic Web hooks that
can be called by any client.
All you need is to register a listener for a
[`WebhookEvent`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/http.hook.html#platypush.message.event.http.hook.WebhookEvent)
```python
from platypush import run, when
from platypush.events.http.hook import WebhookEvent
hook_token = "abcdefabcdef"
# Expose the hook under the /hook/at_home endpoint
@when(WebhookEvent, hook="at_home")
def at_home_webhook(event: WebhookEvent):
# Unlike the calls to /execute, custom web hooks are unauthenticated.
# If you want authentication, you'll need to implement your custom logic by
# parsing the event headers
if event.headers.get("X-Token") != hook_token:
# Tuple with <response, http-code, [response-headers]>
event.send_response(("Unauthorized", 401))
return
run('procedure.at_home')
# Return anything back to the client
return {'status': 'ok'}
```
Then you can invoke your custom logic over HTTP:
```bash
❯ curl -H 'X-Token: abcdefabcdef' 'http://localhost:8008/hook/at_home'
```
## Entities
Entities are another building block of Platypush. Many integrations will store
their state or connected devices in the form of entities - e.g. the sensors
detected by the Z-Wave/Zigbee/Bluetooth integration, or the lights connected to
a Hue bridge, or your cloud nodes, or your custom Arduino/ESP machinery, and so
on.
Entities provide a consistent interface to interact with your integrations
regardless of their type and the plugin that handles them. For instance, all
temperature sensors will expose the same interface, regardless if they are
Bluetooth or Zigbee sensors, and all the media plugins will expose the same
interface, regardless if they manage Chromecasts, Kodi, Plex, Jellyfin or a
local VLC player.
Once you enable the HTTP backend and a few integrations that export entities
and register a user, you can query the detected entities via:
```shell
curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-H "Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN" \
-d '{"type":"request", "action":"entities.get"}' \
http://localhost:8008/execute
```
All the entities expose the same interface and can be manipulated through the
same API. Also, when an entity is updated it always emits an
[`EntityUpdateEvent`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/entities.html#platypush.message.event.entities.EntityUpdateEvent),
so you can easily create hooks that react to these events and act on multiple
types of entities.
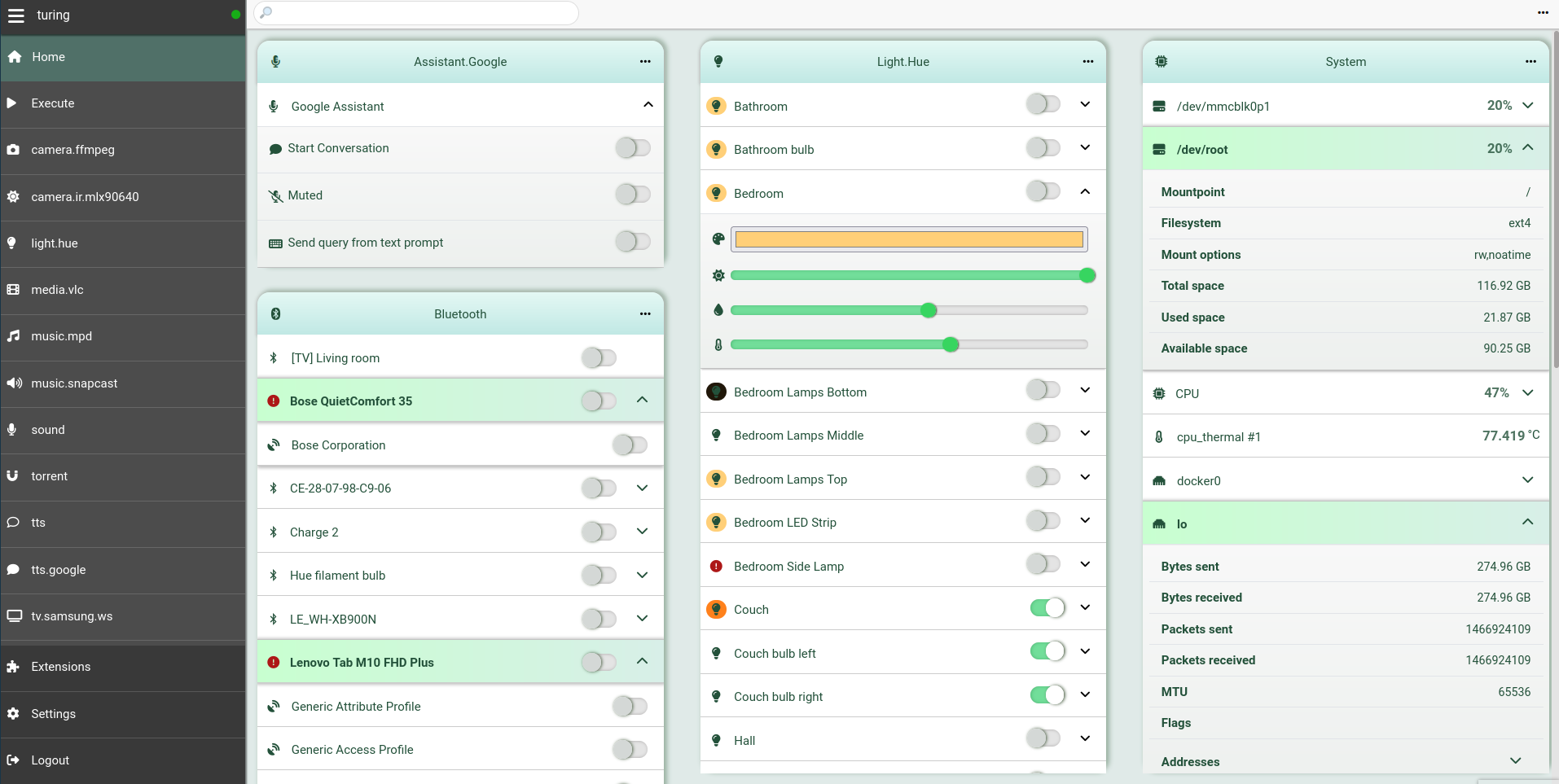
If you enabled the HTTP backend, then you can also access all the entities from
the home panel of the Web UI.
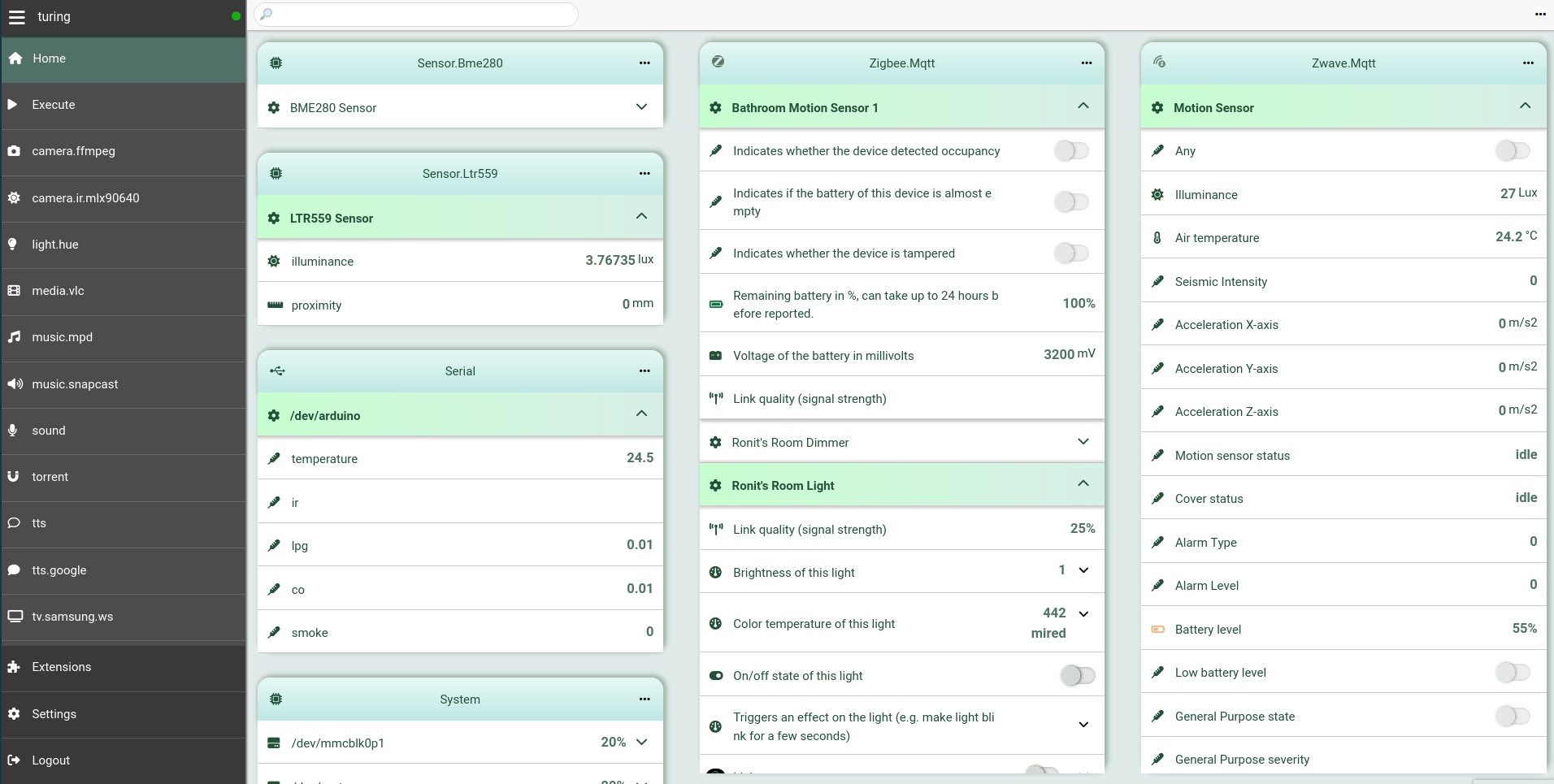
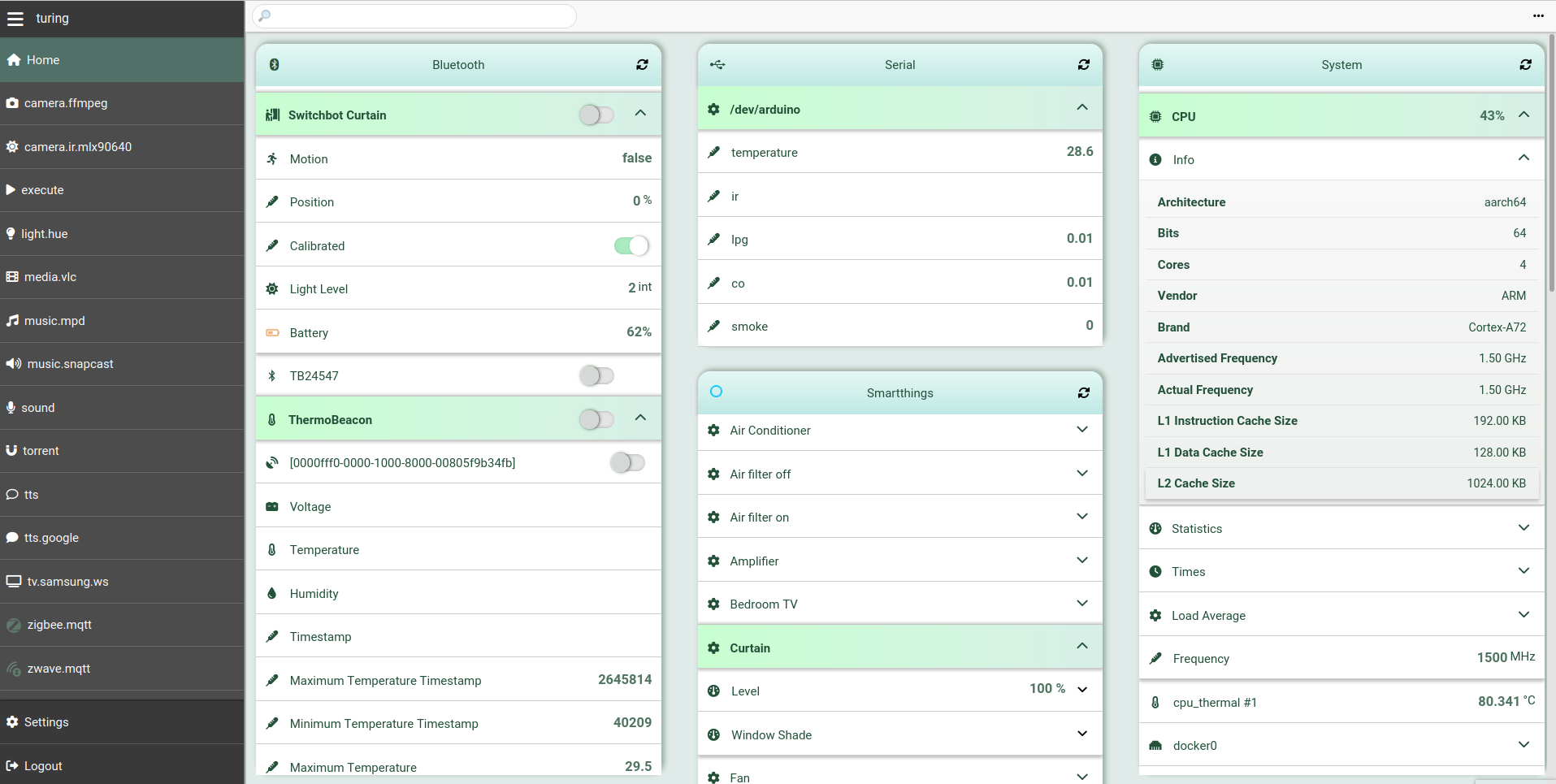
## Configuration
### Configuration file
You can use the [default
`config.yaml`](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/platypush/config/config.yaml)
as a template/reference.
The location of the `config.yaml` to be used by the application is determined
in the following way:
1. It can be passed through the command-line `-c`/`--config` argument.
2. If not specified via `-c`, it will be read from the `PLATYPUSH_CONFIG`
environment variable.
3. If not specified, use `./config.yaml` if available.
4. If not available, and you are running Platypush within a Docker container,
or as a privileged user (and usually you shouldn't), or as a systemd service
created by a supported package manager, then `/etc/platypush/config.yaml`
will be used if available.
5. Otherwise, if you are running Platypush as a non-privileged user or in a
virtual environment, `$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/platypush/config.yaml` will be used
(defaults to `~/.config/platypush/config.yaml`).
#### Scripts directory
By default, any custom Python scripts will be searched under
`<CONFDIR>/scripts`, where `<CONFDIR>` is the path to your `config.yaml`.
You can override it in your `config.yaml`:
```yaml
scripts_dir: /path/to/custom/scripts
```
Since everything under the scripts directory will be imported as a submodule,
you can create your own libraries of scripts that can import other scripts:
```python
# Content of scripts/music.py
from platypush import run
def music_play(plugin='music.mopidy', resource=None):
run(f'{plugin}.play', resource)
# Content of scripts/lights.py
from platypush import run
def lights_toggle(plugin='light.hue', groups=('Living Room',)):
run(f'{plugin}.toggle', groups=groups)
# Content of scripts/home.py
from platypush import procedure
from scripts.music import music_play
from scripts.lights import lights_toggle
@procedure
def at_home():
music_play()
lights_toggle()
```
#### Splitting configuration on multiple files
The `config.yaml` file can become very complex, especially if you embed many
hooks and procedures in it in YAML format.
To make the configuration more maintainable, and also to isolate modules that
you can reuse across multiple instances, you can leverage the `include`
directive:
```yaml
# All paths are relative to config.yaml, or to the location of the current file
include:
- assistant.yaml
- db.yaml
- media.yaml
- mqtt.yaml
- sensors.yaml
# ...
```
### Working directory
This is where the application will store its data and integration plugins will
store their data. The order of precedence is:
* `-w`/`--workdir` command line argument.
* The `PLATYPUSH_WORKDIR` environment variable.
* The `workdir` field in the configuration file.
* `$XDG_DATA_HOME/platypush` (default: `~/.local/share/platypush`) if launched
with a non-privileged user, `/var/lib/platypush` if launched as root or with
a system user.
### Database
The application stores entities, variables, users, integrations state and more
on a database. The engine configuration supports the [SQLAlchemy engine
syntax](https://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/20/core/engines.html).
**Note**: The application uses a local SQLite database by default, which is
natively supported by SQLAlchemy. The application has also been tested against
MySQL/MariaDB and Postgres, and should work fine with any modern relational
database supported by SQLAlchemy. However, any backend other than SQLite may
require an additional Python dependency for the SQLAlchemy driver (for example
[`pg8000`](https://pypi.org/project/pg8000/) for PostgreSQL).
Order of precedence for the engine:
* `--main-db`/`--db` command line argument.
* The `PLATYPUSH_DB` environment variable.
* The `main.db` field in the configuration file.
* `sqlite:///<WORKDIR>/main.db`
### Device ID
The device ID is a unique identifier for a Platypush instance on a network and
is used to reliably dispatch messages when multiple instances use a shared
backend.
The order of precedence is:
* `--device-id` command line argument.
* The `PLATYPUSH_DEVICE_ID` environment variable.
* The `device_id` field in the configuration file.
* The hostname of the machine.
### systemd service
If you installed Platypush from a system package manager then you'll also have
a `systemd` service installed for it.
You can start/enable Platypush like any other `systemd` service:
```
# systemctl start platypush
# systemctl enable platypush
```
Or, if you want to run the Platypush service as a generic user:
```bash
❯ systemctl --user start platypush
❯ systemctl --user enable platypush
```
Otherwise, you can create your own `systemd` service copying the [provided
`.service`
file](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/examples/systemd/platypush.service)
to e.g. `~/.config/systemd/user` or `/etc/systemd/system`.
### Redis
Platypush uses Redis as a in-memory queue to deliver messages and as a pub/sub
bus for inter-process communication.
If you installed Platypush through a package manager, then the Redis service
will automatically be installed and started if you launch the Platypush service
as a privileged user.
If you run Platypush in a container then by default it'll start its own Redis
instance through the `--start-redis` command-line option.
You can customize the Redis configuration through the:
1. `--redis-host`, `--redis-port` and `--redis-queue` command-line options.
2. `PLATYPUSH_REDIS_HOST`, `PLATYPUSH_REDIS_PORT` and `PLATYPUSH_REDIS_QUEUE`
environment variables.
3. Through your `config.yaml`:
```yaml
# See https://redis-py.readthedocs.io/en/latest/connections.html#redis.Redis
# for the full list of supported parameters
redis:
host: redis-host
port: 6379
username: redis-user
password: redis-pass
```
If `--start-redis` is set, the application can be configured to start a custom
`redis-server` executable through the:
1. `--redis-bin` command-line option.
2. `PLATYPUSH_REDIS_BIN` environment variable.
Alternative drop-in implementations such as `keydb-server`, `valkey` or
`redict` are also supported.
### nginx
If you want to access your Platypush web panel outside your home network, it may
be a good idea to use an nginx/Apache reverse proxy with a valid SSL certificate
(e.g. managed by certbot). A [sample an nginx
configuration](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/examples/nginx/nginx.sample.conf)
is provided in the repository.
## The Web interface
### Other Web panels
Besides the built-in panels that we've already seen in the other sections,
Several integrations add their own feature-rich panels to the Web view, turning
Platypush into a gateway to all of your services - from Zigbee sensors, to
media players and services, to your music cloud, and more.
For example, the music view is available to most of the `music` plugins.
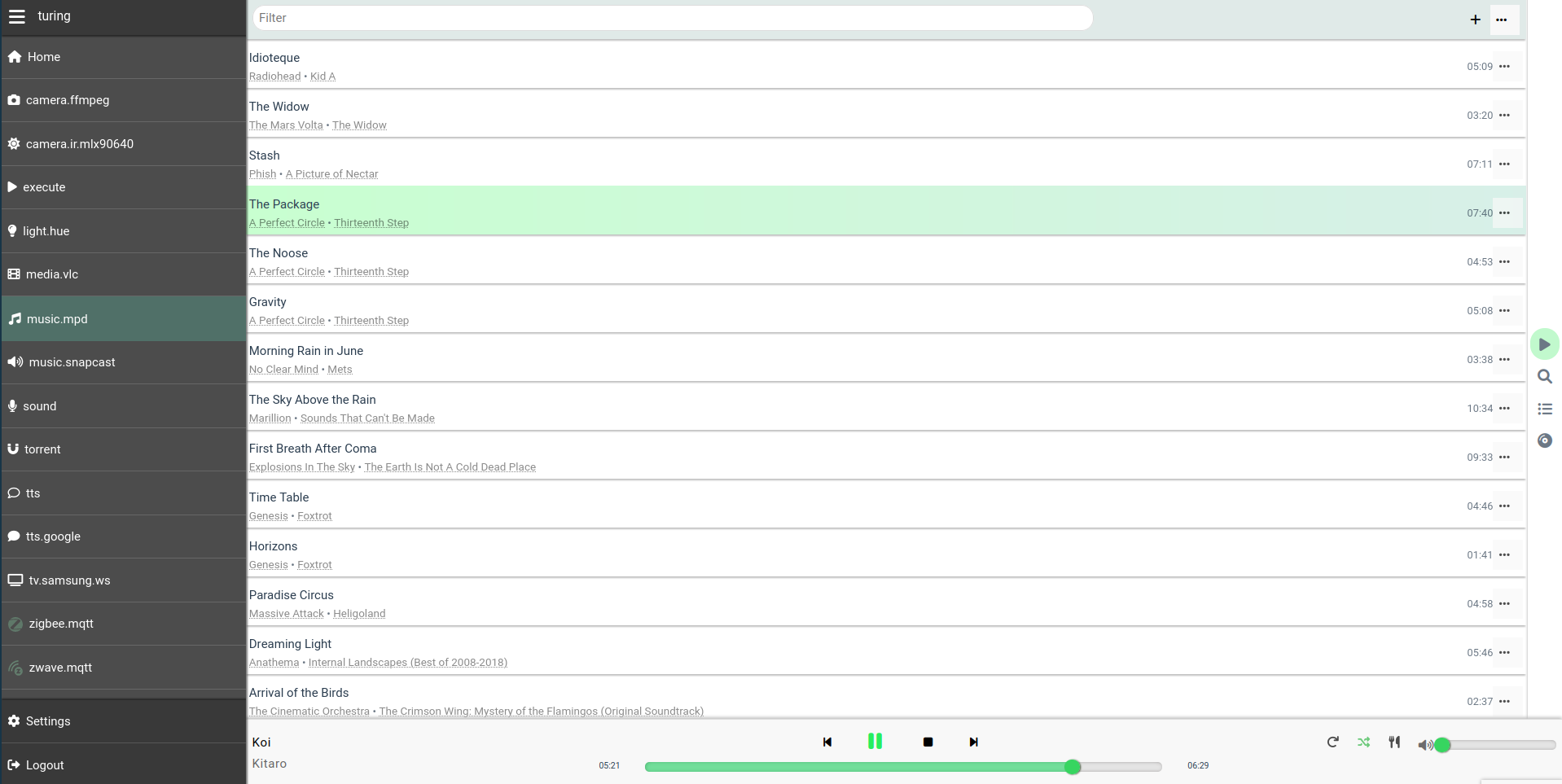
Another example is the camera panel, to monitor your cameras, get stand-alone
feed URLs, and take photos. This becomes available in the UI if you enable at
least a `camera` plugin.
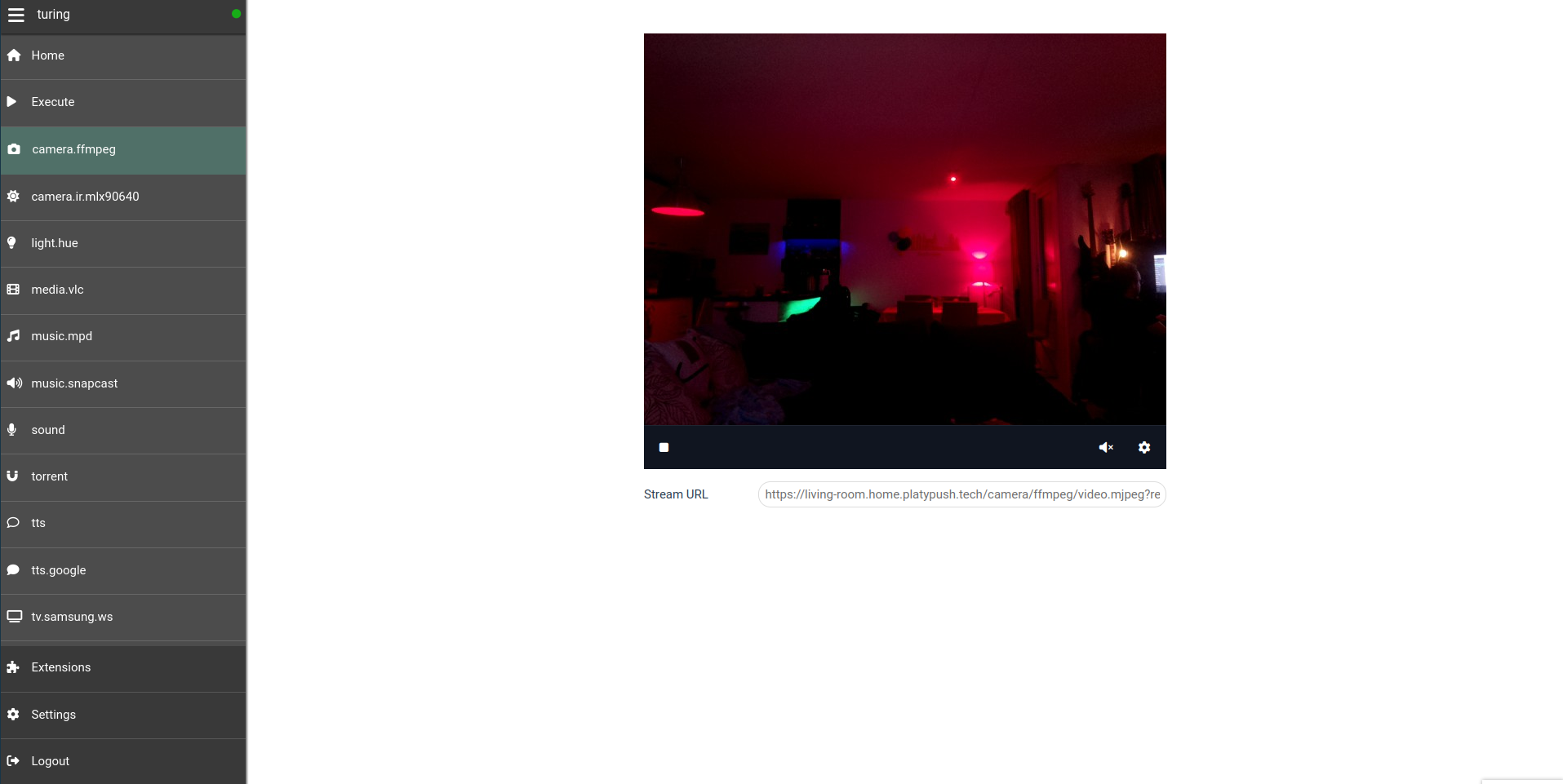
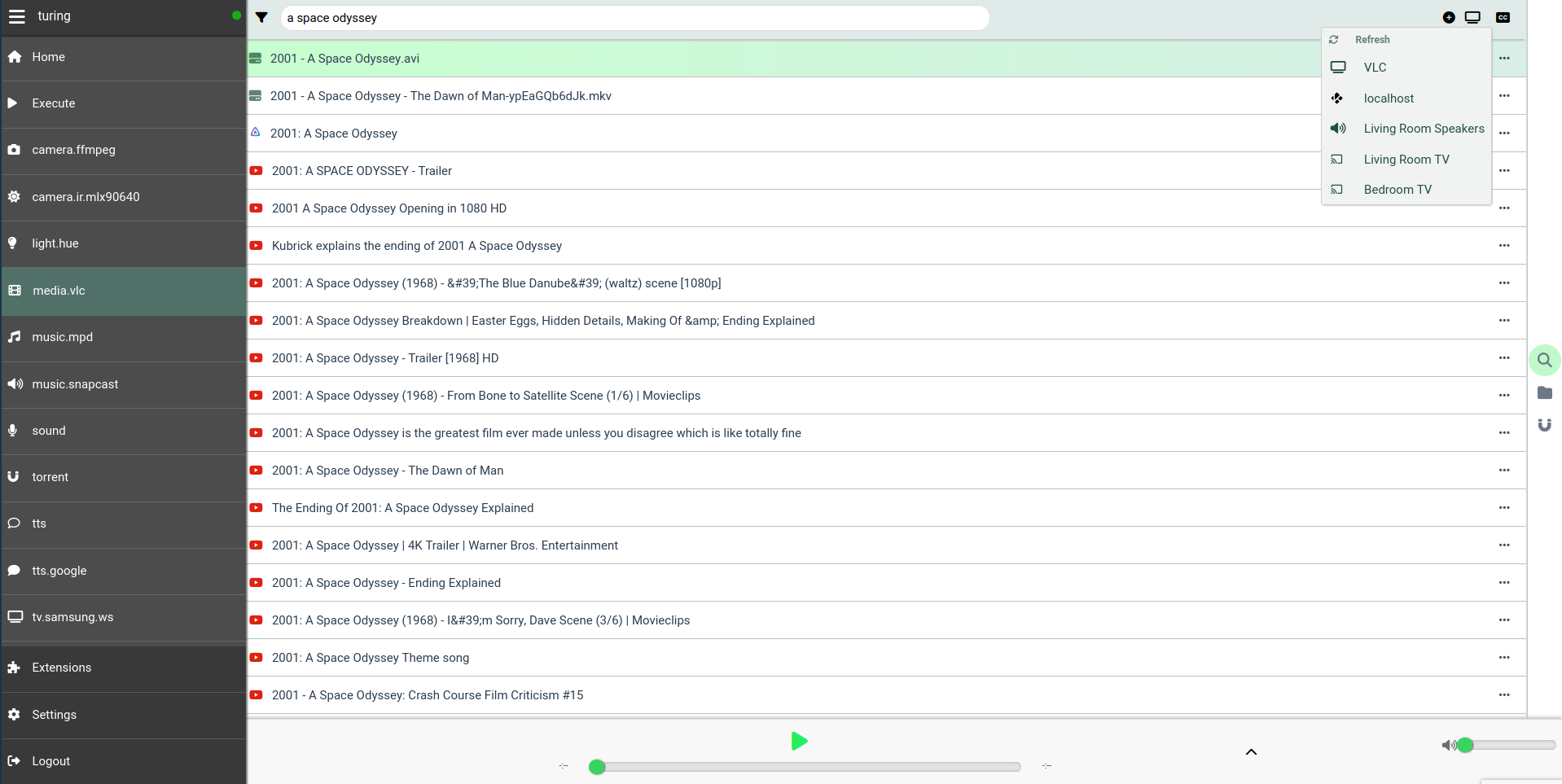
If you enabled at least one local `media` plugin (like `media.vlc`,
`media.mplayer` etc.) then you'll also unlock the media UI, which allows you to
index, search, view and cast media files under the configured `media_dirs`, and
it also integrates with other configured/supported backends such as YouTube,
Plex and Jellyfin.
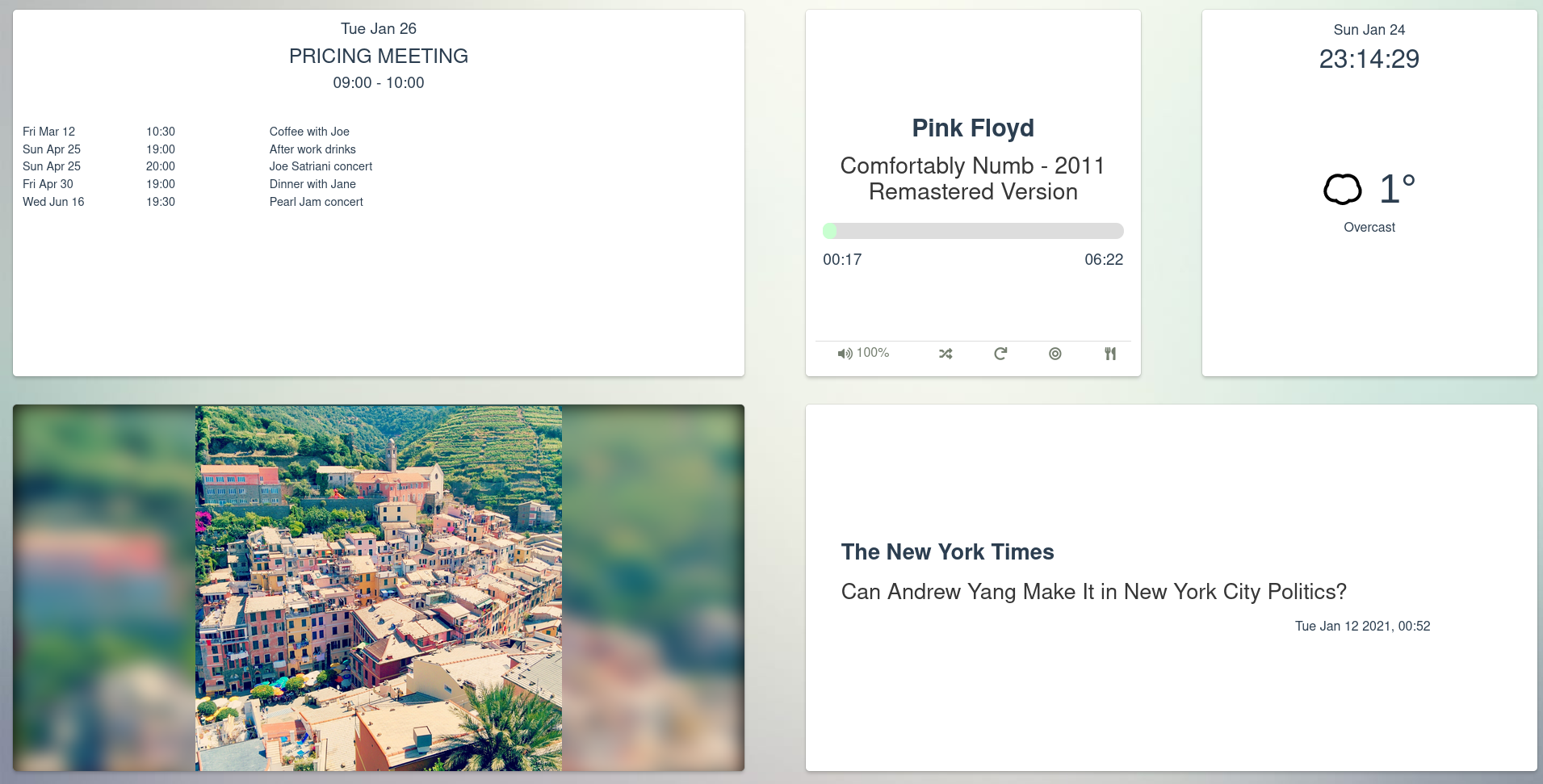
### Dashboards
The web service also provides means for the user to create [custom
dashboards](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/examples/conf/dashboard.xml)
that can be used to show information from multiple sources on a large screen.
### PWA support
Note that having the web application served over SSL is a requirement for the
PWA (progressive web app) to work. The Platypush PWA allows you to install a
Platypush native-like client on your mobile devices if you don't want to use the
full Android app.
## Two-factor authentication
Support for 2FA over OTP codes requires to enable the
[`otp`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/otp.html) and
[`qrcode`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/qrcode.html) plugins.
After installing the dependencies, you can enable it by navigating to
_Settings_ -> _Users_ from the Web panel. Then select your user, choose _Set up
2FA_ and proceed with the steps on screen to set up your authenticator.
## Mobile app
An [official Android
app](https://f-droid.org/en/packages/tech.platypush.platypush/) is provided on
the F-Droid store. It allows to easily discover and manage multiple Platypush
services on a network through the web interface, and it easily brings the power
of Platypush to your fingertips.
## Browser extension
A [browser extension](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush-webext) is
available for [Chrome](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush-webext)
and [Firefox](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/platypush/).
The browser extension allows you to run Platypush actions and procedures
directly from your browser, associate keybindings with them, so you can run
your favourite routines with a few keystrokes anywhere in your browser, and
provides an advanced API to interact with the Web pages you visit - for
example, you can build an action that gets the content of a page you're
visiting and uses Platypush to distill it in readable format, or send the URL
to another service.
## Tests
To run the tests simply run `pytest` either from the project root folder or the
`tests/` folder.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "platypush",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.6",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "home-automation, automation, iot, mqtt, websockets, redis, dashboard, notifications",
"author": null,
"author_email": "Fabio Manganiello <fabio@manganiello.tech>",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/77/a9/6a28f9bfc6990046159ae12a64f6f5023dce507c3314cc46e0b082f0628c/platypush-1.3.5.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "\n\n[](https://ci-cd.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush)\n[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/issues)\n[](https://github.com/blacklight/platypush)\n[](https://github.com/blacklight/platypush)\n[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/commits/branch/master)\n[](https://lemmy.platypush.tech/c/platypush)\n[](https://matrix.to/#/#platypush:matrix.platypush.tech)\n\n[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/platypush/)\n[](https://www.codefactor.io/repository/github/blacklight/platypush)\n[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/CONTRIBUTING.md)\n[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/LICENSE.txt)\n[](https://github.com/sponsors/blacklight)\n[](https://blog.platypush.tech)\n[](https://docs.platypush.tech)\n[](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/wiki)\n[](irc://platypush@irc.platypush.tech:6697)\n[](https://paypal.me/fabiomanganiello)\n\n<!-- toc -->\n\n- [Introduction](#introduction)\n * [What it can do](#what-it-can-do)\n- [Core concepts](#core-concepts)\n- [A few examples](#a-few-examples)\n * [Turn on the lights when I say so](#turn-on-the-lights-when-i-say-so)\n * [Play the music when I say so](#play-the-music-when-i-say-so)\n * [Turn on the lights when the sun goes down](#turn-on-the-lights-when-the-sun-goes-down)\n * [Event matching and token extraction through hook templates](#event-matching-and-token-extraction-through-hook-templates)\n * [Complex hook conditions](#complex-hook-conditions)\n * [Turn off the lights at 1 AM](#turn-off-the-lights-at-1-am)\n * [Greet me with lights and music when I come home](#greet-me-with-lights-and-music-when-i-come-home)\n- [Core Installation](#core-installation)\n * [System package manager installation](#system-package-manager-installation)\n + [Arch Linux](#arch-linux)\n + [Debian/Ubuntu](#debianubuntu)\n + [Fedora](#fedora)\n * [`pip`](#pip)\n * [Docker](#docker)\n + [Base image installation](#base-image-installation)\n + [The docker-compose way](#the-docker-compose-way)\n + [Exposing host devices](#exposing-host-devices)\n * [Manual installation](#manual-installation)\n- [Plugins installation](#plugins-installation)\n * [`pip`](#pip-1)\n * [Web interface](#web-interface)\n * [Docker (`platydock`)](#docker-platydock)\n * [Virtual environment (`platyvenv`)](#virtual-environment-platyvenv)\n * [Manual installation](#manual-installation-1)\n- [HTTP API](#http-api)\n * [The _Execute_ tab](#the-_execute_-tab)\n- [Websocket API](#websocket-api)\n * [Events](#events)\n * [Actions](#actions)\n- [Web hooks](#web-hooks)\n- [Entities](#entities)\n- [Configuration](#configuration)\n * [Configuration file](#configuration-file)\n + [Scripts directory](#scripts-directory)\n + [Splitting configuration on multiple files](#splitting-configuration-on-multiple-files)\n * [Working directory](#working-directory)\n * [Database](#database)\n * [Device ID](#device-id)\n * [systemd service](#systemd-service)\n * [Redis](#redis)\n * [nginx](#nginx)\n- [The Web interface](#the-web-interface)\n * [Other Web panels](#other-web-panels)\n * [Dashboards](#dashboards)\n * [PWA support](#pwa-support)\n- [Two-factor authentication](#two-factor-authentication)\n- [Mobile app](#mobile-app)\n- [Browser extension](#browser-extension)\n- [Tests](#tests)\n\n<!-- tocstop -->\n\n## Introduction\n\nPlatypush is a general-purpose and extensible platform for automation across\nmultiple services and devices with [hundreds of supported\nintegrations](https://docs.platypush.tech/plugins.html).\n\nIt enables users to create their own self-hosted pieces of automation based on\nevents (*if this happens then do that*)\nand it provides a comprehensive and customizable user interface that collects\neverything you need to visualize and control under one roof.\n\nIt borrows concepts from [IFTTT](https://ifttt.com),\n[Tasker](https://tasker.joaoapps.com/) and [Home\nAssistant](https://www.home-assistant.io/) to provide an environment where the\nuser can easily connect things together. It focuses on an automation-as-code\nand API-first approach, offering power users great flexibility in customizing\ntheir routines.\n\nIt's built with compatibility and flexibility in mind, and it can easily run on\nany device that can run a Python interpreter - from a Raspberry Pi, to an old\nsmartphone, to a beefy server.\n\n### What it can do\n\nYou can use Platypush to do things like:\n\n- [Control your smart\n lights](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Ultimate-self-hosted-automation-with-Platypush)\n- [Control your music across multiple\n devices](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Build-your-open-source-multi-room-and-multi-provider-sound-server-with-Platypush-Mopidy-and-Snapcast)\n- [Create custom and privacy-secure voice assistants that run custom hooks on\n your\n phrases](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Build-custom-voice-assistants)\n- Build integrations between sensors,\n [cameras](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/camera.pi.html),\n [microphones](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/sound.html)\n and [machine learning\n models](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/tensorflow.html)\n to create smart pieces of automation for e.g. [people\n detection](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Detect-people-with-a-RaspberryPi-a-thermal-camera-Platypush-and-a-pinch-of-machine-learning)\n or [sound\n detection](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Create-your-smart-baby-monitor-with-Platypush-and-Tensorflow)\n- [Display events from your calendars and build automation on\n them](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/calendar.html)\n- [Build automation routines and visualizations from your sensors\n data](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/How-to-build-your-personal-infrastructure-for-data-collection-and-visualization)\n- [Control and automate a self-built\n robot](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/gpio.zeroborg.html)\n- [Deliver automated newsletters from custom RSS\n digests](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Deliver-customized-newsletters-from-RSS-feeds-with-Platypush)\n- [Synchronize the clipboards on your\n devices](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/clipboard.html)\n- [Implement custom text-to-speech\n logic](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/tts.html)\n- [Build any kind of automation routines with your Android device using\n Tasker](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/How-to-build-your-personal-infrastructure-for-data-collection-and-visualization)\n- Play local\n videos,\n YouTube videos and torrent media from any device and service, to any device, with support for [Kodi](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.kodi.html), [Chromecast](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.chromecast.html), [VLC](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.vlc.html), [Jellyfin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.jellyfin.html), [Plex](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.plex.html) and more\n- [Get weather forecast events for your location and build automation routines on them](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/weather.darksky.html)\n- [Create a custom single hub for Zigbee and Z-Wave smart devices](https://blog.platypush.tech/article/Transform-a-RaspberryPi-into-a-universal-Zigbee-and-Z-Wave-bridge)\n- Build your own web dashboard with calendar, weather, news and music controls\n (basically, anything that has a Platypush web widget)\n- ...and much more (basically, anything that comes with a [Platypush plugin](https://docs.platypush.tech)).\n\nThe full list of available integrations is available at\n[docs.platypush.tech](https://docs.platypush.tech), which also contains a more\nin-depth wiki on the features supported by the platform.\n\nThe wiki is also mirrored on\n[git.platypush.tech](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/wiki).\n\n[The blog](https://blog.platypush.tech) regularly publishes content with\nstep-by-step tutorials and recipes.\n\n## Core concepts\n\nThe foundations of Platypush rest on a few simple building blocks that offer\ngreat versatility to build arbitrarily complex automation routines:\n\n- \ud83e\udde9 **Plugins**. Plugins are the bread-and-butter of the platform. Each plugin\n exposes an API to interact with an integration - there are plugins for media\n players and devices, calendars, sensors, voice assistants, smart devices,\n cloud services, and so on.\n\n - \u23fb **Actions**. These are the methods of a plugin transparently exposed to the\n user over a simple JSON RPC API, and they are always expressed in the\n format `<plugin_name>.<action_name>`. For instance,\n [`light.hue.on`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/light.hue.html#platypush.plugins.light.hue.LightHuePlugin.on)\n can be used to turn on Philips Hue-compatible lights,\n [`media.vlc.play`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/media.vlc.html#platypush.plugins.media.vlc.MediaVlcPlugin.play)\n to play some media on a VLC player, etc.\n\n - \u2699\ufe0f **Backends**. These are special integrations whose main purpose is to\n deliver messages to the main application. The principal one is the\n [`http` backend](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/http.html),\n which exposes the HTTP and WebSocket APIs, serves the main UI and is used\n by several integrations to provide additional services. A [`nodered`\n backend](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/nodered.html) is\n also available to expose a Platypush action component to a Node-RED\n instance, as well as an internal [`redis`\n backend](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/redis.html) and an\n (insecure) [`tcp`\n backend](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/tcp.html) to receive\n raw messages.\n\n- \ud83d\udce7 **Events**. Plugins emit _events_ whenever some particular conditions happen\n for example, a [new media track is\n played](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/media.html#platypush.message.event.media.MediaPlayEvent),\n a [voice assistant conversation has\n started](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/assistant.html#platypush.message.event.assistant.ConversationStartEvent),\n and so on.\n\n - \ud83e\ude9d **Hooks**. Users can define custom callbacks on events in the form of\n *hooks*. Hooks can contain lists of actions to execute when a certain event\n matches the hook *condition*, or any kind of custom logic - for example,\n *send a notification on my phone when the presence sensor in my garage goes\n on*, or *use a TTS plugin to process the digest of the latest RSS feeds if\n I tell the voice assistant \"play the news\"*. Event hooks can be expressed\n either in YAML format or as Python runtime scripts.\n\n- \ud83d\udcdc **Procedures**. Procedures are custom snippets of logic that can be invoked\n using the Platypush API. For example, you can define an `at_home` procedure\n that will be executed when you arrive home, which turns on the lights, plays\n the music, sets the thermostat temperature etc., and then call it using the\n Platypush API from any device. Like event hooks, procedures can be defined\n both in YAML format (good if you just want to execute lists of actions\n without much added logic), or as Python scripts.\n\n - \ud83d\udd57 **Cronjobs**. Cronjobs are special procedures that can be executed either\n at regular intervals (the [UNIX cron\n syntax](https://linuxhandbook.com/crontab/) is supported), or at a specific\n time (one-shot). Just like procedures, they can be defined either in YAML or\n as Python scripts.\n\n- \ud83d\udca1 **Entities**. Some plugins expose generic _entities_ - such a lights,\n sensors, media players, switches, voice assistants etc. These entities can be\n controlled through [the same generic\n APIs](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/entities.html), emit [the\n same types of\n events](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/entities.html), can\n be controlled from the same Web view or dashboard, and their state is\n persisted across runs.\n\n## A few examples\n\nThe bulk of the configuration of Platypush lives under the `config.yaml` file.\nAn extensive [`config.yaml`\nexample](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/platypush/config/config.yaml)\nis provided in the repo. All the sections are optional - the only one enabled by\ndefault is the HTTP server, `backend.http`, but that is optional too.\n\nLet's take an example where we want to control the following entities:\n\n- A Philips Hue bridge and its connected smart lights.\n\n- An on-device voice assistant (we'll consider the Google Assistant in this\n example as it's the easiest to configure, although Google deprecated the\n Assistant libraries long ago).\n\n- A compatible music player - we'll consider MPD/Mopidy in this example as they\n are the ones best supported in Platypush, and Mopidy also offers plugins with\n basically any audio backend out there.\n\nWe'll need the following plugins enabled in the `config.yaml`:\n\n- [`light.hue`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/light.hue.html)\n- [`assistant.google`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/assistant.google.html)\n- [`music.mopidy`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/music.mopidy.html)\n or\n [`music.mpd`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/music.mpd.html)\n (they expose the same API)\n\nThe documentation pages of these plugins already provide some comprehensive\nconfiguration snippets that you can use.\n\nThe most basic configuration would be something like this:\n\n```yaml\n# Enable it if you want the enable the HTTP API and the Web interface\nbackend.http:\n\nlight.hue:\n # IP/hostname of the Hue bridge\n bridge: 192.168.1.10\n # Default groups that should be targeted by actions if none is specified\n # (default: all lights/groups)\n groups:\n - Living Room\n\n# Check the plugin documentation on how to get the credentials\nassistant.google:\n\nmusic.mopidy: # Or music.mpd\n # IP/hostname of the MPD/Mopidy server\n host: 192.168.1.2\n```\n\nNow that we have our integrations configured, let's build some automation routines.\n\n### Turn on the lights when I say so\n\nIn this case we will have to create a hook that listens to a\n[`SpeechRecognizedEvent`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/assistant.html#platypush.message.event.assistant.SpeechRecognizedEvent)\ntriggered by the assistant - for example, when we say \"_OK, Google_\" followed\nby \"_turn on the lights_\".\n\nWe can declare the hook in YAML format directly in the `config.yaml`, or in one\nof the files included in it through the `include:` directive:\n\n```yaml\nevent.hook.turn_lights_on_voice_command:\n if:\n type: platypush.message.event.assistant.SpeechRecognizedEvent\n # Note that a minimal regex-like syntax is supported here.\n # This condition matches both a phrase that contains\n # \"turn on the lights\" and one that contains \"turn on lights\"\n phrase: \"turn on (the)? lights\"\n then:\n - action: light.hue.on\n args:\n groups:\n - Living Room\n```\n\nOr we can declare the hook in a Python script - you just have to create a `.py`\nfile (e.g. `lights.py`) under a `scripts` directory located under the same\nfolder as your `config.yaml`:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import run, when\nfrom platypush.events.assistant import SpeechRecognizedEvent\n\n@when(SpeechRecognizedEvent, phrase=\"turn on (the)? lights\")\ndef lights_on_voice_command(): # Also accepts an optional `event` argument\n run('light.hue.on', groups=['Living Room'])\n```\n\nOr, using the `get_plugin` API:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import get_plugin, when\nfrom platypush.events.assistant import SpeechRecognizedEvent\n\n@when(SpeechRecognizedEvent, phrase=\"turn on (the)? lights\")\ndef lights_on_voice_command():\n get_plugin('light.hue').on(groups=['Living Room'])\n```\n\n### Play the music when I say so\n\nThe approach is similar for a \"_play the music_\" voice command. YAML:\n\n```yaml\nevent.hook.play_music_voice_command:\n if:\n type: platypush.message.event.assistant.SpeechRecognizedEvent\n phrase: \"play (the)? music\"\n then:\n - action: music.mopidy.play\n```\n\nPython:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import run, when\nfrom platypush.events.assistant import SpeechRecognizedEvent\n\n@when(SpeechRecognizedEvent, phrase=\"play (the)? music\")\ndef lights_on_voice_command():\n run('music.mopidy.play')\n```\n\n### Turn on the lights when the sun goes down\n\nThis example requires the [`sun`\nplugin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/sun.html) configured:\n\n```yaml\nsun:\n latitude: LAT\n longitude: LONG\n```\n\nYou can then simply subscribe to\n[`SunsetEvent`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/sun.html#platypush.message.event.sun.SunsetEvent).\nYAML:\n\n```yaml\nevent.hook.sunset_lights_on:\n if:\n type: platypush.message.event.sun.SunsetEvent\n then:\n - action: light.hue.on\n```\n\nPython:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import run, when\nfrom platypush.events.sun import SunsetEvent\n\n@when(SunsetEvent)\ndef sunset_lights_on():\n run('light.hue.on')\n```\n\n### Event matching and token extraction through hook templates\n\nYou can also operate token extraction from event arguments if the values are\nstrings.\n\nFor example, you can use advanced pattern matching and token extraction to\ncreate voice assistant hooks that will match a template with parametrized field\nwhich will be passed as arguments to your event hook:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import run, when\nfrom platypush.events.assistant import SpeechRecognizedEvent\n\n@when(SpeechRecognizedEvent, phrase='play ${title} by ${artist}')\ndef on_music_play_command(event, title, artist):\n results = run(\n 'music.mpd.search',\n filter={\n 'artist': artist,\n 'title': title,\n }\n )\n\n if results:\n run('music.mpd.play', results[0]['file'])\n```\n\n### Complex hook conditions\n\nYour event hooks can include more complex filters too. Structured filters\nagainst partial event arguments are also possible, and relational operators are\nsupported as well. For example:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import when\nfrom platypush.events.sensor import SensorDataChangeEvent\n\n@when(SensorDataChangeEvent, data=1):\ndef hook_1(event):\n \"\"\"\n Triggered when event.data == 1\n \"\"\"\n\n@when(SensorDataChangeEvent, data={'state': 1}):\ndef hook_2(event):\n \"\"\"\n Triggered when event.data['state'] == 1\n \"\"\"\n\n@when(SensorDataChangeEvent, data={\n 'temperature': {'$gt': 25},\n 'humidity': {'$le': 15}\n}):\ndef hook_3(event):\n \"\"\"\n Triggered when event.data['temperature'] > 25 and\n event.data['humidity'] <= 15.\n \"\"\"\n```\n\nThe supported relational fields are the same supported by ElasticSearch - `$gt`\nfor greater than, `$lt` for lesser than, `$ge` for greater or equal, `$ne` for\nnot equal, etc.\n\n### Turn off the lights at 1 AM\n\nWe can use a `cron` for this case. YAML:\n\n```yaml\ncron.lights_off_night:\n # Run this every day at 1 AM\n cron_expression: '0 1 * * *'\n actions:\n - action: light.hue.off\n```\n\nPython:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import cron, run\n\n@cron('0 1 * * *')\ndef lights_off_night():\n run('light.hue.off')\n```\n\n### Greet me with lights and music when I come home\n\nLet's create an `at_home` procedure for this purpose. We can also use a\ntext-to-speech plugin like the [`tts`\nplugin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/tts.html) (it requires no\nconfiguration as it relies on the Google Translate frontend API, but other,\nmore sophisticated plugins are also available) to have a warm voice to welcome\nus home. YAML:\n\n```yaml\n# Make sure that the sound plugin is also enabled, for audio processing\nsound:\n\nprocedure.at_home:\n - action: tts.say\n args:\n text: \"Welcome home!\"\n\n # Get luminosity data from a sensor - e.g. LTR559\n - action: gpio.sensor.ltr559.get_data\n\n # If it's lower than a certain threshold, turn on the lights.\n # Note that we can directly access attributes returned by the\n # previous request(s) as local context variables within the\n # procedure/hook/cron. In this case, `light` is an attribute returned\n # on the response of the previous command.\n\n # Otherwise, you can also use the special `output` variable to get only\n # the response of the latest action, e.g. `output['light']`\n\n # Also note the use of the special `if ${}` construct. It accepts\n # a snippet of Python code and it can access variables within the\n # current context.\n - if ${light is not None and light < 110}:\n - action: light.hue.on\n\n - action: music.mopidy.play\n args:\n resource: \"uri:to:my:favourite:playlist\"\n```\n\nPython:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import procedure, run\n\n@procedure(\"at_home\")\ndef at_home_proc():\n run('tts.say', text='Welcome home!')\n\n luminosity = run('gpio.sensor.ltr559.get_data').get('light', 0)\n if luminosity < 110:\n run('light.hue.on')\n\n run('music.mopidy.play', resource='uri:to:my:favourite:playlist')\n```\n\nYou can then call the procedure from a hook or another script:\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import run\n\nrun('procedure.at_home')\n```\n\nOr, from YAML:\n\n```yaml\nprocedure.some_other_procedure:\n - action: procedure.at_home\n```\n\nOr using the [available APIs](#http-api).\n\n## Core Installation\n\n### System package manager installation\n\n#### Arch Linux\n\nYou can either install the\n[`platypush`](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/platypush) package (for the\nlatest stable version) or the\n[`platypush-git`](https://aur.archlinux.org/packages/platypush-git) package\n(for the latest git version) through your favourite AUR package manager. For\nexample, using `yay`:\n\n```bash\n$ yay platypush\n# Or\n$ yay platypush-git\n```\n\nThe Arch Linux packages on AUR are automatically updated upon new git commits\nor tags.\n\n#### Debian/Ubuntu\n\n1. Add the Platypush APT key to your trusted keyring:\n\n ```\n # wget -q -O \\\n /etc/apt/trusted.gpg.d/platypush.asc \\\n https://apt.platypush.tech/pubkey.txt\n ```\n\n2. Add the Platypush repository to your APT sources:\n\n ```\n # wget -q -O \\\n /etc/apt/sources.list.d/platypush.list \\\n https://apt.platypush.tech/lists/platypush-<deb_version>-<branch>.list\n ```\n\n Where:\n\n - `deb_version` can be either:\n\n - `stable`: current Debian stable\n - `oldstable`: previous Debian stable\n - `ubuntu`: latest Ubuntu release\n\n - `branch` can be either:\n\n - `main`: latest stable release\n - `dev`: a package always in sync with the latest git version\n\n For example, to install the latest stable tags on Debian stable:\n\n ```\n # wget -q -O \\\n /etc/apt/sources.list.d/platypush.list \\\n https://apt.platypush.tech/lists/platypush-stable-main.list\n ```\n\n3. Update your repos and install Platypush:\n\n ```\n # apt update\n # apt install platypush\n ```\n\n#### Fedora\n\nRPM builds targeting the latest Fedora release are automatically built on every\npush pipeline.\n\nTo install Platypush via RPM on Fedora:\n\n- Add the Platypush RPM repository configuration to the package manager:\n\n```\n# yum config-manager --add-repo https://rpm.platypush.tech/platypush.repo\n```\n\n- Install Platypush, either the latest stable release or the rolling release\n updated on every commit to the main branch:\n\n```\n# yum install platypush\n# Or\n# yum install platypush-git\n```\n\n### `pip`\n\n```bash\n$ pip install platypush\n```\n\nOr, for the latest git version:\n\n```bash\n# Official repo\n$ pip install git+https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush\n# Github mirror\n$ pip install git+https://github.com/blacklight/platypush\n```\n\n### Docker\n\n#### Base image installation\n\n```bash\n$ docker run -it --name platypush \\\n -p 8008:8008 \\\n -e \"PLATYPUSH_DEVICE_ID=my-device\" \\\n -v /path/to/your/platypush/config:/etc/platypush \\\n -v /path/to/your/platypush/share:/var/lib/platypush \\\n quay.io/platypush/platypush\n```\n\nThe following architectures are currently supported:\n\n- `amd64`/`x86_64` (standard Intel-based architectures)\n- `arm64`/`aarch64` (ARM64, such as modern ARM-based MacBooks, most of the\n Android devices or RaspberryPi 4 and 5)\n- `armv7l` (older ARM-based devices, such as RaspberryPi 2 and 3 or older\n Android devices)\n\nThe Web service will be available on `http://localhost:8008`, and a default\nconfiguration file will be initialized under\n`/path/to/your/platypush/config/config.yaml` if not available. The next\nexecutions of the service can be triggered via `docker start platypush`.\n\nNote that this will install an Alpine-based image. For other base images (e.g.\nDebian, Ubuntu or Fedora) please consult the [custom docker-compose\nway](#the-docker-compose-way).\n\nAlso note that any extra plugin dependencies installed in the container will be\nlost if the container is removed.\n\nIn order to preserve the state of the container after installing and configuring\nyour plugins, you can leverage the `docker commit` command:\n\n```bash\n\u276f docker ps\nCONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES\nf00546d3bd35 quay.io/platypush/platypush \"/bin/sh -c 'platypu\u2026\" 38 minutes ago Up 8 minutes 0.0.0.0:8008->8008/tcp, :::8008->8008/tcp platypush\n\u276f docker commit f00546d3bd35 my-custom-platypush-image\nsha256:13d4a4cae4e7eedee924a8a79deae9a9978aa70b46699c1f2abfd16bf5ed910b\n# You can now use the my-custom-platypush-image even if the container is destroyed\n```\n\nAlternatively, you can use [the `platydock` command](#docker-(platydock)) to\ndirectly create a Docker image or a `Dockerfile` from a configuration, with all\nthe required plugins and dependencies pre-installed.\n\n#### The docker-compose way\n\n```bash\n$ git clone https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush.git\n$ cd platypush\n# Copy .env.example to .env and edit docker-compose.yml if required.\n# In particular, you may want /etc/platypush and /var/lib/platypush\n# to point to directories on your hosts\n$ docker compose up\n```\n\nNote that the default `Dockerfile` uses Alpine, but in `docker-compose.yml` you\ncan also specify an alternative `Dockerfile` - Debian, Ubuntu and Fedora are\nsupported.\n\n#### Exposing host devices\n\nNote that some plugins may require access to the host hardware - such as USB\ndevices, Bluetooth adapters etc.\n\nIn order to make these devices visible to the Docker container you may need to\nexplicitly mount them as volumes.\n\nFor example, the [`serial`\nplugin](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/serial.html) may need to\naccess an Arduino/ESP device over USB. You can export only that device to the\nDocker container:\n\n```bash\n$ docker run --device=/dev/ttyUSB0 ...\n# Or, if you set up static naming via udev rules\n$ docker run --device=/dev/arduino ...\n```\n\nOr, through `docker-compose.yml`:\n\n```yaml\nservices:\n platypush:\n # ...\n devices:\n - /dev/ttyUSB0\n```\n\nOtherwise, for privileged access to the USB bus on a Linux host:\n\n```bash\n$ docker run --priviliged -v /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb ...\n```\n\nOr, through `docker-compose.yml`:\n\n```yaml\nservices:\n platypush:\n # ...\n volumes:\n - /dev/bus/usb:/dev/bus/usb\n```\n\n### Manual installation\n\n```shell\n$ git clone https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush.git\n$ cd platypush\n$ pip install .\n```\n\n## Plugins installation\n\nAll the plugins included in the main repo will be available once you have\ninstalled the core platform.\n\nHowever, some plugins may require extra (optional) dependencies. You have\nseveral ways of installing those dependencies:\n\n### `pip`\n\nYou can install extra dependencies via pip extras:\n\n```shell\npip install 'platypush[plugin1,plugin2,...]'\n```\n\nFor example:\n\n```shell\npip install 'platypush[light.hue,music.mpd,rss]'\n```\n\nWill install Platypush with the dependencies for the `light.hue`, `music.mpd`\nand `rss` plugins.\n\n### Web interface\n\nPlugins can be installed from the Web interface too. Navigate to the\n_Extensions_ entry in the sidebar, select the extension that you want to install,\nselect the _Install_ tab and click _Install_.\n\n\n\nThis section also includes the _Configuration_ tab, with a ready-to-paste\nconfiguration snippet template for that plugin, as well as a documentation page\nthat includes all the actions supported by a given plugin and the events it\ntriggers.\n\n### Docker (`platydock`)\n\nIf you already have the base installation of Platypush on your machine, and you\nhave a configuration file with a custom set of integrations, then you may opt\nto generate a custom Docker image from your configuration file, with all the\nextra dependencies configured, using the `platydock` command.\n\nThe following command:\n\n```shell\n\u276f platydock -c /path/to/your/config.yaml -d platypush-test\n```\n\nWill create a Platypush Docker image for a device with ID `platypush-test`,\nwith all the requirements for the additional integrations listed in\n`config.yaml`.\n\nYou can pass the `--print` option if you just want to print the content of the\noutput `Dockerfile` instead of generating the image.\n\nBy default the image will use Alpine Linux as a base. You can use the\n`-i`/`--image` to specify another supported base image - `ubuntu`, `debian` or\n`fedora`.\n\n### Virtual environment (`platyvenv`)\n\nIf you already have the base installation of Platypush on your machine, and you\nhave a configuration file with a custom set of integrations, then you may opt\nto generate a custom virtual environment from your configuration file, with all\nthe extra dependencies configured, using the `platyvenv` command.\n\nThe following command:\n\n```bash\n\u276f platyvenv -c /path/to/your/config.yaml -o /path/to/your/venv\n```\n\nWill create a new virtual environment under `/path/to/your/venv` using the\nspecified `config.yaml` to determine which optional dependencies should be installed.\n\nYou can then run Platypush after activating your new environment:\n\n```bash\n\u276f source /path/to/your/venv/bin/activate\n\u276f platypush -c /path/to/your/config.yaml\n```\n\n### Manual installation\n\nThe [plugin/backend documentation](https://docs.platypush.tech) reports all the\ndependencies required by each plugin, as well as the commands to install them\non multiple platforms.\n\nIf you want to customize your installation, or if you need to install\ndependencies for a plugin that requires some manual steps, you can check out\nany plugin-specific installation steps from its documentation.\n\n## HTTP API\n\nActions and procedures can also be called using the JSON-RPC API exposed by\nPlatypush.\n\nYour configuration requires the [`backend.http`\nsection](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/backend/http.html) enabled if\nyou want to use the HTTP API - default listen port: `8008`.\n\nAfter ensuring that the HTTP backend is enabled, head to\n`http://localhost:8008` and register a new user.\n\n\n\nFrom the Web UI, head to _Settings_ \u2192 _Tokens_, insert your password again and\nclick _Generate JWT token_.\n\n\n\nAlternatively, you can retrieve a token via HTTP request:\n\n```shell\n\u276f curl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d '\n{\n \"username\": \"$YOUR_USER\",\n \"password\": \"$YOUR_PASSWORD\"\n}' http://localhost:8008/auth\n```\n\nYou can then send requests to Platypush using a simple RPC API:\n\n```bash\n\u276f curl -XPOST \\\n -d '{\"type\":\"request\", \"action\":\"procedure.at_home\"}' \\\n -H \"Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN\" \\\n -H \"Content-Type: application/json\" \\\n http://localhost:8008/execute\n\u276e\n{\n \"id\": \"724754df98968247a284557ce32f74bb\",\n \"type\": \"response\",\n \"target\": \"http\",\n \"origin\": \"myhost\",\n \"_timestamp\": 1716575901.046127,\n \"response\": {\n \"output\": {\n \"success\": true\n },\n \"errors\": []\n }\n}\n```\n\nIf your procedure returned something, then that will be returned on the API\nresponse too, so downstream consumers can use it.\n\nThe `POST /execute` endpoint accepts a payload in the format:\n\n```javascript\n{\n \"type\": \"request\", // Constant\n \"action\": \"<plugin-name>.<action-name>\", // Or procedure.<name>\n \"args\": {\n \"arg1\": \"arg2\",\n // ...\n }\n}\n```\n\nIn our `procedure.at_home` example, you can for instance create an automation\nsnippet paired with your phone that runs the routine whenever you arrive home\n(or your phone does):\n\n1. Install an app like [Tasker](https://tasker.joaoapps.com/) to create\n automation tasks on your Android device.\n\n2. Install a plugin like [AutoLocation](https://joaoapps.com/autolocation/) to\n create automation tasks based on your phone's location.\n\n3. Create a profile that triggers whenever you enter your home location (and/or\n exit it).\n\n\n\n4. Leverage the [HTTP\n Request](https://tasker.joaoapps.com/userguide/en/help/ah_http_request.html)\n Tasker action to send a request to your Platypush API to trigger the routine.\n\n### The _Execute_ tab\n\nThe Web interface also provides an _Execute_ tab under the menu sidebar. You\ncan use this tab to dynamically discover the actions exposed by various plugins\n(and also your own procedures):\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n## Websocket API\n\n### Events\n\nYou can subscribe to events generated by the application over the `/ws/events`\nWebsocket endpoint, and send events to this endpoint too.\n\nThis is useful if you want to synchronize Platypush events with another client,\nor send custom events outside of those native to the application and build\ncustom automation hooks on them.\n\nSending events:\n\n```bash\n\u276f wscat -H \"Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN\" \\\n -c \"ws://localhost:8008/ws/events\" \\\n -w 1 \\\n -x '\n{\n \"type\": \"event\",\n \"args\": {\n \"type\": \"platypush.message.event.custom.CustomEvent\",\n \"subtype\": \"foo\",\n \"args\": {\n \"bar\": \"baz\"\n }\n }\n}'\n```\n\nReceiving events:\n\n```bash\n\u276f wscat -H \"Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN\" -c \"ws://localhost:8008/ws/events\"\n```\n\n### Actions\n\nYou can also send requests to the `/ws/requests` Websocket endpoint, and get\nresponses asynchronously on the same channel:\n\n```bash\n\u276f wscat -H \"Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN\" \\\n -c \"ws://localhost:8008/ws/requests\" \\\n -w 1 \\\n -x '{\"type\": \"requests\", \"action\": \"procedure.foo.bar\"}'\n```\n\n## Web hooks\n\nYou can use Platypush to expose your custom routines as dynamic Web hooks that\ncan be called by any client.\n\nAll you need is to register a listener for a\n[`WebhookEvent`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/http.hook.html#platypush.message.event.http.hook.WebhookEvent)\n\n```python\nfrom platypush import run, when\nfrom platypush.events.http.hook import WebhookEvent\n\nhook_token = \"abcdefabcdef\"\n\n# Expose the hook under the /hook/at_home endpoint\n@when(WebhookEvent, hook=\"at_home\")\ndef at_home_webhook(event: WebhookEvent):\n # Unlike the calls to /execute, custom web hooks are unauthenticated.\n # If you want authentication, you'll need to implement your custom logic by\n # parsing the event headers\n if event.headers.get(\"X-Token\") != hook_token:\n # Tuple with <response, http-code, [response-headers]>\n event.send_response((\"Unauthorized\", 401))\n return\n\n run('procedure.at_home')\n\n # Return anything back to the client\n return {'status': 'ok'}\n```\n\nThen you can invoke your custom logic over HTTP:\n\n```bash\n\u276f curl -H 'X-Token: abcdefabcdef' 'http://localhost:8008/hook/at_home'\n```\n\n## Entities\n\nEntities are another building block of Platypush. Many integrations will store\ntheir state or connected devices in the form of entities - e.g. the sensors\ndetected by the Z-Wave/Zigbee/Bluetooth integration, or the lights connected to\na Hue bridge, or your cloud nodes, or your custom Arduino/ESP machinery, and so\non.\n\nEntities provide a consistent interface to interact with your integrations\nregardless of their type and the plugin that handles them. For instance, all\ntemperature sensors will expose the same interface, regardless if they are\nBluetooth or Zigbee sensors, and all the media plugins will expose the same\ninterface, regardless if they manage Chromecasts, Kodi, Plex, Jellyfin or a\nlocal VLC player.\n\nOnce you enable the HTTP backend and a few integrations that export entities\nand register a user, you can query the detected entities via:\n\n```shell\ncurl -XPOST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \\\n -H \"Authorization: Bearer $YOUR_TOKEN\" \\\n -d '{\"type\":\"request\", \"action\":\"entities.get\"}' \\\n http://localhost:8008/execute\n```\n\nAll the entities expose the same interface and can be manipulated through the\nsame API. Also, when an entity is updated it always emits an\n[`EntityUpdateEvent`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/events/entities.html#platypush.message.event.entities.EntityUpdateEvent),\nso you can easily create hooks that react to these events and act on multiple\ntypes of entities.\n\nIf you enabled the HTTP backend, then you can also access all the entities from\nthe home panel of the Web UI.\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n## Configuration\n\n### Configuration file\n\nYou can use the [default\n`config.yaml`](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/platypush/config/config.yaml)\nas a template/reference.\n\nThe location of the `config.yaml` to be used by the application is determined\nin the following way:\n\n1. It can be passed through the command-line `-c`/`--config` argument.\n2. If not specified via `-c`, it will be read from the `PLATYPUSH_CONFIG`\n environment variable.\n3. If not specified, use `./config.yaml` if available.\n4. If not available, and you are running Platypush within a Docker container,\n or as a privileged user (and usually you shouldn't), or as a systemd service\n created by a supported package manager, then `/etc/platypush/config.yaml`\n will be used if available.\n5. Otherwise, if you are running Platypush as a non-privileged user or in a\n virtual environment, `$XDG_CONFIG_HOME/platypush/config.yaml` will be used\n (defaults to `~/.config/platypush/config.yaml`).\n\n#### Scripts directory\n\nBy default, any custom Python scripts will be searched under\n`<CONFDIR>/scripts`, where `<CONFDIR>` is the path to your `config.yaml`.\n\nYou can override it in your `config.yaml`:\n\n```yaml\nscripts_dir: /path/to/custom/scripts\n```\n\nSince everything under the scripts directory will be imported as a submodule,\nyou can create your own libraries of scripts that can import other scripts:\n\n```python\n# Content of scripts/music.py\n\nfrom platypush import run\n\ndef music_play(plugin='music.mopidy', resource=None):\n run(f'{plugin}.play', resource)\n\n# Content of scripts/lights.py\n\nfrom platypush import run\n\ndef lights_toggle(plugin='light.hue', groups=('Living Room',)):\n run(f'{plugin}.toggle', groups=groups)\n\n# Content of scripts/home.py\n\nfrom platypush import procedure\n\nfrom scripts.music import music_play\nfrom scripts.lights import lights_toggle\n\n@procedure\ndef at_home():\n music_play()\n lights_toggle()\n```\n\n#### Splitting configuration on multiple files\n\nThe `config.yaml` file can become very complex, especially if you embed many\nhooks and procedures in it in YAML format.\n\nTo make the configuration more maintainable, and also to isolate modules that\nyou can reuse across multiple instances, you can leverage the `include`\ndirective:\n\n```yaml\n# All paths are relative to config.yaml, or to the location of the current file\ninclude:\n - assistant.yaml\n - db.yaml\n - media.yaml\n - mqtt.yaml\n - sensors.yaml\n # ...\n```\n\n### Working directory\n\nThis is where the application will store its data and integration plugins will\nstore their data. The order of precedence is:\n\n* `-w`/`--workdir` command line argument.\n* The `PLATYPUSH_WORKDIR` environment variable.\n* The `workdir` field in the configuration file.\n* `$XDG_DATA_HOME/platypush` (default: `~/.local/share/platypush`) if launched\n with a non-privileged user, `/var/lib/platypush` if launched as root or with\n a system user.\n\n### Database\n\nThe application stores entities, variables, users, integrations state and more\non a database. The engine configuration supports the [SQLAlchemy engine\nsyntax](https://docs.sqlalchemy.org/en/20/core/engines.html).\n\n**Note**: The application uses a local SQLite database by default, which is\nnatively supported by SQLAlchemy. The application has also been tested against\nMySQL/MariaDB and Postgres, and should work fine with any modern relational\ndatabase supported by SQLAlchemy. However, any backend other than SQLite may\nrequire an additional Python dependency for the SQLAlchemy driver (for example\n[`pg8000`](https://pypi.org/project/pg8000/) for PostgreSQL).\n\nOrder of precedence for the engine:\n\n* `--main-db`/`--db` command line argument.\n* The `PLATYPUSH_DB` environment variable.\n* The `main.db` field in the configuration file.\n* `sqlite:///<WORKDIR>/main.db`\n\n### Device ID\n\nThe device ID is a unique identifier for a Platypush instance on a network and\nis used to reliably dispatch messages when multiple instances use a shared\nbackend.\n\nThe order of precedence is:\n\n* `--device-id` command line argument.\n* The `PLATYPUSH_DEVICE_ID` environment variable.\n* The `device_id` field in the configuration file.\n* The hostname of the machine.\n\n### systemd service\n\nIf you installed Platypush from a system package manager then you'll also have\na `systemd` service installed for it.\n\nYou can start/enable Platypush like any other `systemd` service:\n\n```\n# systemctl start platypush\n# systemctl enable platypush\n```\n\nOr, if you want to run the Platypush service as a generic user:\n\n```bash\n\u276f systemctl --user start platypush\n\u276f systemctl --user enable platypush\n```\n\nOtherwise, you can create your own `systemd` service copying the [provided\n`.service`\nfile](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/examples/systemd/platypush.service)\nto e.g. `~/.config/systemd/user` or `/etc/systemd/system`.\n\n### Redis\n\nPlatypush uses Redis as a in-memory queue to deliver messages and as a pub/sub\nbus for inter-process communication.\n\nIf you installed Platypush through a package manager, then the Redis service\nwill automatically be installed and started if you launch the Platypush service\nas a privileged user.\n\nIf you run Platypush in a container then by default it'll start its own Redis\ninstance through the `--start-redis` command-line option.\n\nYou can customize the Redis configuration through the:\n\n1. `--redis-host`, `--redis-port` and `--redis-queue` command-line options.\n2. `PLATYPUSH_REDIS_HOST`, `PLATYPUSH_REDIS_PORT` and `PLATYPUSH_REDIS_QUEUE`\n environment variables.\n3. Through your `config.yaml`:\n\n```yaml\n# See https://redis-py.readthedocs.io/en/latest/connections.html#redis.Redis\n# for the full list of supported parameters\nredis:\n host: redis-host\n port: 6379\n username: redis-user\n password: redis-pass\n```\n\nIf `--start-redis` is set, the application can be configured to start a custom\n`redis-server` executable through the:\n\n1. `--redis-bin` command-line option.\n2. `PLATYPUSH_REDIS_BIN` environment variable.\n\nAlternative drop-in implementations such as `keydb-server`, `valkey` or\n`redict` are also supported.\n\n### nginx\n\nIf you want to access your Platypush web panel outside your home network, it may\nbe a good idea to use an nginx/Apache reverse proxy with a valid SSL certificate\n(e.g. managed by certbot). A [sample an nginx\nconfiguration](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/examples/nginx/nginx.sample.conf)\nis provided in the repository.\n\n## The Web interface\n\n### Other Web panels\n\nBesides the built-in panels that we've already seen in the other sections,\nSeveral integrations add their own feature-rich panels to the Web view, turning\nPlatypush into a gateway to all of your services - from Zigbee sensors, to\nmedia players and services, to your music cloud, and more.\n\nFor example, the music view is available to most of the `music` plugins.\n\n\n\n\n\nAnother example is the camera panel, to monitor your cameras, get stand-alone\nfeed URLs, and take photos. This becomes available in the UI if you enable at\nleast a `camera` plugin.\n\n\n\nIf you enabled at least one local `media` plugin (like `media.vlc`,\n`media.mplayer` etc.) then you'll also unlock the media UI, which allows you to\nindex, search, view and cast media files under the configured `media_dirs`, and\nit also integrates with other configured/supported backends such as YouTube,\nPlex and Jellyfin.\n\n\n\n### Dashboards\n\nThe web service also provides means for the user to create [custom\ndashboards](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush/src/branch/master/examples/conf/dashboard.xml)\nthat can be used to show information from multiple sources on a large screen.\n\n\n\n### PWA support\n\nNote that having the web application served over SSL is a requirement for the\nPWA (progressive web app) to work. The Platypush PWA allows you to install a\nPlatypush native-like client on your mobile devices if you don't want to use the\nfull Android app.\n\n## Two-factor authentication\n\nSupport for 2FA over OTP codes requires to enable the\n[`otp`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/otp.html) and\n[`qrcode`](https://docs.platypush.tech/platypush/plugins/qrcode.html) plugins.\n\nAfter installing the dependencies, you can enable it by navigating to\n_Settings_ -> _Users_ from the Web panel. Then select your user, choose _Set up\n2FA_ and proceed with the steps on screen to set up your authenticator.\n\n## Mobile app\n\nAn [official Android\napp](https://f-droid.org/en/packages/tech.platypush.platypush/) is provided on\nthe F-Droid store. It allows to easily discover and manage multiple Platypush\nservices on a network through the web interface, and it easily brings the power\nof Platypush to your fingertips.\n\n## Browser extension\n\nA [browser extension](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush-webext) is\navailable for [Chrome](https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush-webext)\nand [Firefox](https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/platypush/).\n\nThe browser extension allows you to run Platypush actions and procedures\ndirectly from your browser, associate keybindings with them, so you can run\nyour favourite routines with a few keystrokes anywhere in your browser, and\nprovides an advanced API to interact with the Web pages you visit - for\nexample, you can build an action that gets the content of a page you're\nvisiting and uses Platypush to distill it in readable format, or send the URL\nto another service.\n\n## Tests\n\nTo run the tests simply run `pytest` either from the project root folder or the\n`tests/` folder.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "A general-purpose framework for automation",
"version": "1.3.5",
"project_urls": {
"blog": "https://blog.platypush.tech",
"documentation": "https://docs.platypush.tech",
"homepage": "https://platypush.tech",
"repository": "https://git.platypush.tech/platypush/platypush"
},
"split_keywords": [
"home-automation",
" automation",
" iot",
" mqtt",
" websockets",
" redis",
" dashboard",
" notifications"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "77a96a28f9bfc6990046159ae12a64f6f5023dce507c3314cc46e0b082f0628c",
"md5": "96e28fc1324c7584b7c46b01c2aa652f",
"sha256": "25c7bbc1cab5d4eb3a66f013c703890acf97da9b3d0ec319a2399e3d4e701082"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "platypush-1.3.5.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "96e28fc1324c7584b7c46b01c2aa652f",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.6",
"size": 7719318,
"upload_time": "2025-02-09T01:39:37",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-02-09T01:39:37.212562Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/77/a9/6a28f9bfc6990046159ae12a64f6f5023dce507c3314cc46e0b082f0628c/platypush-1.3.5.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-02-09 01:39:37",
"github": false,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"lcname": "platypush"
}