
# Interfacing with experimental results file from TAM Air calorimeters made easy.
After collecting multiple experimental results files from a TAM Air calorimeter you will be left with multiple *.xls*-files obtained as exports from the device control software. To achieve a side by side comparison of theses results and some basic extraction of relevant parameters, **TAInstCalorimetry** is here to get this done smoothly.
*Note: **TAInstCalorimetry** has been developed without involvement of **TA Instruments** and is thus independent from the company and its software.*
## Info / Downloads
[](https://pepy.tech/project/tainstcalorimetry)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/tainstcalorimetry)
[](https://pypi.org/project/tainstcalorimetry/)
## Table of Contents
- [Example Usage](#example-usage)<br>
- [Basic plotting](#basic-plotting)<br>
- [Getting cumulated heat values](#getting-cumulated-heat-values)<br>
- [Identifying peaks](#identifying-peaks)<br>
- [Identifying peak onsets](#identifying-peak-onsets)<br>
- [Plotting by Category](#plotting-by-category)<br>
- [Installation](#installation)<br>
- [Contributing](#contributing)
## Example Usage
Import the ```tacalorimetry``` module from **TAInstCalorimetry**.
```python
# import
import os
from TAInstCalorimetry import tacalorimetry
```
Next, we define where the exported files are stored. With this information at hand, a ```Measurement``` is initialized. Experimental raw data and the metadata passed in the course of the measurement are retrieved by the methods ```get_data()``` and ```get_information()```, respectively.
```python
# define data path
# "mycalodata" is the subfoldername where the calorimetry
# data files (both .csv or .xlsx) are stored
pathname = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
path_to_data = pathname + os.sep + "mycalodata"
# Example: if projectfile is at "C:\Users\myname\myproject\myproject.py", then "mydata"
# refers to "C:\Users\myname\myproject\mycalodata" where the data is stored
# load experiments via class, i.e. instantiate tacalorimetry object with data
tam = tacalorimetry.Measurement(folder=path_to_data)
# get sample and information
data = tam.get_data()
info = tam.get_information()
```
### Basic plotting
Furthermore, the ```Measurement``` features a ```plot()```-method for readily visualizing the collected results.
```python
# make plot
tam.plot()
# show plot
tacalorimetry.plt.show()
```
Without further options specified, the ```plot()```-method yields the following.
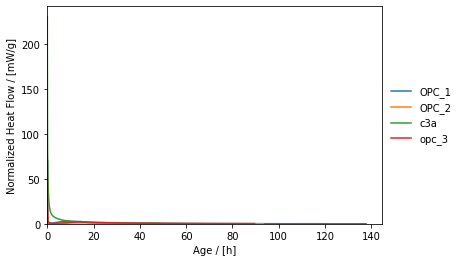
The ```plot()```-method can also be tuned to show the temporal course of normalized heat. On the one hand, this "tuning" refers to the specification of further keyword arguments such as ```t_unit``` and ```y```. On the other hand, the ```plot()```-method returns an object of type ```matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot```, which can be used to further customize the plot. In the following, a guide-to-the-eye line is introduced next to adjuting the axes limts, which is not provided for via the ```plot()```-method's signature.
```python
# show cumulated heat plot
ax = tam.plot(
t_unit="h",
y='normalized_heat',
y_unit_milli=False
)
# define target time
target_h = 1.5
# guide to the eye line
ax.axvline(target_h, color="gray", alpha=0.5, linestyle=":")
# set upper limits
ax.set_ylim(top=250)
ax.set_xlim(right=6)
# show plot
tacalorimetry.plt.show()
```
The following plot is obtained:
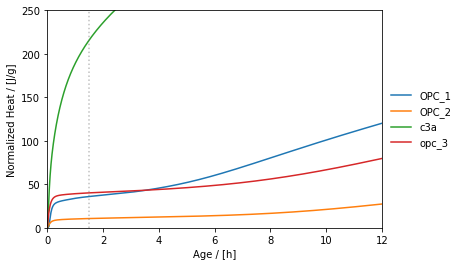
### Getting cumulated heat values
The cumulated heat after a certain period of time ```target_h``` from starting the measurement is a relevant quantity for answering different types of questions. For this purpose, the method ```get_cumulated_heat_at_hours``` returns an overview of this parameter for all the samples in the specified folder.
```python
# get table of cumulated heat at certain age
cumulated_heats = tam.get_cumulated_heat_at_hours(
target_h=target_h,
cutoff_min=10
)
# show result
print(cumulated_heats)
```
The return value of the method, ```cumulated_heats``` is a ```pd.DataFrame```.
### Identifying peaks
Next to cumulated heat values detected after a certain time frame from starting the reaction, peaks characteristics can be obtained from the experimental data via the ```get_peaks```-method.
```python
# get peaks
peaks = tam.get_peaks(
show_plot=True,
prominence=0.00001, # "sensitivity of peak picking"
cutoff_min=60, # how much to discard at the beginning of the measurement
plt_right_s=4e5,
plt_top=1e-2,
regex=".*_\d" # filter samples
)
```
Tweaking some of the available keyword arguments, the following plot is obtained:

Please keep in mind, that in particular for samples of ordinary Portland cement (OPC) a clear and unambiguous identification/assigment of peaks remains a challenging task which cannot be achieved in each and every case by **TAInstCalorimetry**. It is left to the user draw meaningful scientific conclusions from the characteristics derived from this method.
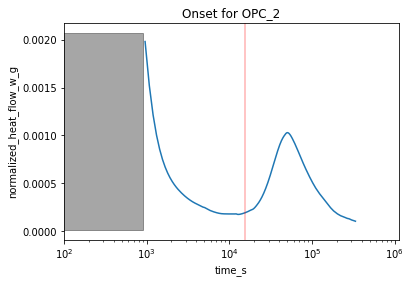
### Identifying peak onsets
Similarly, the peak onset characteristics are accessible via the ```get_peak_onsets```-method. The resulting plot is shown below.
```python
# get onsets
onsets = tam.get_peak_onsets(
gradient_threshold=0.000001,
rolling=10,
exclude_discarded_time=True,
show_plot=True,
regex="OPC"
)
```
### Plotting by Category
For introducing the idea of plotting calorimetry data "by category" another set of experimental data will be introduced. Next to the calorimetry data alone, information on investigated samples is supplied via an additional source file. In the present example via the file ```mini_metadata.csv```.
To begin with, a ```TAInstCalorimetry.tacalorimetry.Measurement```-object is initialized for selected files from the specified ````path```.
```python
import pathlib
from TAInstCalorimetry import tacalorimetry
# path to experimental calorimetry files
path = pathlib.Path().cwd().parent / "TAInstCalorimetry" / "DATA"
# initialize TAInstCalorimetry.tacalorimetry.Measurement object
tam_II = tacalorimetry.Measurement(
path, regex="myexp.*", show_info=True, cold_start=True, auto_clean=False
)
```
Next, we need to connect the previously defined object to our metadata provided by the ```mini_metadata.csv```-file. To establish this mapping between experimental results and metadata, the file location, i.e. path, and the column name containing the exact(!) names of the calorimetry files needs to be passed to the ```add_metadata_source```-method. In our case, we declare the column ```experiment_nr``` for this purpose
```python
# add metadata
tam.add_metadata_source("mini_metadata.csv", "experiment_nr")
```
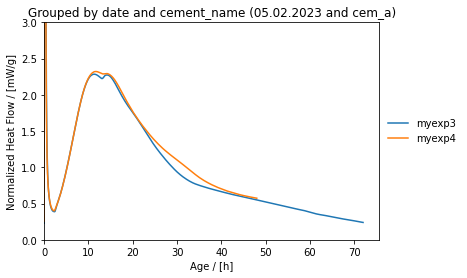
Finally, a plotting by category can be carried out by one or multiple categories as shown in the following.
```python
# define action by one category
categorize_by = "cement_name" # 'date', 'cement_amount_g', 'water_amount_g'
# # define action by two or more categories
categorize_by = ["date", "cement_name"]
# loop through plots via generator
for this_plot in tam.plot_by_category(categorize_by):
# extract parts obtained from generator
category_value, ax = this_plot
# fine tuning of plot/cosmetics
ax.set_ylim(0, 3)
# show plot
tacalorimetry.plt.show()
```
This yields plots of the following kind.

## Installation
Use the package manager [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/) to install TAInstCalorimetry.
```bash
pip install TAInstCalorimetry
```
## Contributing
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.
List of contributors:
- [mj-hofmann](https://github.com/mj-hofmann)
- [tgaedt](https://github.com/tgaedt)
## License
[GNU GPLv3](https://choosealicense.com/licenses/gpl-3.0/#)
## Test

## Code Styling
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/mj-hofmann/TAInstCalorimetry",
"name": "tainstcalorimetry",
"maintainer": "",
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.8.1,<3.12",
"maintainer_email": "",
"keywords": "calorimetry,TAM Air,TA Instruments,analysis,vizualisation",
"author": "mj-hofmann",
"author_email": "aCodingChemist@gmail.com",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/4d/95/c081ff1913c90f1d0564e30079ae4a1a50d7aac058352d2411c12ca51045/tainstcalorimetry-0.1.16.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "\n\n# Interfacing with experimental results file from TAM Air calorimeters made easy.\n\nAfter collecting multiple experimental results files from a TAM Air calorimeter you will be left with multiple *.xls*-files obtained as exports from the device control software. To achieve a side by side comparison of theses results and some basic extraction of relevant parameters, **TAInstCalorimetry** is here to get this done smoothly.\n\n*Note: **TAInstCalorimetry** has been developed without involvement of **TA Instruments** and is thus independent from the company and its software.*\n\n## Info / Downloads\n\n[](https://pepy.tech/project/tainstcalorimetry)\n[](https://pepy.tech/project/tainstcalorimetry)\n[](https://pypi.org/project/tainstcalorimetry/) \n\n## Table of Contents \n- [Example Usage](#example-usage)<br>\n - [Basic plotting](#basic-plotting)<br>\n - [Getting cumulated heat values](#getting-cumulated-heat-values)<br>\n - [Identifying peaks](#identifying-peaks)<br>\n - [Identifying peak onsets](#identifying-peak-onsets)<br>\n - [Plotting by Category](#plotting-by-category)<br>\n- [Installation](#installation)<br>\n- [Contributing](#contributing)\n\n## Example Usage\n\nImport the ```tacalorimetry``` module from **TAInstCalorimetry**.\n\n```python\n# import\nimport os\nfrom TAInstCalorimetry import tacalorimetry\n```\n\nNext, we define where the exported files are stored. With this information at hand, a ```Measurement``` is initialized. Experimental raw data and the metadata passed in the course of the measurement are retrieved by the methods ```get_data()``` and ```get_information()```, respectively.\n\n```python\n# define data path\n# \"mycalodata\" is the subfoldername where the calorimetry\n# data files (both .csv or .xlsx) are stored\n\npathname = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))\npath_to_data = pathname + os.sep + \"mycalodata\"\n\n# Example: if projectfile is at \"C:\\Users\\myname\\myproject\\myproject.py\", then \"mydata\"\n# refers to \"C:\\Users\\myname\\myproject\\mycalodata\" where the data is stored\n\n# load experiments via class, i.e. instantiate tacalorimetry object with data\ntam = tacalorimetry.Measurement(folder=path_to_data)\n\n# get sample and information\ndata = tam.get_data()\ninfo = tam.get_information()\n```\n\n### Basic plotting\n\nFurthermore, the ```Measurement``` features a ```plot()```-method for readily visualizing the collected results.\n\n```python\n# make plot\ntam.plot()\n# show plot\ntacalorimetry.plt.show()\n```\n\nWithout further options specified, the ```plot()```-method yields the following.\n\n\n\nThe ```plot()```-method can also be tuned to show the temporal course of normalized heat. On the one hand, this \"tuning\" refers to the specification of further keyword arguments such as ```t_unit``` and ```y```. On the other hand, the ```plot()```-method returns an object of type ```matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot```, which can be used to further customize the plot. In the following, a guide-to-the-eye line is introduced next to adjuting the axes limts, which is not provided for via the ```plot()```-method's signature.\n\n```python\n# show cumulated heat plot\nax = tam.plot(\n t_unit=\"h\",\n y='normalized_heat',\n y_unit_milli=False\n)\n\n# define target time\ntarget_h = 1.5\n\n# guide to the eye line\nax.axvline(target_h, color=\"gray\", alpha=0.5, linestyle=\":\")\n\n# set upper limits\nax.set_ylim(top=250)\nax.set_xlim(right=6)\n# show plot\ntacalorimetry.plt.show()\n```\nThe following plot is obtained:\n\n\n\n### Getting cumulated heat values\n\nThe cumulated heat after a certain period of time ```target_h``` from starting the measurement is a relevant quantity for answering different types of questions. For this purpose, the method ```get_cumulated_heat_at_hours``` returns an overview of this parameter for all the samples in the specified folder.\n\n```python\n# get table of cumulated heat at certain age\ncumulated_heats = tam.get_cumulated_heat_at_hours(\n target_h=target_h,\n cutoff_min=10\n )\n \n# show result\nprint(cumulated_heats)\n```\n\nThe return value of the method, ```cumulated_heats``` is a ```pd.DataFrame```.\n\n### Identifying peaks\n\nNext to cumulated heat values detected after a certain time frame from starting the reaction, peaks characteristics can be obtained from the experimental data via the ```get_peaks```-method.\n\n```python\n# get peaks\npeaks = tam.get_peaks(\n show_plot=True,\n prominence=0.00001, # \"sensitivity of peak picking\"\n cutoff_min=60, # how much to discard at the beginning of the measurement\n plt_right_s=4e5,\n plt_top=1e-2,\n regex=\".*_\\d\" # filter samples\n )\n```\n\nTweaking some of the available keyword arguments, the following plot is obtained:\n\n\n\nPlease keep in mind, that in particular for samples of ordinary Portland cement (OPC) a clear and unambiguous identification/assigment of peaks remains a challenging task which cannot be achieved in each and every case by **TAInstCalorimetry**. It is left to the user draw meaningful scientific conclusions from the characteristics derived from this method.\n\n### Identifying peak onsets\n\nSimilarly, the peak onset characteristics are accessible via the ```get_peak_onsets```-method. The resulting plot is shown below.\n\n```python\n# get onsets\nonsets = tam.get_peak_onsets(\n gradient_threshold=0.000001,\n rolling=10,\n exclude_discarded_time=True,\n show_plot=True,\n regex=\"OPC\"\n)\n```\n\n\n### Plotting by Category\n\nFor introducing the idea of plotting calorimetry data \"by category\" another set of experimental data will be introduced. Next to the calorimetry data alone, information on investigated samples is supplied via an additional source file. In the present example via the file ```mini_metadata.csv```.\n\nTo begin with, a ```TAInstCalorimetry.tacalorimetry.Measurement```-object is initialized for selected files from the specified ````path```.\n\n```python\nimport pathlib\nfrom TAInstCalorimetry import tacalorimetry\n\n# path to experimental calorimetry files\npath = pathlib.Path().cwd().parent / \"TAInstCalorimetry\" / \"DATA\"\n\n# initialize TAInstCalorimetry.tacalorimetry.Measurement object\ntam_II = tacalorimetry.Measurement(\n path, regex=\"myexp.*\", show_info=True, cold_start=True, auto_clean=False\n)\n```\n\nNext, we need to connect the previously defined object to our metadata provided by the ```mini_metadata.csv```-file. To establish this mapping between experimental results and metadata, the file location, i.e. path, and the column name containing the exact(!) names of the calorimetry files needs to be passed to the ```add_metadata_source```-method. In our case, we declare the column ```experiment_nr``` for this purpose\n\n```python\n# add metadata\ntam.add_metadata_source(\"mini_metadata.csv\", \"experiment_nr\")\n```\n\nFinally, a plotting by category can be carried out by one or multiple categories as shown in the following.\n\n```python\n# define action by one category\ncategorize_by = \"cement_name\" # 'date', 'cement_amount_g', 'water_amount_g'\n\n# # define action by two or more categories\ncategorize_by = [\"date\", \"cement_name\"]\n\n# loop through plots via generator\nfor this_plot in tam.plot_by_category(categorize_by):\n # extract parts obtained from generator\n category_value, ax = this_plot\n # fine tuning of plot/cosmetics\n ax.set_ylim(0, 3)\n # show plot\n tacalorimetry.plt.show()\n```\n\nThis yields plots of the following kind.\n\n\n\n\n\n## Installation\n\nUse the package manager [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/) to install TAInstCalorimetry.\n\n```bash\npip install TAInstCalorimetry\n```\n\n## Contributing\nPull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.\n\nPlease make sure to update tests as appropriate.\n\nList of contributors:\n- [mj-hofmann](https://github.com/mj-hofmann)\n- [tgaedt](https://github.com/tgaedt)\n\n## License\n[GNU GPLv3](https://choosealicense.com/licenses/gpl-3.0/#)\n\n\n## Test\n\n\n## Code Styling\n\n[](https://github.com/psf/black)\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE",
"summary": "Handling TAM Air calorimetry files made easy.",
"version": "0.1.16",
"project_urls": {
"Documentation": "https://mj-hofmann.github.io/TAInstCalorimetry/",
"Homepage": "https://github.com/mj-hofmann/TAInstCalorimetry",
"Repository": "https://github.com/mj-hofmann/TAInstCalorimetry"
},
"split_keywords": [
"calorimetry",
"tam air",
"ta instruments",
"analysis",
"vizualisation"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "864f81700dad28be17b3a0190e056b2df32a834e083299065a9250f068fff646",
"md5": "a84e9fa793201f2d40ae4fb18c8fa28c",
"sha256": "34de6ed36376ee482fcdd8e718fc8a203cad30ff09f36db17d0eb9c466a621ba"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "tainstcalorimetry-0.1.16-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "a84e9fa793201f2d40ae4fb18c8fa28c",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.8.1,<3.12",
"size": 4497045,
"upload_time": "2024-01-03T06:49:13",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-01-03T06:49:13.545589Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/86/4f/81700dad28be17b3a0190e056b2df32a834e083299065a9250f068fff646/tainstcalorimetry-0.1.16-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "4d95c081ff1913c90f1d0564e30079ae4a1a50d7aac058352d2411c12ca51045",
"md5": "f6c6daa35ccb460e8f62c19143aa778e",
"sha256": "d5ddd4cb5162237ec49476d568e64e9f8d624d8e793927096f8f928fd316be26"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "tainstcalorimetry-0.1.16.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "f6c6daa35ccb460e8f62c19143aa778e",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.8.1,<3.12",
"size": 4501918,
"upload_time": "2024-01-03T06:49:31",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-01-03T06:49:31.638668Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/4d/95/c081ff1913c90f1d0564e30079ae4a1a50d7aac058352d2411c12ca51045/tainstcalorimetry-0.1.16.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-01-03 06:49:31",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "mj-hofmann",
"github_project": "TAInstCalorimetry",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"requirements": [],
"lcname": "tainstcalorimetry"
}
