# **stemflow** :bird:
<p align="center">
<img src="https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/assets/logo_with_words.png" alt="stemflow logo" width="600"/>
</p>
<!-- -->
<p align="center">
<em>A Python Package for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model (AdaSTEM)</em>
</p>






[](https://codecov.io/gh/chenyangkang/stemflow)
[](https://joss.theoj.org/papers/50a385b3283faf346fc16484f50f6add)
<!-- -->
<!--  -->
<!--  -->
-----
## Documentation :book:
[stemflow Documentation](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/)
[JOSS paper](https://joss.theoj.org/papers/10.21105/joss.06158#)
<!-- stemflow -->
-----
## Installation :wrench:
```py
pip install stemflow
```
To install the latest beta version from github:
```py
pip install stemflow@git+https://github.com/chenyangkang/stemflow.git
```
Or using conda:
```py
conda install -c conda-forge stemflow
```
-----
## Brief introduction :information_source:
**stemflow** is a toolkit for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model (AdaSTEM \[[1](https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/8484), [2](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/eap.2056)\]) in Python. Typical usage is daily abundance estimation using [eBird](https://ebird.org/home) citizen science data (survey data).
**stemflow** adopts ["split-apply-combine"](https://vita.had.co.nz/papers/plyr.pdf) philosophy. It
1. Splits input data using [Quadtree](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quadtree#:~:text=A%20quadtree%20is%20a%20tree,into%20four%20quadrants%20or%20regions.) or [Sphere Quadtree](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/146380).
1. Trains each spatiotemporal split (called stixel) separately.
1. Aggregates the ensemble to make the prediction.
The framework leverages the "adjacency" information of surroundings in space and time to model/predict the values of target spatiotemporal points. This framework ameliorates the **long-distance/long-range prediction problem** [[3](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1890/09-1340.1)], and has a good spatiotemporal smoothing effect.
For more information, please see [an introduction to stemflow](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/A_brief_introduction/A_brief_introduction.html) and [learning curve analysis](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/02.AdaSTEM_learning_curve_analysis.html)
-----
## Model and data :slot_machine:
| Main functionality of `stemflow` | Supported indexing | Supported tasks |
| :-- | :-- | :-- |
| :white_check_mark: Spatiotemporal modeling & prediction<br> | :white_check_mark: User-defined 2D spatial indexing (CRS)<br> | :white_check_mark: Binary classification task<br> |
| :white_check_mark: Calculate overall feature importances<br> | :white_check_mark: 3D spherical indexing <br> | :white_check_mark: Regression task<br> |
| :white_check_mark: Plot spatiotemporal dynamics<br> | :white_check_mark: User-defined temporal indexing<br> | :white_check_mark: Hurdle task (two step regression – classify then regress the non-zero part)<br> |
| | :white_check_mark: Spatial-only modeling<br> | |
| For details see [AdaSTEM Demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/01.AdaSTEM_demo.html) | For details and tips see [Tips for spatiotemporal indexing](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_spatiotemporal_indexing.html) | For details and tips see [Tips for different tasks](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_different_tasks.html) |
<!-- column 1 -->
<!-- | Main functionality of `stemflow`
| --
| :white_check_mark: Spatiotemporal modeling & prediction<br>
| :white_check_mark: Calculate overall feature importances<br>
| :white_check_mark: Plot spatiotemporal dynamics<br>
| For details see [AdaSTEM Demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/01.AdaSTEM_demo.html) -->
<!-- column 2 -->
<!-- | Supported indexing
| --
| :white_check_mark: User-defined 2D spatial indexing (CRS)<br>
| :white_check_mark: 3D Spherical indexing <br>
| :white_check_mark: User-defined temporal indexing<br>
| :white_check_mark: Spatial-only modeling<br>
| For details and tips see [Tips for spatiotemporal indexing](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_spatiotemporal_indexing.html) -->
<!-- column 3 -->
<!-- | Supported tasks
| --
| :white_check_mark: Binary classification task<br>
| :white_check_mark: Regression task<br>
| :white_check_mark: Hurdle task (two step regression – classify then regress the non-zero part)<br>
| For details and tips see [Tips for different tasks](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_different_tasks.html) -->
| Supported data types | Supported base models |
| -- | -- |
| :white_check_mark: Both continuous and categorical features (prefer one-hot encoding)<br> | :white_check_mark: sklearn style `BaseEstimator` classes ([you can make your own base model](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/developers/develop.html)), for example [here](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/06.Base_model_choices.html)<br> |
| :white_check_mark: Both static (e.g., yearly mean temperature) and dynamic features (e.g., daily temperature)<br> | :white_check_mark: sklearn style Maxent model. [Example here](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/03.Binding_with_Maxent.html). |
| For details and tips see [Tips for data types](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_data_types.html) | For details see [Base model choices](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/06.Base_model_choices.html) |
<!-- column 4 -->
<!-- | Supported data types
| --
| :white_check_mark: Both continuous and categorical features (prefer one-hot encoding)<br>
| :white_check_mark: Both static (e.g., yearly mean temperature) and dynamic features (e.g., daily temperature)<br>
| For details and tips see [Tips for data types](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_data_types.html) -->
<!-- column 5 -->
<!-- | Supported base models
| --
| :white_check_mark: sklearn style `BaseEstimator` classes ([you can make your own base model](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/developers/develop.html)), for example [here](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/06.Base_model_choices.html)<br>
| :white_check_mark: sklearn style Maxent model. [Example here](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/03.Binding_with_Maxent.html).
| For details see [Base model choices](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/06.Base_model_choices.html) -->
## Usage :star:
Use Hurdle model as the base model of AdaSTEMRegressor:
```py
from stemflow.model.AdaSTEM import AdaSTEM, AdaSTEMClassifier, AdaSTEMRegressor
from stemflow.model.Hurdle import Hurdle
from xgboost import XGBClassifier, XGBRegressor
## "hurdle in Ada"
model = AdaSTEMRegressor(
base_model=Hurdle(
classifier=XGBClassifier(tree_method='hist',random_state=42, verbosity = 0, n_jobs=1),
regressor=XGBRegressor(tree_method='hist',random_state=42, verbosity = 0, n_jobs=1)
), # hurdel model for zero-inflated problem (e.g., count)
save_gridding_plot = True,
ensemble_fold=50, # data are modeled 50 times, each time with jitter and rotation in Quadtree algo
min_ensemble_required=30, # Only points covered by > 30 ensembles will be predicted
grid_len_upper_threshold=25, # force splitting if the grid length exceeds 25
grid_len_lower_threshold=5, # stop splitting if the grid length fall short 5
temporal_start=1, # The next 4 params define the temporal sliding window
temporal_end=366,
temporal_step=20, # The window takes steps of 20 DOY (see AdaSTEM demo for details)
temporal_bin_interval=50, # Each window will contain data of 50 DOY
points_lower_threshold=50, # Only stixels with more than 50 samples are trained and used for prediction
Spatio1='longitude', # The next three params define the name of
Spatio2='latitude', # spatial coordinates shown in the dataframe
Temporal1='DOY',
use_temporal_to_train=True, # In each stixel, whether 'DOY' should be a predictor
n_jobs=1,
random_state=42
)
```
Fitting and prediction methods follow the style of sklearn `BaseEstimator` class:
```py
## fit
model = model.fit(X_train.reset_index(drop=True), y_train)
## predict
pred = model.predict(X_test)
pred = np.where(pred<0, 0, pred)
eval_metrics = AdaSTEM.eval_STEM_res('hurdle',y_test, pred_mean)
print(eval_metrics)
```
Where the `pred` is the mean of the predicted values across ensembles.
See [AdaSTEM demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/01.AdaSTEM_demo.html) for further functionality.<br>
See [Optimizing stixel size](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/07.Optimizing_stixel_size.html) for why and how you should tune the important gridding parameters.
-----
## Plot QuadTree ensembles :evergreen_tree:
```py
model.gridding_plot
# Here, the model is a AdaSTEM class, not a hurdle class
```
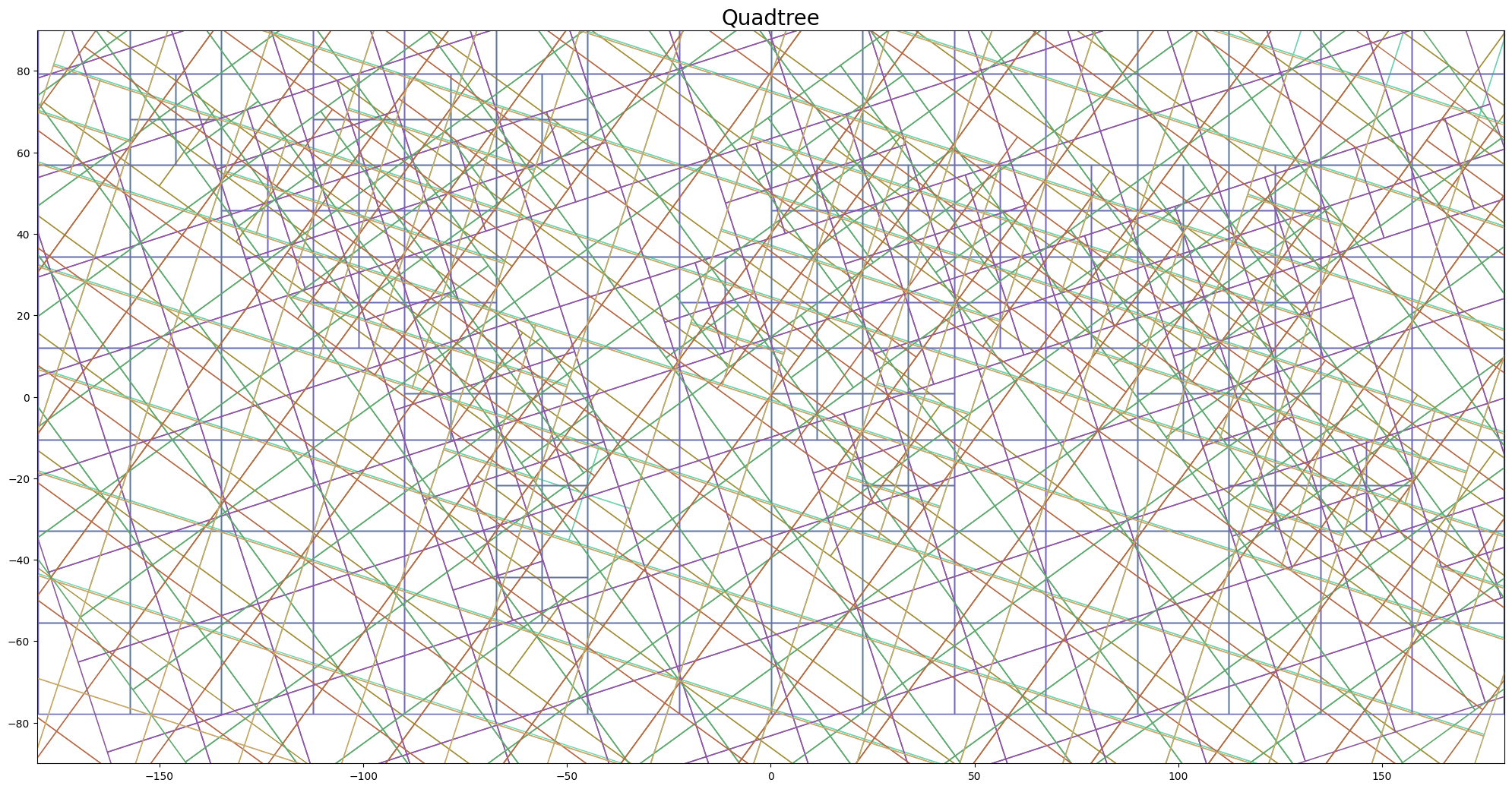
Here, each color shows an ensemble generated during model fitting. In each of the 10 ensembles, regions (in terms of space and time) with more training samples were gridded into finer resolution, while the sparse one remained coarse. Prediction results were aggregated across the ensembles (that is, in this example, data were modeled 10 times).
If you use `SphereAdaSTEM` module, the gridding plot is a `plotly` generated interactive object by default:
<p align="center">
<img src="https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/assets/Sphere_gridding.png" width="500"/>
</p>
See [SphereAdaSTEM demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/04.SphereAdaSTEM_demo.html) and [Interactive spherical gridding plot](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/assets/Sphere_gridding.html).
----
## Example of visualization :world_map:
Daily Abundance Map of Barn Swallow

See section [AdaSTEM demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/01.AdaSTEM_demo.html) for how to generate this GIF.
----
## Citation
Chen et al., (2024). stemflow: A Python Package for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model. Journal of Open Source Software, 9(94), 6158, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.06158
```bibtex
@article{Chen2024,
doi = {10.21105/joss.06158},
url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.06158},
year = {2024},
publisher = {The Open Journal},
volume = {9},
number = {94},
pages = {6158},
author = {Yangkang Chen and Zhongru Gu and Xiangjiang Zhan},
title = {stemflow: A Python Package for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software}
}
```
----
## Contribute to stemflow :purple_heart:
We welcome pull requests. Contributors should follow [contributor guidelines](https://github.com/chenyangkang/stemflow/blob/main/docs/CONTRIBUTING.md).
Application-level cooperation is also welcomed. We recognized that stemflow may consume large computational resources especially as data volume boosts in the future. We always welcome research collaboration of all kinds.
-----
References:
1. [Fink, D., Damoulas, T., & Dave, J. (2013, June). Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Models: Hemisphere-wide species distributions from massively crowdsourced eBird data. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 1284-1290).](https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/8484)
1. [Fink, D., Auer, T., Johnston, A., Ruiz‐Gutierrez, V., Hochachka, W. M., & Kelling, S. (2020). Modeling avian full annual cycle distribution and population trends with citizen science data. Ecological Applications, 30(3), e02056.](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/eap.2056)
1. [Fink, D., Hochachka, W. M., Zuckerberg, B., Winkler, D. W., Shaby, B., Munson, M. A., ... & Kelling, S. (2010). Spatiotemporal exploratory models for broad‐scale survey data. Ecological Applications, 20(8), 2131-2147.](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1890/09-1340.1)
1. [Johnston, A., Fink, D., Reynolds, M. D., Hochachka, W. M., Sullivan, B. L., Bruns, N. E., ... & Kelling, S. (2015). Abundance models improve spatial and temporal prioritization of conservation resources. Ecological Applications, 25(7), 1749-1756.](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1890/14-1826.1)
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/chenyangkang/stemflow",
"name": "stemflow",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.8.0",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "python, spatial-temporal model, ebird, citizen science, spatial temporal exploratory model, STEM, AdaSTEM, abundance, phenology",
"author": "Yangkang Chen",
"author_email": "chenyangkang24@outlook.com",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/42/cb/8c4335c729d12d97ef54c4846c56e31d2f7cfe619c88fbb9ef88e1cdb552/stemflow-1.1.4.tar.gz",
"platform": "any",
"description": "\n# **stemflow** :bird:\n<p align=\"center\">\n <img src=\"https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/assets/logo_with_words.png\" alt=\"stemflow logo\" width=\"600\"/>\n</p>\n<!-- -->\n<p align=\"center\">\n <em>A Python Package for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model (AdaSTEM)</em>\n</p>\n\n\n\n\n\n\n\n[](https://codecov.io/gh/chenyangkang/stemflow)\n[](https://joss.theoj.org/papers/50a385b3283faf346fc16484f50f6add)\n <!-- -->\n <!--  -->\n<!--  -->\n\n-----\n\n## Documentation :book:\n[stemflow Documentation](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/)\n\n[JOSS paper](https://joss.theoj.org/papers/10.21105/joss.06158#)\n<!-- stemflow -->\n\n-----\n\n\n## Installation :wrench:\n\n```py\npip install stemflow\n```\n\nTo install the latest beta version from github:\n\n```py\npip install stemflow@git+https://github.com/chenyangkang/stemflow.git\n```\n\nOr using conda:\n\n```py\nconda install -c conda-forge stemflow\n```\n\n-----\n\n## Brief introduction :information_source:\n**stemflow** is a toolkit for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model (AdaSTEM \\[[1](https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/8484), [2](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/eap.2056)\\]) in Python. Typical usage is daily abundance estimation using [eBird](https://ebird.org/home) citizen science data (survey data). \n\n**stemflow** adopts [\"split-apply-combine\"](https://vita.had.co.nz/papers/plyr.pdf) philosophy. It \n\n1. Splits input data using [Quadtree](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Quadtree#:~:text=A%20quadtree%20is%20a%20tree,into%20four%20quadrants%20or%20regions.) or [Sphere Quadtree](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/146380).\n1. Trains each spatiotemporal split (called stixel) separately.\n1. Aggregates the ensemble to make the prediction.\n\n\nThe framework leverages the \"adjacency\" information of surroundings in space and time to model/predict the values of target spatiotemporal points. This framework ameliorates the **long-distance/long-range prediction problem** [[3](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1890/09-1340.1)], and has a good spatiotemporal smoothing effect.\n\nFor more information, please see [an introduction to stemflow](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/A_brief_introduction/A_brief_introduction.html) and [learning curve analysis](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/02.AdaSTEM_learning_curve_analysis.html)\n\n-----\n\n## Model and data :slot_machine:\n\n| Main functionality of `stemflow` | Supported indexing | Supported tasks |\n| :-- | :-- | :-- |\n| :white_check_mark: Spatiotemporal modeling & prediction<br> | :white_check_mark: User-defined 2D spatial indexing (CRS)<br> | :white_check_mark: Binary classification task<br> |\n| :white_check_mark: Calculate overall feature importances<br> | :white_check_mark: 3D spherical indexing <br> | :white_check_mark: Regression task<br> |\n| :white_check_mark: Plot spatiotemporal dynamics<br> | :white_check_mark: User-defined temporal indexing<br> | :white_check_mark: Hurdle task (two step regression \u2013 classify then regress the non-zero part)<br> |\n| | :white_check_mark: Spatial-only modeling<br> | |\n| For details see [AdaSTEM Demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/01.AdaSTEM_demo.html) | For details and tips see [Tips for spatiotemporal indexing](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_spatiotemporal_indexing.html) | For details and tips see [Tips for different tasks](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_different_tasks.html) |\n\n\n\n<!-- column 1 -->\n<!-- | Main functionality of `stemflow` \n| -- \n| :white_check_mark: Spatiotemporal modeling & prediction<br> \n| :white_check_mark: Calculate overall feature importances<br> \n| :white_check_mark: Plot spatiotemporal dynamics<br> \n| For details see [AdaSTEM Demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/01.AdaSTEM_demo.html) -->\n\n\n<!-- column 2 -->\n<!-- | Supported indexing\n| -- \n| :white_check_mark: User-defined 2D spatial indexing (CRS)<br>\n| :white_check_mark: 3D Spherical indexing <br>\n| :white_check_mark: User-defined temporal indexing<br> \n| :white_check_mark: Spatial-only modeling<br> \n| For details and tips see [Tips for spatiotemporal indexing](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_spatiotemporal_indexing.html) -->\n\n<!-- column 3 -->\n<!-- | Supported tasks\n| --\n| :white_check_mark: Binary classification task<br> \n| :white_check_mark: Regression task<br> \n| :white_check_mark: Hurdle task (two step regression \u2013 classify then regress the non-zero part)<br> \n| For details and tips see [Tips for different tasks](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_different_tasks.html) -->\n\n\n| Supported data types | Supported base models |\n| -- | -- |\n| :white_check_mark: Both continuous and categorical features (prefer one-hot encoding)<br> | :white_check_mark: sklearn style `BaseEstimator` classes ([you can make your own base model](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/developers/develop.html)), for example [here](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/06.Base_model_choices.html)<br> |\n| :white_check_mark: Both static (e.g., yearly mean temperature) and dynamic features (e.g., daily temperature)<br> | :white_check_mark: sklearn style Maxent model. [Example here](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/03.Binding_with_Maxent.html). |\n| For details and tips see [Tips for data types](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_data_types.html) | For details see [Base model choices](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/06.Base_model_choices.html) |\n\n<!-- column 4 -->\n<!-- | Supported data types\n| -- \n| :white_check_mark: Both continuous and categorical features (prefer one-hot encoding)<br> \n| :white_check_mark: Both static (e.g., yearly mean temperature) and dynamic features (e.g., daily temperature)<br>\n| For details and tips see [Tips for data types](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Tips/Tips_for_data_types.html) -->\n\n\n<!-- column 5 -->\n<!-- | Supported base models \n| --\n| :white_check_mark: sklearn style `BaseEstimator` classes ([you can make your own base model](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/developers/develop.html)), for example [here](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/06.Base_model_choices.html)<br> \n| :white_check_mark: sklearn style Maxent model. [Example here](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/03.Binding_with_Maxent.html). \n| For details see [Base model choices](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/06.Base_model_choices.html) -->\n\n\n\n## Usage :star:\n\nUse Hurdle model as the base model of AdaSTEMRegressor:\n\n```py\nfrom stemflow.model.AdaSTEM import AdaSTEM, AdaSTEMClassifier, AdaSTEMRegressor\nfrom stemflow.model.Hurdle import Hurdle\nfrom xgboost import XGBClassifier, XGBRegressor\n\n## \"hurdle in Ada\"\nmodel = AdaSTEMRegressor(\n base_model=Hurdle(\n classifier=XGBClassifier(tree_method='hist',random_state=42, verbosity = 0, n_jobs=1),\n regressor=XGBRegressor(tree_method='hist',random_state=42, verbosity = 0, n_jobs=1)\n ), # hurdel model for zero-inflated problem (e.g., count)\n save_gridding_plot = True,\n ensemble_fold=50, # data are modeled 50 times, each time with jitter and rotation in Quadtree algo\n min_ensemble_required=30, # Only points covered by > 30 ensembles will be predicted\n grid_len_upper_threshold=25, # force splitting if the grid length exceeds 25\n grid_len_lower_threshold=5, # stop splitting if the grid length fall short 5 \n temporal_start=1, # The next 4 params define the temporal sliding window\n temporal_end=366, \n temporal_step=20, # The window takes steps of 20 DOY (see AdaSTEM demo for details)\n temporal_bin_interval=50, # Each window will contain data of 50 DOY\n points_lower_threshold=50, # Only stixels with more than 50 samples are trained and used for prediction\n Spatio1='longitude', # The next three params define the name of \n Spatio2='latitude', # spatial coordinates shown in the dataframe\n Temporal1='DOY',\n use_temporal_to_train=True, # In each stixel, whether 'DOY' should be a predictor\n n_jobs=1,\n random_state=42\n)\n```\n\n\nFitting and prediction methods follow the style of sklearn `BaseEstimator` class:\n\n```py\n## fit\nmodel = model.fit(X_train.reset_index(drop=True), y_train)\n\n## predict\npred = model.predict(X_test)\npred = np.where(pred<0, 0, pred)\neval_metrics = AdaSTEM.eval_STEM_res('hurdle',y_test, pred_mean)\nprint(eval_metrics)\n```\n\nWhere the `pred` is the mean of the predicted values across ensembles.\n\nSee [AdaSTEM demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/01.AdaSTEM_demo.html) for further functionality.<br>\nSee [Optimizing stixel size](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/07.Optimizing_stixel_size.html) for why and how you should tune the important gridding parameters.\n\n-----\n\n## Plot QuadTree ensembles :evergreen_tree:\n\n\n```py\nmodel.gridding_plot\n# Here, the model is a AdaSTEM class, not a hurdle class\n```\n\n\n\nHere, each color shows an ensemble generated during model fitting. In each of the 10 ensembles, regions (in terms of space and time) with more training samples were gridded into finer resolution, while the sparse one remained coarse. Prediction results were aggregated across the ensembles (that is, in this example, data were modeled 10 times).\n\nIf you use `SphereAdaSTEM` module, the gridding plot is a `plotly` generated interactive object by default:\n\n\n<p align=\"center\">\n <img src=\"https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/assets/Sphere_gridding.png\" width=\"500\"/>\n</p>\n\n\n\nSee [SphereAdaSTEM demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/04.SphereAdaSTEM_demo.html) and [Interactive spherical gridding plot](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/assets/Sphere_gridding.html).\n\n\n\n----\n## Example of visualization :world_map:\n\nDaily Abundance Map of Barn Swallow\n\n\n\nSee section [AdaSTEM demo](https://chenyangkang.github.io/stemflow/Examples/01.AdaSTEM_demo.html) for how to generate this GIF.\n\n----\n\n## Citation\n\nChen et al., (2024). stemflow: A Python Package for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model. Journal of Open Source Software, 9(94), 6158, https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.06158\n\n```bibtex\n@article{Chen2024, \n doi = {10.21105/joss.06158}, \n url = {https://doi.org/10.21105/joss.06158}, \n year = {2024}, \n publisher = {The Open Journal}, \n volume = {9}, \n number = {94}, \n pages = {6158}, \n author = {Yangkang Chen and Zhongru Gu and Xiangjiang Zhan}, \n title = {stemflow: A Python Package for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model}, \n journal = {Journal of Open Source Software} \n}\n```\n\n----\n\n## Contribute to stemflow :purple_heart:\n\nWe welcome pull requests. Contributors should follow [contributor guidelines](https://github.com/chenyangkang/stemflow/blob/main/docs/CONTRIBUTING.md).\n\nApplication-level cooperation is also welcomed. We recognized that stemflow may consume large computational resources especially as data volume boosts in the future. We always welcome research collaboration of all kinds.\n\n\n-----\nReferences:\n\n1. [Fink, D., Damoulas, T., & Dave, J. (2013, June). Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Models: Hemisphere-wide species distributions from massively crowdsourced eBird data. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 1284-1290).](https://ojs.aaai.org/index.php/AAAI/article/view/8484)\n\n1. [Fink, D., Auer, T., Johnston, A., Ruiz\u2010Gutierrez, V., Hochachka, W. M., & Kelling, S. (2020). Modeling avian full annual cycle distribution and population trends with citizen science data. Ecological Applications, 30(3), e02056.](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/eap.2056)\n\n1. [Fink, D., Hochachka, W. M., Zuckerberg, B., Winkler, D. W., Shaby, B., Munson, M. A., ... & Kelling, S. (2010). Spatiotemporal exploratory models for broad\u2010scale survey data. Ecological Applications, 20(8), 2131-2147.](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1890/09-1340.1)\n\n1. [Johnston, A., Fink, D., Reynolds, M. D., Hochachka, W. M., Sullivan, B. L., Bruns, N. E., ... & Kelling, S. (2015). Abundance models improve spatial and temporal prioritization of conservation resources. Ecological Applications, 25(7), 1749-1756.](https://esajournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1890/14-1826.1)\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "A package for Adaptive Spatio-Temporal Exploratory Model (AdaSTEM) in python",
"version": "1.1.4",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/chenyangkang/stemflow"
},
"split_keywords": [
"python",
" spatial-temporal model",
" ebird",
" citizen science",
" spatial temporal exploratory model",
" stem",
" adastem",
" abundance",
" phenology"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "bc1b5f9e09df29aa3410788eab90745190f30819e6b32defdf0c83dabd69b938",
"md5": "ac8564fa9861c07578ddc30a867b1fe2",
"sha256": "974ab8cb04b6809d86b9a7294f38ea7592bc58b13c41cdb07d1d9a06bcf2c0e5"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "stemflow-1.1.4-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "ac8564fa9861c07578ddc30a867b1fe2",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.8.0",
"size": 83434,
"upload_time": "2025-09-02T03:42:44",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-09-02T03:42:44.496837Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/bc/1b/5f9e09df29aa3410788eab90745190f30819e6b32defdf0c83dabd69b938/stemflow-1.1.4-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "42cb8c4335c729d12d97ef54c4846c56e31d2f7cfe619c88fbb9ef88e1cdb552",
"md5": "1c4120a94bdf7943fd440e060b73a30e",
"sha256": "799c40a3b5de4775d1321ccc581cca260d232eca073aed7c52d6d709baddfb75"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "stemflow-1.1.4.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "1c4120a94bdf7943fd440e060b73a30e",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.8.0",
"size": 79896,
"upload_time": "2025-09-02T03:42:45",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-09-02T03:42:45.960346Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/42/cb/8c4335c729d12d97ef54c4846c56e31d2f7cfe619c88fbb9ef88e1cdb552/stemflow-1.1.4.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-09-02 03:42:45",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "chenyangkang",
"github_project": "stemflow",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"requirements": [
{
"name": "joblib",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"1.3.0"
]
]
},
{
"name": "matplotlib",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"3.7.1"
]
]
},
{
"name": "numpy",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"1.24.3"
],
[
"<",
"2"
]
]
},
{
"name": "pandas",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"1.5.3"
]
]
},
{
"name": "plotly",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"5.9.0"
]
]
},
{
"name": "scikit_learn",
"specs": [
[
"<",
"1.6"
],
[
">=",
"1.2.2"
]
]
},
{
"name": "scipy",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"1.10.1"
]
]
},
{
"name": "setuptools",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"68.2.0"
]
]
},
{
"name": "tqdm",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"4.65.0"
]
]
}
],
"lcname": "stemflow"
}
