| Name | texenv JSON |
| Version |
0.0.10
 JSON
JSON |
| download |
| home_page | None |
| Summary | latex inside a python virtual environment |
| upload_time | 2024-08-28 00:37:09 |
| maintainer | None |
| docs_url | None |
| author | None |
| requires_python | >=3.7 |
| license | None |
| keywords |
latex
tex
environment
|
| VCS |
 |
| bugtrack_url |
|
| requirements |
No requirements were recorded.
|
| Travis-CI |
No Travis.
|
| coveralls test coverage |
No coveralls.
|
# texenv
Create lightweight TeX virtual environments, and use Python methods in TeX code.
## Installation
`texenv` requires `texlive` to be installed on the system. Follow the reccommended install steps here:
https://www.tug.org/texlive/quickinstall.html
Ensure at least the "basic" TeXLive scheme is selected during installation. On linux, the "basic" scheme can be installed by using the `--scheme=basic` option in the install script. On Windows, the option is under the "Advanced Options" button in the installer.
`texenv` also requires an existing Python virtual environment, create one with the following command,
```bash
python -m venv .venv
```
Install `texenv` inside a Python virtual environment,
```bash
pip install texenv
```
To create a standalone TeX installation visible only to the current environment,
```bash
texenv init
```
This installs a bare-bones version of LaTeX in `.venv/tex`.
## Usage
To install packages into the TeX environment,
```bash
texenv install <package name>
```
The package name refers to the TeXLive package name, which is often different than the package name in [CTAN](https://ctan.org/). To find the TeXLive package name, search for the package on CTAN and find the "Contained in" section. The package name will be listed next to "TeXLive as".
For example,

To write all currently installed TeX packages in the environment to a file (excluding core packages required for LaTeX to run),
```bash
texenv freeze > texrequirements.txt
```
Or to print to the console:
```bash
texenv list
```
To synchronize the TeX installation with the packages found in a requirements file,
```bash
texenv sync texrequirements.txt
```
To compile a .tex file with pdflatex:
```bash
texenv run <.tex filepath>
```
`texenv` provides a preprocessor that can be used to call Python methods directly from TeX code. This is useful for generating figures and tables in python, or writing complicated macros that are difficult in LaTeX. The example below shows a simple use case:
Contents of `example.tex`:
```tex
\documentclass{article}
% required package for inserting figures
\usepackage{graphicx}
% import a python module either installed in the environment, or just a file in the same folder as the .tex file.
% In this case figures.py is in the same folder.
\import\figures
% preprocessor variables can be defined with \pydef followed by the variable name and value.
\pydef\cleanfig true
\begin{document}
% call a python method. Supports arguments and kwargs, but all are passed in as string types. The return type of
% the method must be a string as it is inserted directly into the TeX code.
\figures\figA[clean=\cleanfig, width=5in]
\end{document}
```
Contents of `figures.py`, located in the same directory as `example.tex`:
```python
from texenv.macros import figure
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def figA(clean="true", width="3in", **kwargs):
if clean == "false":
return figure(file="figA.pdf", width=width, **kwargs)
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(1, 1)
ax1.plot(range(11, 17))
fig.savefig("figA.pdf")
return figure(file="figA.pdf", width=width, **kwargs)
```
The `run` command invokes the preprocessor, and then calls `pdflatex` on the post-processed `.tex` file. The synctex file is modified after running `pdflatex` so the intermediate file is transparent to synctex.
```bash
texenv run example.tex
```
Full example:
[examples/macro_example/macro_example.tex](examples/macro_example/macro_example.tex)
## Slideshows
`texenv` provides a simple way to generate PDF slideshow presentations directly from Python. Matplotlib figures, images, and LaTeX code can be assembled together into a slide using the `Presentation` class:
```python
from texenv import Presentation, datatable
...
# text to place on slide. This is interpreted as an enumerate list if \item appears first in the string.
# Otherwise, the text is inserted directly as LaTeX code and supports math macros etc...
text = r"""
\item Bullet 1
\item Bullet 2
\[ \nabla \times \mathbf{E} = -\mu {\partial \mathbf{H} \over \partial t} \]
\[ \nabla \times \mathbf{H} = \varepsilon {\partial \mathbf{E} \over \partial t} \]
"""
# create a table with header names, and a format string applied to each cell
table = datatable(
np.arange(16).reshape((4, 4)), header_row=[f"Header {i}" for i in range(4)], formatter="{:.2f}"
)
pres = Presentation("example_slides.pdf")
# add the content to the first slide. The layout will be a 2x2 grid, with the figure centered along both rows in the
# second column. The text and table will split the first column.
pres.add_slide(
content=[[text, fig],
[table, None]],
title="Example TeX Slides",
width_ratio=(1, 2) # make the second column twice as wide as the first column.
)
pres.save()
```
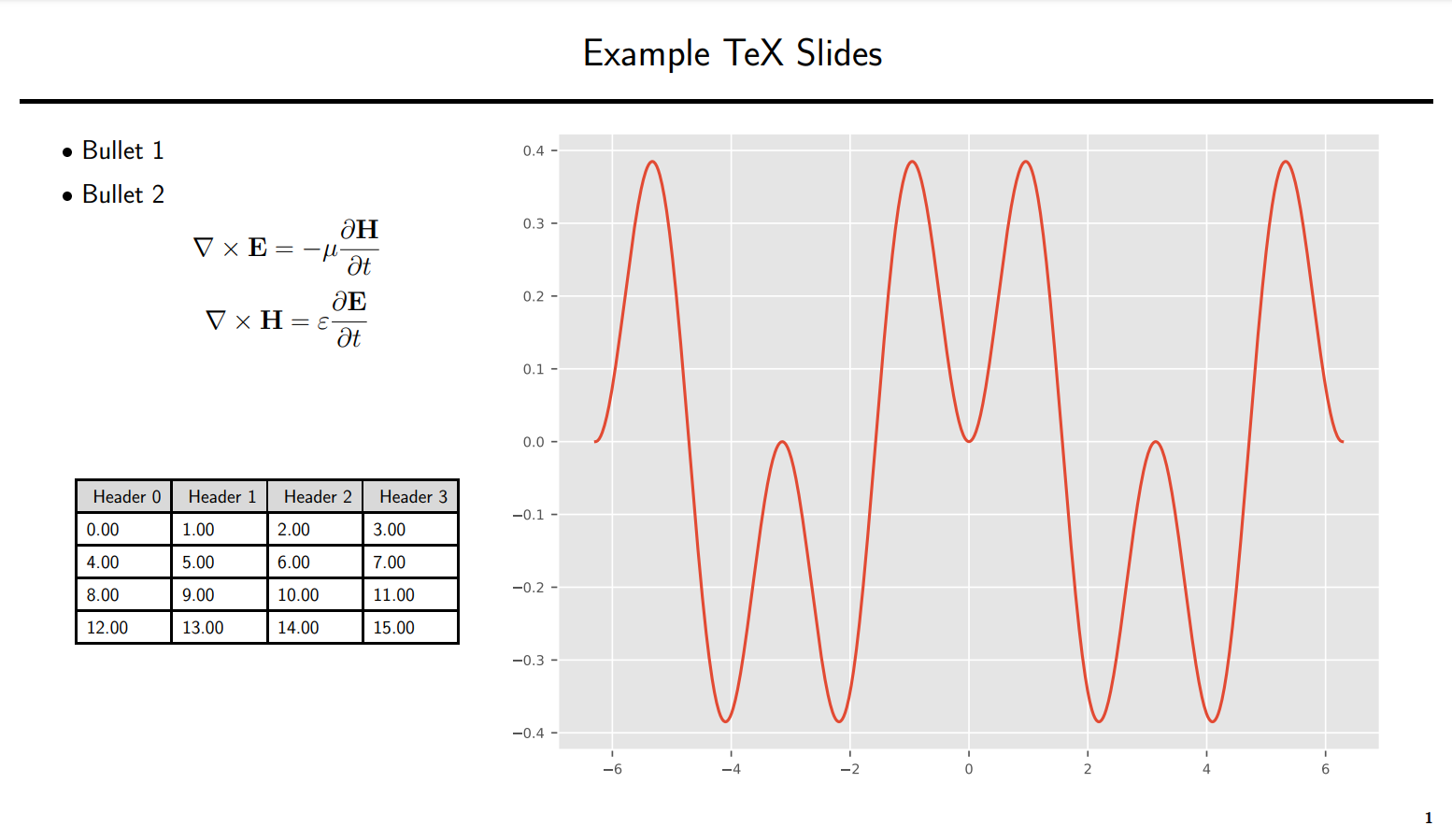
Full example:
[examples/slideshow/slideshow.py](examples/slideshow/slideshow.py)
## VSCode Setup
`texenv` is designed to work with the Latex Workshop extension in VSCode. The following settings in `settings.json` should configure `texenv` on Unix platforms. Note that the "build on save" feature only works when VSCode is opened as a workspace.
```json
"[latex]": {
"editor.formatOnSave": false,
"editor.wordWrap": "on"
},
"latex-workshop.latex.recipes": [
{
"name": "texenv",
"tools": [
"texenv"
]
},
],
"latex-workshop.latex.tools": [
{
"name": "texenv",
"command": "texenv",
"args": [
"run",
"%DOC_EXT%"
],
"env": {
"PATH": "%WORKSPACE_FOLDER%/.venv/tex/bin/x86_64-linux:%WORKSPACE_FOLDER%/.venv/bin"
}
}
],
"latex-workshop.view.pdf.internal.synctex.keybinding": "double-click",
"latex-workshop.latex.autoBuild.run": "onSave",
"latex-workshop.latex.autoClean.run": "never",
```
If the Unix platform is not `x86_64-linux`, change the `PATH` to match the platform.
On Windows, change `env` under `"latex-workshop.latex.tools"` to:
```json
"env": {
"Path": "%WORKSPACE_FOLDER%/.venv/tex/bin/windows;%WORKSPACE_FOLDER%/.venv/Scripts"
}
```
## Troubleshooting
Even if the full TexLive distribution is installed on the system, `texenv` installs a lightweight version of LaTeX into the virtual environment (equivalent to the "basic" TeXLive distribution). Most packages and fonts will need to be installed after the environment is initialized. A couple of useful TeXLive packages that will solve a lot of missing package errors:
```bash
texenv install collection-latexrecommended
texenv install collection-fontsrecommended
```
`texenv` includes a parser for the rather verbose pdflatex log files, and attempts to show only the relevant error messages. For example,
```
RuntimeError: pdfTEX Error on line: 9. LaTeX Error: File `hyphenat.sty' not found.
Emergency stop.
```
A link to the full log file is also included below the error message.
## License
`texenv` is licensed under the MIT License.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "texenv",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.7",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "latex, tex, environment",
"author": null,
"author_email": "Rick Lyon <rlyon14@gmail.com>",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d1/b3/dd5ad36f7ff5e36b53896fd4fc93ecb23250d09c541dd00bff07d5a5e900/texenv-0.0.10.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "# texenv\n\nCreate lightweight TeX virtual environments, and use Python methods in TeX code. \n\n## Installation\n\n`texenv` requires `texlive` to be installed on the system. Follow the reccommended install steps here: \nhttps://www.tug.org/texlive/quickinstall.html\n\nEnsure at least the \"basic\" TeXLive scheme is selected during installation. On linux, the \"basic\" scheme can be installed by using the `--scheme=basic` option in the install script. On Windows, the option is under the \"Advanced Options\" button in the installer. \n\n`texenv` also requires an existing Python virtual environment, create one with the following command,\n```bash\npython -m venv .venv\n```\n\nInstall `texenv` inside a Python virtual environment,\n\n```bash\npip install texenv\n```\n\nTo create a standalone TeX installation visible only to the current environment, \n```bash\ntexenv init\n```\nThis installs a bare-bones version of LaTeX in `.venv/tex`.\n\n## Usage\n\nTo install packages into the TeX environment,\n```bash\ntexenv install <package name>\n```\n\nThe package name refers to the TeXLive package name, which is often different than the package name in [CTAN](https://ctan.org/). To find the TeXLive package name, search for the package on CTAN and find the \"Contained in\" section. The package name will be listed next to \"TeXLive as\". \nFor example, \n\n\n\nTo write all currently installed TeX packages in the environment to a file (excluding core packages required for LaTeX to run),\n```bash\ntexenv freeze > texrequirements.txt\n```\n\nOr to print to the console:\n```bash\ntexenv list\n```\n\nTo synchronize the TeX installation with the packages found in a requirements file,\n```bash\ntexenv sync texrequirements.txt\n```\n\nTo compile a .tex file with pdflatex:\n```bash\ntexenv run <.tex filepath>\n```\n\n`texenv` provides a preprocessor that can be used to call Python methods directly from TeX code. This is useful for generating figures and tables in python, or writing complicated macros that are difficult in LaTeX. The example below shows a simple use case:\n\nContents of `example.tex`:\n```tex\n\\documentclass{article}\n\n% required package for inserting figures\n\\usepackage{graphicx}\n\n% import a python module either installed in the environment, or just a file in the same folder as the .tex file.\n% In this case figures.py is in the same folder.\n\\import\\figures\n\n% preprocessor variables can be defined with \\pydef followed by the variable name and value.\n\\pydef\\cleanfig true\n\n\\begin{document}\n \n % call a python method. Supports arguments and kwargs, but all are passed in as string types. The return type of \n % the method must be a string as it is inserted directly into the TeX code.\n \\figures\\figA[clean=\\cleanfig, width=5in]\n \n\\end{document}\n```\nContents of `figures.py`, located in the same directory as `example.tex`:\n```python\nfrom texenv.macros import figure\nimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n\ndef figA(clean=\"true\", width=\"3in\", **kwargs):\n \n if clean == \"false\":\n return figure(file=\"figA.pdf\", width=width, **kwargs)\n\n fig, ax1 = plt.subplots(1, 1)\n ax1.plot(range(11, 17))\n\n fig.savefig(\"figA.pdf\")\n\n return figure(file=\"figA.pdf\", width=width, **kwargs)\n\n```\n\nThe `run` command invokes the preprocessor, and then calls `pdflatex` on the post-processed `.tex` file. The synctex file is modified after running `pdflatex` so the intermediate file is transparent to synctex.\n\n```bash\ntexenv run example.tex\n```\n\nFull example:\n[examples/macro_example/macro_example.tex](examples/macro_example/macro_example.tex)\n\n## Slideshows\n\n`texenv` provides a simple way to generate PDF slideshow presentations directly from Python. Matplotlib figures, images, and LaTeX code can be assembled together into a slide using the `Presentation` class:\n\n```python\nfrom texenv import Presentation, datatable\n\n... \n\n# text to place on slide. This is interpreted as an enumerate list if \\item appears first in the string.\n# Otherwise, the text is inserted directly as LaTeX code and supports math macros etc...\ntext = r\"\"\"\n\\item Bullet 1\n\\item Bullet 2\n\\[ \\nabla \\times \\mathbf{E} = -\\mu {\\partial \\mathbf{H} \\over \\partial t} \\]\n\\[ \\nabla \\times \\mathbf{H} = \\varepsilon {\\partial \\mathbf{E} \\over \\partial t} \\]\n\"\"\"\n\n# create a table with header names, and a format string applied to each cell\ntable = datatable(\n np.arange(16).reshape((4, 4)), header_row=[f\"Header {i}\" for i in range(4)], formatter=\"{:.2f}\"\n)\n\npres = Presentation(\"example_slides.pdf\")\n\n# add the content to the first slide. The layout will be a 2x2 grid, with the figure centered along both rows in the\n# second column. The text and table will split the first column. \npres.add_slide(\n content=[[text, fig], \n [table, None]], \n title=\"Example TeX Slides\", \n width_ratio=(1, 2) # make the second column twice as wide as the first column.\n)\n\npres.save()\n```\n\n\n\nFull example:\n[examples/slideshow/slideshow.py](examples/slideshow/slideshow.py)\n\n\n## VSCode Setup\n\n`texenv` is designed to work with the Latex Workshop extension in VSCode. The following settings in `settings.json` should configure `texenv` on Unix platforms. Note that the \"build on save\" feature only works when VSCode is opened as a workspace.\n\n```json\n \"[latex]\": {\n \"editor.formatOnSave\": false,\n \"editor.wordWrap\": \"on\"\n },\n \"latex-workshop.latex.recipes\": [\n {\n \"name\": \"texenv\",\n \"tools\": [\n \"texenv\"\n ]\n },\n ],\n \"latex-workshop.latex.tools\": [\n {\n \"name\": \"texenv\",\n \"command\": \"texenv\",\n \"args\": [\n \"run\",\n \"%DOC_EXT%\"\n ],\n \"env\": {\n \"PATH\": \"%WORKSPACE_FOLDER%/.venv/tex/bin/x86_64-linux:%WORKSPACE_FOLDER%/.venv/bin\"\n }\n }\n ],\n \"latex-workshop.view.pdf.internal.synctex.keybinding\": \"double-click\",\n \"latex-workshop.latex.autoBuild.run\": \"onSave\",\n \"latex-workshop.latex.autoClean.run\": \"never\",\n```\n\nIf the Unix platform is not `x86_64-linux`, change the `PATH` to match the platform. \n\nOn Windows, change `env` under `\"latex-workshop.latex.tools\"` to:\n```json\n\"env\": {\n \"Path\": \"%WORKSPACE_FOLDER%/.venv/tex/bin/windows;%WORKSPACE_FOLDER%/.venv/Scripts\"\n}\n```\n\n## Troubleshooting\n\nEven if the full TexLive distribution is installed on the system, `texenv` installs a lightweight version of LaTeX into the virtual environment (equivalent to the \"basic\" TeXLive distribution). Most packages and fonts will need to be installed after the environment is initialized. A couple of useful TeXLive packages that will solve a lot of missing package errors:\n\n```bash\ntexenv install collection-latexrecommended\ntexenv install collection-fontsrecommended\n```\n\n`texenv` includes a parser for the rather verbose pdflatex log files, and attempts to show only the relevant error messages. For example, \n```\nRuntimeError: pdfTEX Error on line: 9. LaTeX Error: File `hyphenat.sty' not found.\nEmergency stop.\n```\n\nA link to the full log file is also included below the error message.\n\n## License\n\n`texenv` is licensed under the MIT License.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "latex inside a python virtual environment",
"version": "0.0.10",
"project_urls": {
"repository": "https://github.com/ricklyon/texenv"
},
"split_keywords": [
"latex",
" tex",
" environment"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "4e88593445295d7bfca3c17d9d91cd133f264748b5d3604107eae9e9034e4849",
"md5": "ba936fec9c737ac594659f0cc3822572",
"sha256": "df2196156139ed9b8ebfffc2f76a7f4cc91ccbf1c35bf3fb822fa1679cdf969f"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "texenv-0.0.10-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "ba936fec9c737ac594659f0cc3822572",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.7",
"size": 22255,
"upload_time": "2024-08-28T00:37:08",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-08-28T00:37:08.385263Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/4e/88/593445295d7bfca3c17d9d91cd133f264748b5d3604107eae9e9034e4849/texenv-0.0.10-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "d1b3dd5ad36f7ff5e36b53896fd4fc93ecb23250d09c541dd00bff07d5a5e900",
"md5": "e05ec052d7f9ab9c06ede9176ca43685",
"sha256": "354996d9f28b1c9acea1bd27e31b02af0c30f6a0fb0b40b499786db5dd09d047"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "texenv-0.0.10.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "e05ec052d7f9ab9c06ede9176ca43685",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.7",
"size": 23433,
"upload_time": "2024-08-28T00:37:09",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-08-28T00:37:09.780357Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/d1/b3/dd5ad36f7ff5e36b53896fd4fc93ecb23250d09c541dd00bff07d5a5e900/texenv-0.0.10.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-08-28 00:37:09",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "ricklyon",
"github_project": "texenv",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": false,
"lcname": "texenv"
}
