---
title: "SolidsPy: 2D-Finite Element Analysis with Python"
---
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/continuum_mechanics)
[](https://solidspy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
[](https://pypistats.org/packages/solidspy)
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/48294591)
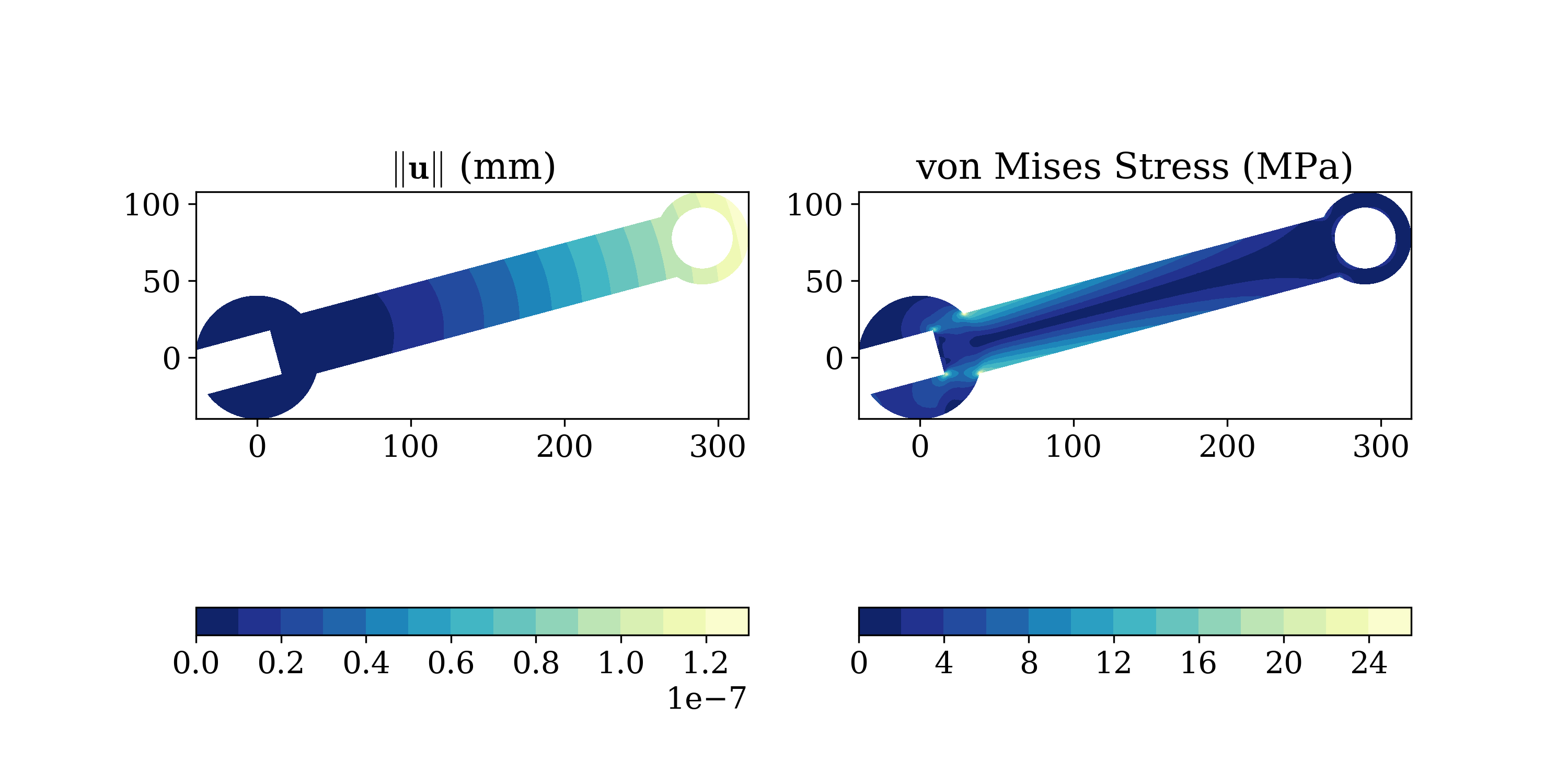
A simple finite element analysis code for 2D elasticity problems. The
code uses as input simple-to-create text files defining a model in terms
of nodal, element, material and load data.
- Documentation: <http://solidspy.readthedocs.io>
- GitHub: <https://github.com/AppliedMechanics-EAFIT/SolidsPy>
- PyPI: <https://pypi.org/project/solidspy/>
- Free and open source software: [MIT
license](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIT_License)
# Features
- It is based on an open-source environment.
- It is easy to use.
- The code allows to find displacement, strain and stress solutions
for arbitrary two-dimensional domains discretized into finite
elements and subject to point loads.
- The code is organized in independent modules for pre-processing,
assembly and post-processing allowing the user to easily modify it
or add features like new elements or analyses pipelines.
- It was created with academic and research purposes.
- It has been used to tech the following courses:
- Computational Modeling.
- Introduction to the Finite Element Methods.
# Installation
The code is written in Python and it depends on `numpy`, and `scipy`
and. It has been tested under Windows, Mac, Linux and Android.
To install *SolidsPy* open a terminal and type:
pip install solidspy
To specify through a GUI the folder where the input files are stored you
will need to install
[easygui](http://easygui.readthedocs.org/en/master/).
To easily generate the required SolidsPy text files out of a
[Gmsh](http://gmsh.info/) model you will need
[meshio](https://github.com/nschloe/meshio).
These two can be installed with:
pip install easygui
pip install meshio
# How to run a simple model
For further explanation check the
[docs](http://solidspy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).
Let\'s suppose that we have a simple model represented by the following
files (see [tutorials/square
example](http://solidspy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/square_example.html)
for further explanation).
- `nodes.txt`
```{=html}
<!-- -->
```
0 0.00 0.00 0 -1
1 2.00 0.00 0 -1
2 2.00 2.00 0 0
3 0.00 2.00 0 0
4 1.00 0.00 -1 -1
5 2.00 1.00 0 0
6 1.00 2.00 0 0
7 0.00 1.00 0 0
8 1.00 1.00 0 0
- `eles.txt`
```{=html}
<!-- -->
```
0 1 0 0 4 8 7
1 1 0 4 1 5 8
2 1 0 7 8 6 3
3 1 0 8 5 2 6
- `mater.txt`
```{=html}
<!-- -->
```
1.0 0.3
- `loads.txt`
```{=html}
<!-- -->
```
3 0.0 1.0
6 0.0 2.0
2 0.0 1.0
Run it in Python as follows:
``` python
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # load matplotlib
from solidspy import solids_GUI # import our package
disp = solids_GUI() # run the Finite Element Analysis
plt.show() # plot contours
```
For Mac users it is suggested to use an IPython console to run the
example.
# License
This project is licensed under the [MIT
license](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIT_License). The documents are
licensed under [Creative Commons Attribution
License](http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
# Citation
To cite SolidsPy in publications use
> Nicolás Guarín-Zapata, Juan Gomez (2020). SolidsPy: Version 1.0.16
> (Version v1.0.16). Zenodo. <http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4029270>
A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
``` bibtex
@software{solidspy,
title = {SolidsPy: 2D-Finite Element Analysis with Python},
version = {1.0.16},
author = {Guarín-Zapata, Nicolás and Gómez, Juan},
year = 2020,
keywords = {Python, Finite elements, Scientific computing, Computational mechanics},
abstract = {SolidsPy is a simple finite element analysis code for
2D elasticity problems. The code uses as input simple-to-create text
files defining a model in terms of nodal, element, material and
load data.},
url = {https://github.com/AppliedMechanics-EAFIT/SolidsPy},
doi = {http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4029270}
}
```
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/AppliedMechanics-EAFIT/SolidsPy",
"name": "solidsk",
"maintainer": "",
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": "",
"maintainer_email": "",
"keywords": "finite-elements fem scientific-computing",
"author": "Nicolas Guarin-Zapata <nguarinz@eafit.edu.co>, Juan Gomez <jgomezc1@eafit.edu.co>",
"author_email": "nguarinz@eafit.edu.co",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bf/f4/437ae9fe9c2e1571950a623bb2d9f5635e45f5769c824c498e9f943b6dc7/solidsk-0.1.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "---\r\r\ntitle: \"SolidsPy: 2D-Finite Element Analysis with Python\"\r\r\n---\r\r\n\r\r\n\r\r\n\r\r\n[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/continuum_mechanics)\r\r\n\r\r\n[](https://solidspy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)\r\r\n\r\r\n[](https://pypistats.org/packages/solidspy)\r\r\n\r\r\n[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/48294591)\r\r\n\r\r\nA simple finite element analysis code for 2D elasticity problems. The\r\r\ncode uses as input simple-to-create text files defining a model in terms\r\r\nof nodal, element, material and load data.\r\r\n\r\r\n- Documentation: <http://solidspy.readthedocs.io>\r\r\n- GitHub: <https://github.com/AppliedMechanics-EAFIT/SolidsPy>\r\r\n- PyPI: <https://pypi.org/project/solidspy/>\r\r\n- Free and open source software: [MIT\r\r\n license](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIT_License)\r\r\n\r\r\n# Features\r\r\n\r\r\n- It is based on an open-source environment.\r\r\n- It is easy to use.\r\r\n- The code allows to find displacement, strain and stress solutions\r\r\n for arbitrary two-dimensional domains discretized into finite\r\r\n elements and subject to point loads.\r\r\n- The code is organized in independent modules for pre-processing,\r\r\n assembly and post-processing allowing the user to easily modify it\r\r\n or add features like new elements or analyses pipelines.\r\r\n- It was created with academic and research purposes.\r\r\n- It has been used to tech the following courses:\r\r\n - Computational Modeling.\r\r\n - Introduction to the Finite Element Methods.\r\r\n\r\r\n# Installation\r\r\n\r\r\nThe code is written in Python and it depends on `numpy`, and `scipy`\r\r\nand. It has been tested under Windows, Mac, Linux and Android.\r\r\n\r\r\nTo install *SolidsPy* open a terminal and type:\r\r\n\r\r\n pip install solidspy\r\r\n\r\r\nTo specify through a GUI the folder where the input files are stored you\r\r\nwill need to install\r\r\n[easygui](http://easygui.readthedocs.org/en/master/).\r\r\n\r\r\nTo easily generate the required SolidsPy text files out of a\r\r\n[Gmsh](http://gmsh.info/) model you will need\r\r\n[meshio](https://github.com/nschloe/meshio).\r\r\n\r\r\nThese two can be installed with:\r\r\n\r\r\n pip install easygui\r\r\n pip install meshio\r\r\n\r\r\n# How to run a simple model\r\r\n\r\r\nFor further explanation check the\r\r\n[docs](http://solidspy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/).\r\r\n\r\r\nLet\\'s suppose that we have a simple model represented by the following\r\r\nfiles (see [tutorials/square\r\r\nexample](http://solidspy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/tutorials/square_example.html)\r\r\nfor further explanation).\r\r\n\r\r\n- `nodes.txt`\r\r\n\r\r\n```{=html}\r\r\n<!-- -->\r\r\n```\r\r\n 0 0.00 0.00 0 -1\r\r\n 1 2.00 0.00 0 -1\r\r\n 2 2.00 2.00 0 0\r\r\n 3 0.00 2.00 0 0\r\r\n 4 1.00 0.00 -1 -1\r\r\n 5 2.00 1.00 0 0\r\r\n 6 1.00 2.00 0 0\r\r\n 7 0.00 1.00 0 0\r\r\n 8 1.00 1.00 0 0\r\r\n\r\r\n- `eles.txt`\r\r\n\r\r\n```{=html}\r\r\n<!-- -->\r\r\n```\r\r\n 0 1 0 0 4 8 7\r\r\n 1 1 0 4 1 5 8\r\r\n 2 1 0 7 8 6 3\r\r\n 3 1 0 8 5 2 6\r\r\n\r\r\n- `mater.txt`\r\r\n\r\r\n```{=html}\r\r\n<!-- -->\r\r\n```\r\r\n 1.0 0.3\r\r\n\r\r\n- `loads.txt`\r\r\n\r\r\n```{=html}\r\r\n<!-- -->\r\r\n```\r\r\n 3 0.0 1.0\r\r\n 6 0.0 2.0\r\r\n 2 0.0 1.0\r\r\n\r\r\nRun it in Python as follows:\r\r\n\r\r\n``` python\r\r\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt # load matplotlib\r\r\nfrom solidspy import solids_GUI # import our package\r\r\ndisp = solids_GUI() # run the Finite Element Analysis\r\r\nplt.show() # plot contours\r\r\n```\r\r\n\r\r\nFor Mac users it is suggested to use an IPython console to run the\r\r\nexample.\r\r\n\r\r\n# License\r\r\n\r\r\nThis project is licensed under the [MIT\r\r\nlicense](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIT_License). The documents are\r\r\nlicensed under [Creative Commons Attribution\r\r\nLicense](http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).\r\r\n\r\r\n# Citation\r\r\n\r\r\nTo cite SolidsPy in publications use\r\r\n\r\r\n> Nicol\u00e1s Guar\u00edn-Zapata, Juan Gomez (2020). SolidsPy: Version 1.0.16\r\r\n> (Version v1.0.16). Zenodo. <http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4029270>\r\r\n\r\r\nA BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is\r\r\n\r\r\n``` bibtex\r\r\n@software{solidspy,\r\r\n title = {SolidsPy: 2D-Finite Element Analysis with Python},\r\r\n version = {1.0.16},\r\r\n author = {Guar\u00edn-Zapata, Nicol\u00e1s and G\u00f3mez, Juan},\r\r\n year = 2020,\r\r\n keywords = {Python, Finite elements, Scientific computing, Computational mechanics},\r\r\n abstract = {SolidsPy is a simple finite element analysis code for\r\r\n 2D elasticity problems. The code uses as input simple-to-create text\r\r\n files defining a model in terms of nodal, element, material and\r\r\n load data.},\r\r\n url = {https://github.com/AppliedMechanics-EAFIT/SolidsPy},\r\r\n doi = {http://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4029270}\r\r\n}\r\r\n```\r\r\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "MIT",
"summary": "A simple Finite Element program",
"version": "0.1",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/AppliedMechanics-EAFIT/SolidsPy"
},
"split_keywords": [
"finite-elements",
"fem",
"scientific-computing"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "bff4437ae9fe9c2e1571950a623bb2d9f5635e45f5769c824c498e9f943b6dc7",
"md5": "8667b97968aaaafb91bde0d0351ad202",
"sha256": "1980aa714d3d6adc4277044b4c1bb8abbc01db490445a31bf72a33ef26155b3d"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "solidsk-0.1.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "8667b97968aaaafb91bde0d0351ad202",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": null,
"size": 35166,
"upload_time": "2023-11-03T17:42:05",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2023-11-03T17:42:05.317322Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bf/f4/437ae9fe9c2e1571950a623bb2d9f5635e45f5769c824c498e9f943b6dc7/solidsk-0.1.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2023-11-03 17:42:05",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "AppliedMechanics-EAFIT",
"github_project": "SolidsPy",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": false,
"requirements": [],
"lcname": "solidsk"
}
