| Name | pystog JSON |
| Version |
0.6.0
 JSON
JSON |
| download |
| home_page | None |
| Summary | Total scattering function manipulator |
| upload_time | 2025-09-19 16:41:27 |
| maintainer | None |
| docs_url | None |
| author | None |
| requires_python | >=3.10 |
| license | GPL version 3.0 |
| keywords |
neutrons
pystog
|
| VCS |
 |
| bugtrack_url |
|
| requirements |
No requirements were recorded.
|
| Travis-CI |
No Travis.
|
| coveralls test coverage |

|
## Total Scattering Function Manipulator:
| Health | Release | Other |
| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| [](https://actions-badge.atrox.dev/neutrons/pystog/goto?ref=master) | [](https://badge.fury.io/py/pystog) | [](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/neutrons/pystog/master?filepath=tutorials) |
| [](https://codecov.io/gh/neutrons/pystog) | [](https://anaconda.org/neutrons/pystog) | [](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0) |
| [](https://pystog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest) | [](https://www.repostatus.org/#active) | |
From total scattering functions, we have reciprocal-space structure factors and real-space pair distribution functions that are related via a Fourier transform.
PyStoG is a package that allows for:
1. Converting between the various functions used by different "communities" (ie researchers who study crystalline versus amorphous or glass materials). Conversions are for either real-space or reciprocal-space.
2. Perform the transform between the different available functions of choice
3. Fourier filter to remove spurious artificats in the data (ie aphysical, sub-angstrom low-r peaks in G(r) from experiments)
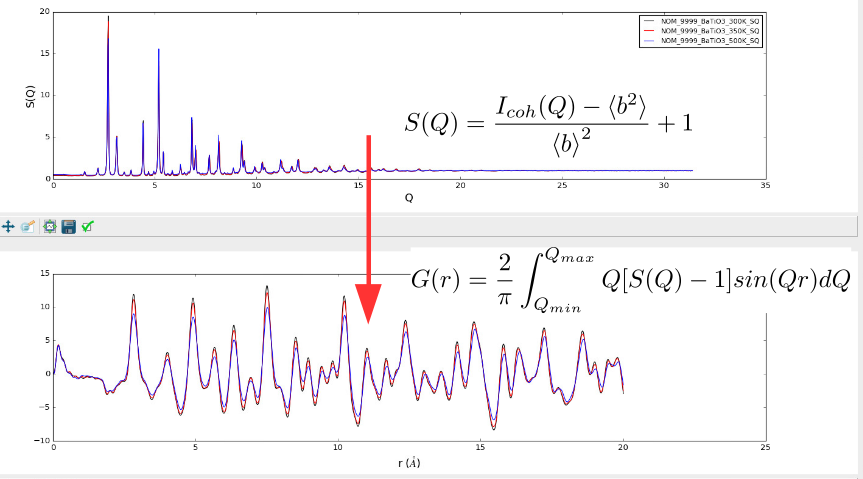
The name **PyStoG** comes from the fact that this is a _Pythonized_ version of **StoG**, a ~30 year old Fortran program that is part of the [RMCProfile software suite](http://www.rmcprofile.org/Main_Page).
**StoG** means **"S(Q) to G(r)"** for the fact that it takes recirpocal-space S(Q) patterns from files and transforms them into a single G(r) pattern.
The original _StoG_ program has been developed, in reverse chronological order, by:
- Matthew Tucker and Martin Dove (~2009)
- Spencer Howells (~1989)
- Jack Carpenter (prior to 1989)
A current state of the **StoG** program is kept in the `fortran` directory of this package.
This project was initially just a "sandbox" for taking the capabilities of **StoG** and migrating them over to the [Mantid Framework](https://github.com/mantidproject/mantid).
Yet, with more and more use cases, **PyStoG** was further developed as the stand-alone project it is now.
Yet, migration to the Mantid Framework is still a goal since it feeds into the [ADDIE project](https://github.com/neutrons/addie)
## Installation
Installation is available via [`pip`](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/):
```bash
pip install pystog
```
And [conda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/):
```bash
conda install -c neutrons pystog
```
## Getting started
Once installed, you can access the packages classes that perform the function manipulation.
```python
import pystog
from pystog import Converter
from pystog import Transformer
from pystog import FourierFilter
from pystog import StoG
```
** WARNING: Testing of the CLI is still ongoing**
A CLI command is also included, which can be run with JSON input files. The script will be installed into the `bin` directory in your virtual environment directory.
For example:
- `.pixi/envs/default/bin/`
- `pystog/.venv/bin/`
- `.../miniconda/envs/pystog/bin/`
You can simply activate your virtual environment (`pixi shell`, `. .venv/bin/activate`, or `conda activate pystog`) and run `pystog-cli`:
```bash
pystog-cli --json <input json>
```
For a list of available options, run:
```bash
pystog-cli --help
```
An example JSON can be found [here](https://github.com/neutrons/pystog/blob/master/data/examples/argon_pystog.json)
## Documentation
The official documentation is hosted on readthedocs.org: [https://pystog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/](https://pystog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
Also, a useful example reference is the [PDFFourierTransform](http://docs.mantidproject.org/nightly/algorithms/PDFFourierTransform-v1.html) algorithm in the Mantid Framework that has similar yet limited capabilities.
Finally, tutorials in the form of Jupyter Notebooks can be launched via Binder by clicking the badge here [](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/neutrons/pystog/master?filepath=tutorials) or at the top of the page.
## Development
Pystog uses [pixi](https://pixi.sh/latest) to manage packaging and dependencies.
To get started, [install pixi](https://pixi.sh/latest/installation), then install pystog by running:
```bash
cd pystog/
pixi install
```
Pixi will automatically create a virtual environment in `pystog/.pixi/`.
A number of convenience "tasks" are available, and can be viewed within the `pyproject.toml`, or by running:
```bash
pixi task list
```
### Testing
[pytest](https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/) is used to write and run the test suite.
To run the tests, simply run:
```bash
pixi run test
```
Any additional flags or options you desire may be passed, for example:
```bash
pixi run test some.specific:test
# or
pixi run test -vv
```
### Formatting and Static analysis
[pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/) is used for style enforcement and static analysis.
To install, after creating the environment run
```sh
pre-commit install
```
and it will run for every commit.
```sh
pre-commit run --all
```
will run it without committing.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "pystog",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "neutrons, pystog",
"author": null,
"author_email": null,
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/73/1b/e0830470eb5e46ce114da9c948bbd28ac4ce70fd40baf960dad12a6f97b9/pystog-0.6.0.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "## Total Scattering Function Manipulator:\n\n| Health | Release | Other |\n| -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |\n| [](https://actions-badge.atrox.dev/neutrons/pystog/goto?ref=master) | [](https://badge.fury.io/py/pystog) | [](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/neutrons/pystog/master?filepath=tutorials) |\n| [](https://codecov.io/gh/neutrons/pystog) | [](https://anaconda.org/neutrons/pystog) | [](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0) |\n| [](https://pystog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest) | [](https://www.repostatus.org/#active) | |\n\nFrom total scattering functions, we have reciprocal-space structure factors and real-space pair distribution functions that are related via a Fourier transform.\nPyStoG is a package that allows for:\n\n1. Converting between the various functions used by different \"communities\" (ie researchers who study crystalline versus amorphous or glass materials). Conversions are for either real-space or reciprocal-space.\n2. Perform the transform between the different available functions of choice\n3. Fourier filter to remove spurious artificats in the data (ie aphysical, sub-angstrom low-r peaks in G(r) from experiments)\n\n\n\nThe name **PyStoG** comes from the fact that this is a _Pythonized_ version of **StoG**, a ~30 year old Fortran program that is part of the [RMCProfile software suite](http://www.rmcprofile.org/Main_Page).\n**StoG** means **\"S(Q) to G(r)\"** for the fact that it takes recirpocal-space S(Q) patterns from files and transforms them into a single G(r) pattern.\nThe original _StoG_ program has been developed, in reverse chronological order, by:\n\n- Matthew Tucker and Martin Dove (~2009)\n- Spencer Howells (~1989)\n- Jack Carpenter (prior to 1989)\n\nA current state of the **StoG** program is kept in the `fortran` directory of this package.\n\nThis project was initially just a \"sandbox\" for taking the capabilities of **StoG** and migrating them over to the [Mantid Framework](https://github.com/mantidproject/mantid).\nYet, with more and more use cases, **PyStoG** was further developed as the stand-alone project it is now.\nYet, migration to the Mantid Framework is still a goal since it feeds into the [ADDIE project](https://github.com/neutrons/addie)\n\n## Installation\n\nInstallation is available via [`pip`](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/):\n\n```bash\npip install pystog\n```\n\nAnd [conda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/):\n\n```bash\nconda install -c neutrons pystog\n```\n\n## Getting started\n\nOnce installed, you can access the packages classes that perform the function manipulation.\n\n```python\nimport pystog\nfrom pystog import Converter\nfrom pystog import Transformer\nfrom pystog import FourierFilter\nfrom pystog import StoG\n```\n\n** WARNING: Testing of the CLI is still ongoing**\n\nA CLI command is also included, which can be run with JSON input files. The script will be installed into the `bin` directory in your virtual environment directory.\nFor example:\n\n- `.pixi/envs/default/bin/`\n- `pystog/.venv/bin/`\n- `.../miniconda/envs/pystog/bin/`\n\nYou can simply activate your virtual environment (`pixi shell`, `. .venv/bin/activate`, or `conda activate pystog`) and run `pystog-cli`:\n\n```bash\npystog-cli --json <input json>\n```\n\nFor a list of available options, run:\n\n```bash\npystog-cli --help\n```\n\nAn example JSON can be found [here](https://github.com/neutrons/pystog/blob/master/data/examples/argon_pystog.json)\n\n## Documentation\n\nThe official documentation is hosted on readthedocs.org: [https://pystog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/](https://pystog.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)\n\nAlso, a useful example reference is the [PDFFourierTransform](http://docs.mantidproject.org/nightly/algorithms/PDFFourierTransform-v1.html) algorithm in the Mantid Framework that has similar yet limited capabilities.\n\nFinally, tutorials in the form of Jupyter Notebooks can be launched via Binder by clicking the badge here [](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/neutrons/pystog/master?filepath=tutorials) or at the top of the page.\n\n## Development\n\nPystog uses [pixi](https://pixi.sh/latest) to manage packaging and dependencies.\nTo get started, [install pixi](https://pixi.sh/latest/installation), then install pystog by running:\n\n```bash\ncd pystog/\npixi install\n```\n\nPixi will automatically create a virtual environment in `pystog/.pixi/`.\nA number of convenience \"tasks\" are available, and can be viewed within the `pyproject.toml`, or by running:\n\n```bash\npixi task list\n```\n\n### Testing\n\n[pytest](https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/) is used to write and run the test suite.\n\nTo run the tests, simply run:\n\n```bash\npixi run test\n```\n\nAny additional flags or options you desire may be passed, for example:\n\n```bash\npixi run test some.specific:test\n# or\npixi run test -vv\n```\n\n### Formatting and Static analysis\n\n[pre-commit](https://pre-commit.com/) is used for style enforcement and static analysis.\nTo install, after creating the environment run\n\n```sh\npre-commit install\n```\n\nand it will run for every commit.\n\n```sh\npre-commit run --all\n```\n\nwill run it without committing.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "GPL version 3.0",
"summary": "Total scattering function manipulator",
"version": "0.6.0",
"project_urls": {
"homepage": "https://github.com/neutrons/pystog/",
"issues": "https://github.com/neutrons/pystog/issues",
"repository": "https://github.com/neutrons/pystog/"
},
"split_keywords": [
"neutrons",
" pystog"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "8e123b8c5d6ca009045a0db5c99301af6dff7f907d3dd1cc6d7fc76f19fb70b5",
"md5": "9d71d53a74e96430c1ba8654145c2ba9",
"sha256": "4035f55ecbdadd817ed38ee29d4e08c306048e41673d1b126db7a584f89d1857"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "pystog-0.6.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "9d71d53a74e96430c1ba8654145c2ba9",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"size": 38152,
"upload_time": "2025-09-19T16:41:25",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-09-19T16:41:25.168664Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/8e/12/3b8c5d6ca009045a0db5c99301af6dff7f907d3dd1cc6d7fc76f19fb70b5/pystog-0.6.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "731be0830470eb5e46ce114da9c948bbd28ac4ce70fd40baf960dad12a6f97b9",
"md5": "aa0bc7b9273657869b8bcd881686f05e",
"sha256": "bd0de4977a3d1758337b0c39b7f862cda42e6f295690eaa07982b984daa257ce"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "pystog-0.6.0.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "aa0bc7b9273657869b8bcd881686f05e",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"size": 21763852,
"upload_time": "2025-09-19T16:41:27",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-09-19T16:41:27.000347Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/73/1b/e0830470eb5e46ce114da9c948bbd28ac4ce70fd40baf960dad12a6f97b9/pystog-0.6.0.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-09-19 16:41:27",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "neutrons",
"github_project": "pystog",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": true,
"github_actions": true,
"lcname": "pystog"
}

