# Torch StainTools for Stain Normalization and Augmentation of Histopathological Images
[](https://github.com/CielAl/torch-staintools/actions/workflows/unittest.yml)
[](https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.10453806)
## Installation
* From Repository:
`pip install git+https://github.com/CielAl/torch-staintools.git`
* From PyPI:
`pip install torch-staintools`
## Documentation
Detail documentation regarding the code base can be found in the [GitPages](https://cielal.github.io/torch-staintools/).
## Citation
If this toolkit helps you in your publication, please feel free to cite with the following bibtex entry:
```bibtex
@software{zhou_2024_10453807,
author = {Zhou, Yufei},
title = {CielAl/torch-staintools: V1.0.3 Release},
month = jan,
year = 2024,
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {v1.0.3},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.10453807},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10453807}
}
```
## Description
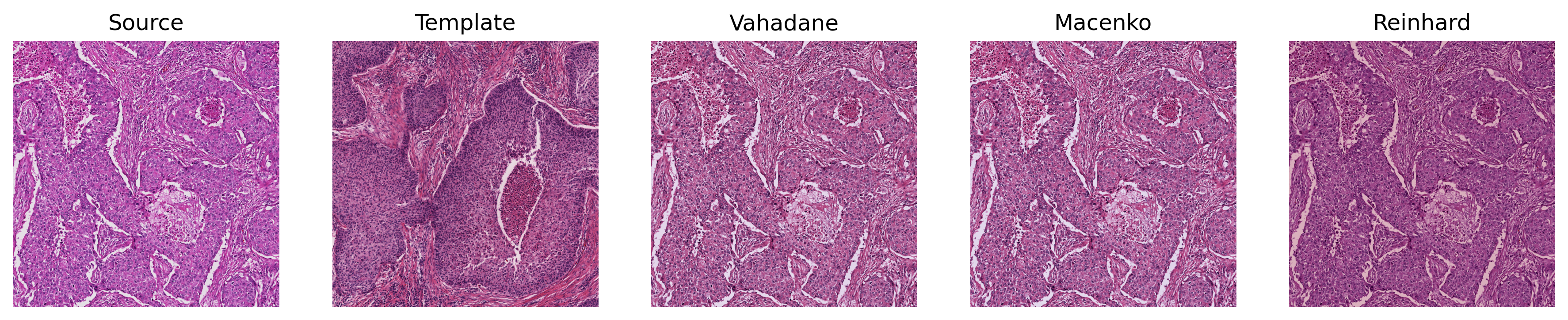
* Stain Normalization (Reinhard, Macenko, and Vahadane) for pytorch. Input tensors (fit and transform) must be in shape of `NxCxHxW`, with value scaled to [0, 1] in format of torch.float32.
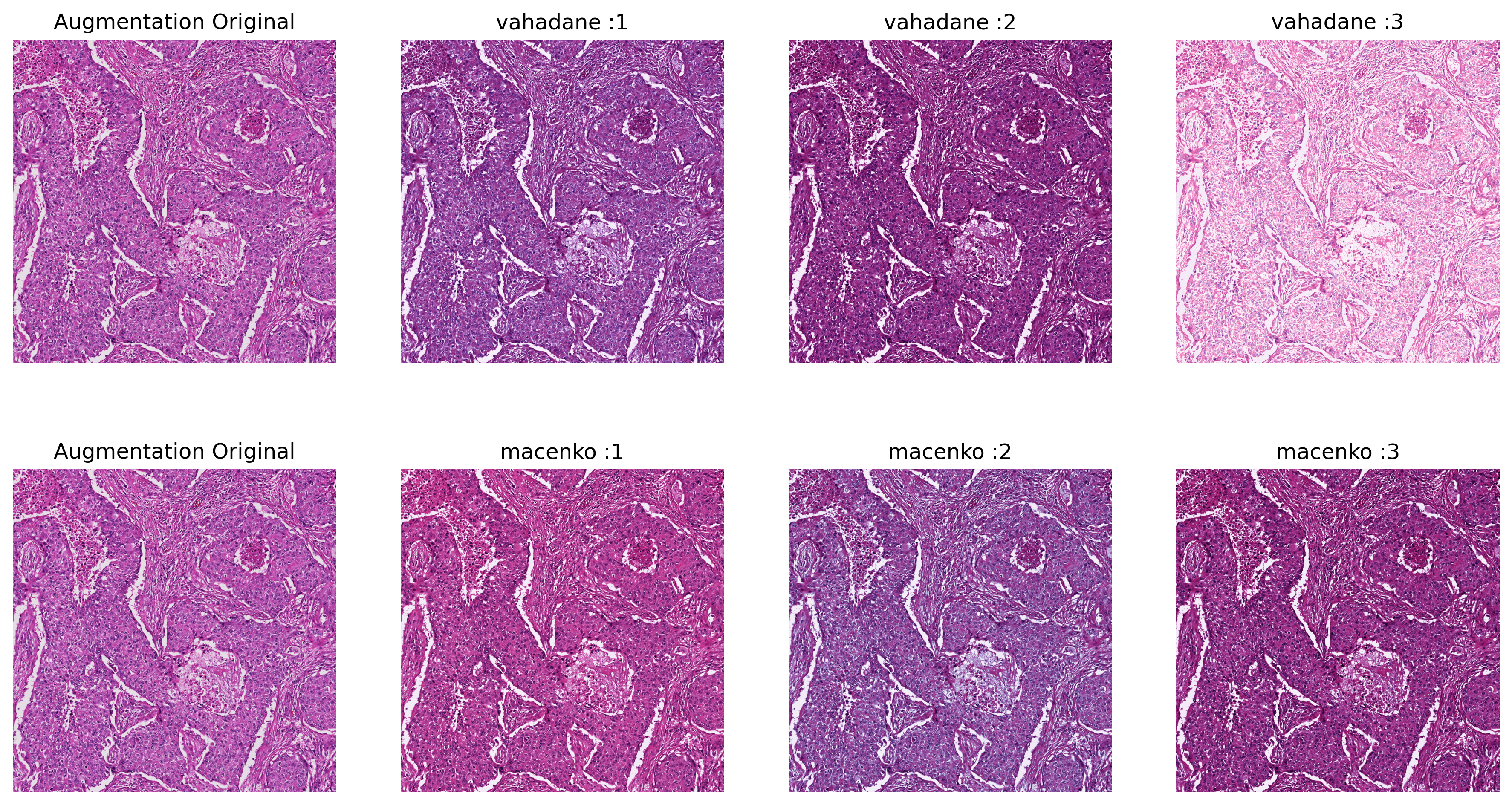
* Stain Augmentation using Macenko and Vahadane as stain extraction.
* Fast normalization/augmentation on GPU with stain matrices caching.
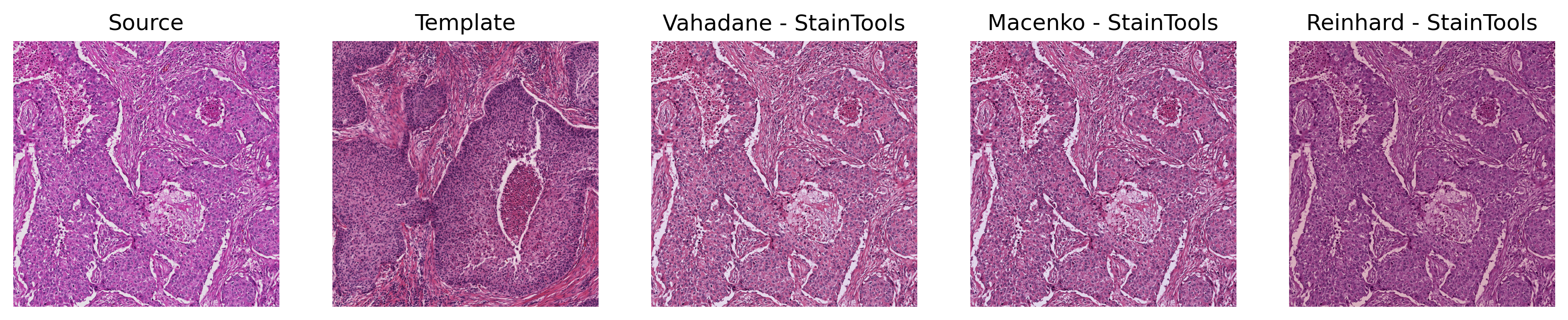
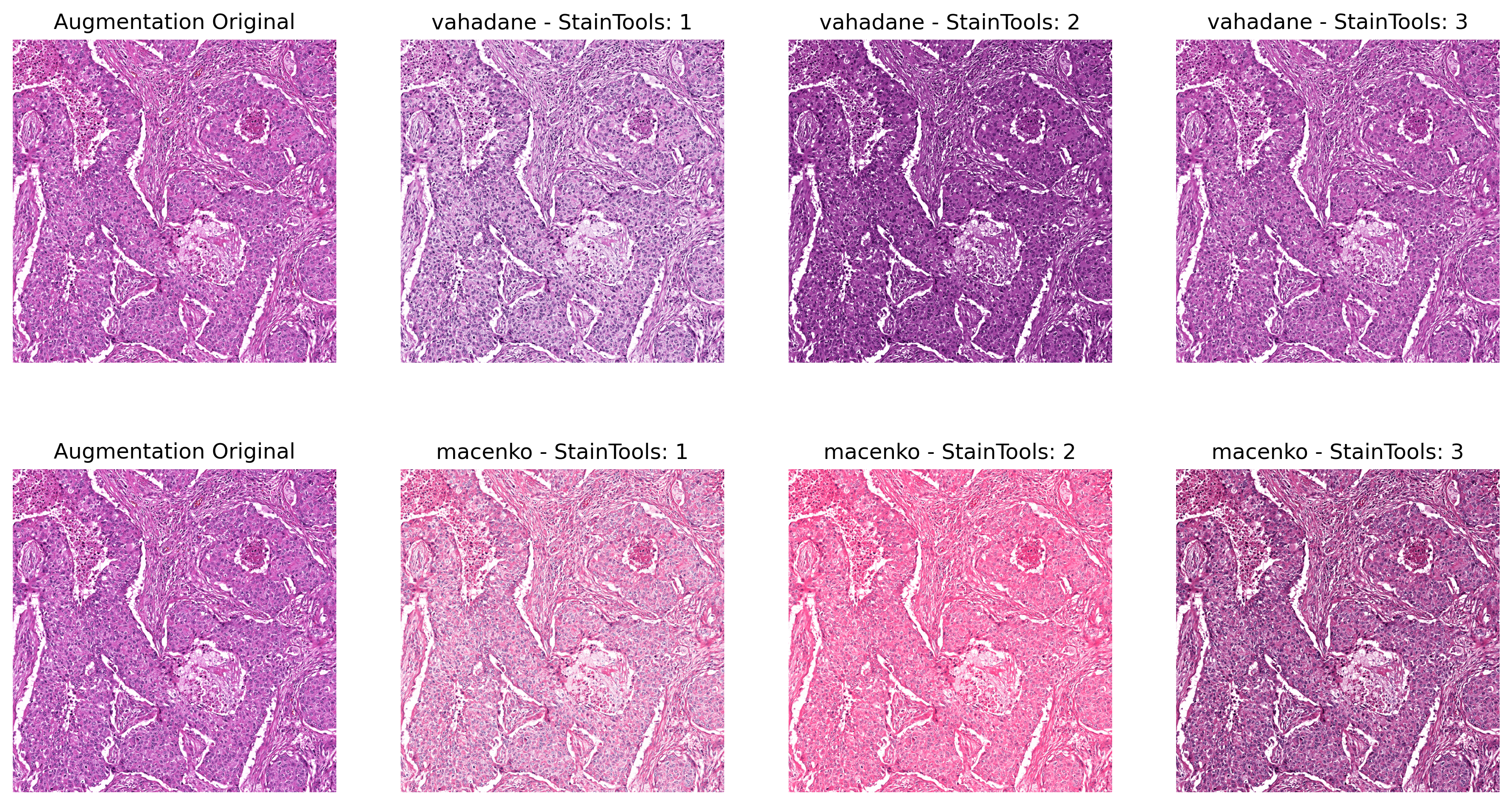
* Simulate the workflow in [StainTools library](https://github.com/Peter554/StainTools) but use the Iterative Shrinkage Thresholding Algorithm (ISTA), or optionally, the coordinate descent (CD) to solve the dictionary learning for stain matrix computation in Vahadane or Macenko (stain concentration only) algorithm. The implementation of ISTA and CD are derived from Cédric Walker's [torchvahadane](https://github.com/cwlkr/torchvahadane)
* Stain Concentration is solved via factorization of `Stain_Matrix x Concentration = Optical_Density`. For efficient sparse solution and more robust outcomes, ISTA can be applied. Alternatively, Least Square solver (LS) from `torch.linalg.lstsq` might be applied for faster non-sparse solution.
* No SPAMS requirement (which is a dependency in StainTools).
<br />
#### Sample Output of Torch-StainTools Normalization
#### Sample Output of StainTools
#### Sample Output of Torch-StainTools Augmentation (Repeat 3 times)
#### Sample Output of StainTools Augmentation (Repeat 3 times)
## Benchmark (No Stain Matrices Caching)
* Use the sample images under ./test_images (size `2500x2500x3`). Mean was computed from 7 runs (1 loop per run) using
timeit. Comparison between torch_stain_tools in CPU/GPU mode, as well as that of the StainTools Implementation.
* For consistency, use ISTA to compute the concentration.
### Transformation
| Method | CPU[s] | GPU[s] | StainTool[s] |
|:---------|:-------|:-------|:-------------|
| Vahadane | 119 | 7.5 | 20.9 |
| Macenko | 5.57 | 0.479 | 20.7 |
| Reinhard | 0.840 | 0.024 | 0.414 |
### Fitting
| Method | CPU[s] | GPU[s] | StainTool[s] |
|:---------|:-------|:-------|:-------------|
| Vahadane | 132 | 8.40 | 19.1 |
| Macenko | 6.99 | 0.064 | 20.0 |
| Reinhard | 0.422 | 0.011 | 0.076 |
### Batchified Concentration Computation
* Split the sample images under ./test_images (size `2500x2500x3`) into 81 non-overlapping `256x256x3` tiles as a batch.
* For the StainTools baseline, a for-loop is implemented to get the individual concentration of each of the numpy array of the 81 tiles.
*
| Method | CPU[s] | GPU[s] |
|:-------------------------------------|:-------|:----------|
| ISTA (`concentration_method='ista'`) | 3.12 | 1.24 |
| CD (`concentration_method='cd'`) | 29.3s | 4.87 |
| LS (`concentration_method='ls'`) | 0.221 | **0.097** |
| StainTools (SPAMS) | 16.6 | N/A |
## Use Cases and Tips
* For details, follow the example in demo.py
* Normalizers are wrapped as `torch.nn.Module`, working similarly to a standalone neural network. This means that for a workflow involving dataloader with multiprocessing, the normalizer
(Note that CUDA has poor support in multiprocessing, and therefore it may not be the best practice to perform GPU-accelerated on-the-fly stain transformation in pytorch's dataset/dataloader)
* `concentration_method='ls'` (i.e., `torch.linalg.lstsq`) can be efficient for batches of many smaller input (e.g., `256x256`) in terms of width and height. However, it may fail on GPU for a single larger input image (width and height). This happens even if the
the total number of pixels of the image is fewer than the aforementioned batch of multiple smaller input. Therefore, `concentration_method='ls'` could be suitable to deal with huge amount of small images in batches on the fly.
```python
import cv2
import torch
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor
from torch_staintools.normalizer import NormalizerBuilder
from torch_staintools.augmentor import AugmentorBuilder
import os
seed = 0
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)
# cpu or gpu
device = torch.device("cuda:0")
root_dir = '.'
target = cv2.imread(os.path.join(root_dir, 'test_images/TCGA-33-4547-01Z-00-DX7.'
'91be6f90-d9ab-4345-a3bd-91805d9761b9_8270_5932_0.png'))
# shape: Height (H) x Width (W) x Channel (C, for RGB C=3)
target = cv2.cvtColor(target, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
norm = cv2.imread(os.path.join(root_dir, 'test_images/TCGA-95-8494-01Z-00-DX1.'
'716299EF-71BB-4095-8F4D-F0C2252CE594_5932_5708_0.png'))
# shape: HWC
norm = cv2.cvtColor(norm, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# shape: Batch x Channel x Height x Width (BCHW); in the showcase here batch size is 1 (B=1) - scaled to [0, 1] torch.float32
target_tensor = ToTensor()(target).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
# shape: BCHW - scaled to [0, 1] torch.float32
norm_tensor = ToTensor()(norm).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
# ######## Normalization
# create the normalizer - using vahadane. Alternatively can use 'macenko' or 'reinhard'.
# note this is equivalent to:
# from torch_staintools.normalizer.separation import StainSeparation
# normalizer_vahadane = StainSeparation.build('vahadane', **arguments)
# we use the 'ista' (ISTA algorithm) to get the sparse solution of the factorization: STAIN_MATRIX * Concentration = OD
# alternatively, 'cd' (coordinate descent) and 'ls' (least square from torch.linalg) is available.
# Note that 'ls' does not can be much faster on batches of smaller input, but may fail on GPU for individual large input
# in terms of width and height, regardless of the batch size
normalizer_vahadane = NormalizerBuilder.build('vahadane', concentration_method='ista')
# move the normalizer to the device (CPU or GPU)
normalizer_vahadane = normalizer_vahadane.to(device)
# fit. For macenko and vahadane this step will compute the stain matrix and concentration
normalizer_vahadane.fit(target_tensor)
# transform
# BCHW - scaled to [0, 1] torch.float32
output = normalizer_vahadane(norm_tensor)
# ###### Augmentation
# augment by: alpha * concentration + beta, while alpha is uniformly randomly sampled from (1 - sigma_alpha, 1 + sigma_alpha),
# and beta is uniformly randomly sampled from (-sigma_beta, sigma_beta).
augmentor = AugmentorBuilder.build('vahadane',
# fix the random number generator seed for reproducibility.
rng=314159,
# the luminosity threshold to find the tissue region to augment
# if set to None means all pixels are treated as tissue
luminosity_threshold=0.8,
# herein we use 'ista' to compute the concentration
concentration_method='ista',
sigma_alpha=0.2,
sigma_beta=0.2, target_stain_idx=(0, 1),
# this allows to cache the stain matrix if it's too time-consuming to recompute.
# e.g., if using Vahadane algorithm
use_cache=True,
# size limit of cache. -1 means no limit (stain matrix is often small in size, e.g., 2 x 3)
cache_size_limit=-1,
# if specified, the augmentor will load the cached stain matrices from file system.
load_path=None,
)
# move augmentor to the corresponding device
augmentor = augmentor.to(device)
num_augment = 5
# multiple copies of different random augmentation of the same tile may be generated
for _ in range(num_augment):
# B x C x H x W
# use a list of Hashable key (e.g., str) to map the batch input to its corresponding stain matrix in cache.
# this key should be unique, e.g., using the filename of the input tile.
# leave it as None if no caching is intended, even if use_cache is enabled.
# note since the inputs are all batchified, the cache_key are in form of a list, with each element in the
# list corresponding to a data point in the batch.
aug_out = augmentor(norm_tensor, cache_keys=['some unique key'])
# do anything to the augmentation output
# dump the cache of stain matrices for future usage
augmentor.dump_cache('./cache.pickle')
# fast batch operation
tile_size = 512
tiles: torch.Tensor = norm_tensor.unfold(2, tile_size, tile_size)\
.unfold(3, tile_size, tile_size).reshape(1, 3, -1, tile_size, tile_size).squeeze(0).permute(1, 0, 2, 3).contiguous()
print(tiles.shape)
# use macenko normalization as example
normalizer_macenko = NormalizerBuilder.build('macenko', use_cache=True,
# use least square solver, along with cache, to perform
# normalization on-the-fly
concentration_method='ls')
normalizer_macenko = normalizer_macenko.to(device)
normalizer_macenko.fit(target_tensor)
normalizer_macenko(tiles)
```
## Stain Matrix Caching
As elaborated in the below in the running time benchmark of fitting, computation of stain matrix could be time-consuming.
Therefore, for both `Augmentor` and `Normalizer`, an in-memory (device-specified) cache is implemented to store the previously computed stain matrices (typically with size 2 x 3 in H&E/RGB cases).
To enable the feature, the `use_cache` must be enabled, should you use the factory builders to instantiate the `Normalizer` or `Augmentor`.
Upon the normalization/augmentation procedure, a unique cache_key corresponding to the image input must be defined (e.g., file name).
Since both `Normalizer` and `Augmentor` are designed as `torch.nn.Module` to accept batch inputs (tensors of shape B x C x H x W), a list of cache_keys must be given along with the batch image
inputs during the forward passing:
```
normalizer_vahadane(input_batch, cache_keys=list_of_keys_corresponding_to_input_batch)
augmentor(input_batch, cache_keys=list_of_keys_corresponding_to_input_batch)
```
The next time `Normalizer` or `Augmentor` process the images, the corresponding stain matrices will be queried and fetched from cache if they are stored already, rather than recomputing from scratch.
## Acknowledgments
* Some codes are derived from [torchvahadane](https://github.com/cwlkr/torchvahadane), [torchstain](https://github.com/EIDOSLAB/torchstain), and [StainTools](https://github.com/Peter554/StainTools)
* Sample images in the demo and ReadMe.md are selected from [The Cancer Genome Atlas Program(TCGA)](https://www.cancer.gov/ccg/research/genome-sequencing/tcga) dataset.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/CielAl/torch-staintools",
"name": "torch-staintools",
"maintainer": "",
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"maintainer_email": "",
"keywords": "",
"author": "Y Z",
"author_email": "cielmercy@gmail.com",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/74/e5/b6726e12d86e7c0264d5470cb7026f4e13d7111393e69228060e35191755/torch-staintools-1.0.4.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "# Torch StainTools for Stain Normalization and Augmentation of Histopathological Images\n\n[](https://github.com/CielAl/torch-staintools/actions/workflows/unittest.yml)\n[](https://zenodo.org/doi/10.5281/zenodo.10453806)\n\n## Installation\n\n* From Repository:\n\n`pip install git+https://github.com/CielAl/torch-staintools.git`\n\n* From PyPI:\n\n`pip install torch-staintools`\n\n## Documentation\nDetail documentation regarding the code base can be found in the [GitPages](https://cielal.github.io/torch-staintools/).\n\n## Citation\nIf this toolkit helps you in your publication, please feel free to cite with the following bibtex entry:\n```bibtex\n@software{zhou_2024_10453807,\n author = {Zhou, Yufei},\n title = {CielAl/torch-staintools: V1.0.3 Release},\n month = jan,\n year = 2024,\n publisher = {Zenodo},\n version = {v1.0.3},\n doi = {10.5281/zenodo.10453807},\n url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.10453807}\n}\n```\n\n## Description\n* Stain Normalization (Reinhard, Macenko, and Vahadane) for pytorch. Input tensors (fit and transform) must be in shape of `NxCxHxW`, with value scaled to [0, 1] in format of torch.float32.\n* Stain Augmentation using Macenko and Vahadane as stain extraction.\n* Fast normalization/augmentation on GPU with stain matrices caching.\n* Simulate the workflow in [StainTools library](https://github.com/Peter554/StainTools) but use the Iterative Shrinkage Thresholding Algorithm (ISTA), or optionally, the coordinate descent (CD) to solve the dictionary learning for stain matrix computation in Vahadane or Macenko (stain concentration only) algorithm. The implementation of ISTA and CD are derived from C\u00e9dric Walker's [torchvahadane](https://github.com/cwlkr/torchvahadane)\n* Stain Concentration is solved via factorization of `Stain_Matrix x Concentration = Optical_Density`. For efficient sparse solution and more robust outcomes, ISTA can be applied. Alternatively, Least Square solver (LS) from `torch.linalg.lstsq` might be applied for faster non-sparse solution.\n* No SPAMS requirement (which is a dependency in StainTools).\n\n<br />\n\n#### Sample Output of Torch-StainTools Normalization\n\n\n#### Sample Output of StainTools\n\n\n#### Sample Output of Torch-StainTools Augmentation (Repeat 3 times)\n\n\n#### Sample Output of StainTools Augmentation (Repeat 3 times)\n\n\n## Benchmark (No Stain Matrices Caching)\n* Use the sample images under ./test_images (size `2500x2500x3`). Mean was computed from 7 runs (1 loop per run) using\ntimeit. Comparison between torch_stain_tools in CPU/GPU mode, as well as that of the StainTools Implementation.\n* For consistency, use ISTA to compute the concentration.\n\n### Transformation\n\n| Method | CPU[s] | GPU[s] | StainTool[s] |\n|:---------|:-------|:-------|:-------------| \n| Vahadane | 119 | 7.5 | 20.9 | \n| Macenko | 5.57 | 0.479 | 20.7 |\n| Reinhard | 0.840 | 0.024 | 0.414 | \n\n### Fitting\n| Method | CPU[s] | GPU[s] | StainTool[s] |\n|:---------|:-------|:-------|:-------------| \n| Vahadane | 132 | 8.40 | 19.1 | \n| Macenko | 6.99 | 0.064 | 20.0 |\n| Reinhard | 0.422 | 0.011 | 0.076 | \n\n### Batchified Concentration Computation\n* Split the sample images under ./test_images (size `2500x2500x3`) into 81 non-overlapping `256x256x3` tiles as a batch.\n* For the StainTools baseline, a for-loop is implemented to get the individual concentration of each of the numpy array of the 81 tiles.\n* \n| Method | CPU[s] | GPU[s] | \n|:-------------------------------------|:-------|:----------| \n| ISTA (`concentration_method='ista'`) | 3.12 | 1.24 | \n| CD (`concentration_method='cd'`) | 29.3s | 4.87 | \n| LS (`concentration_method='ls'`) | 0.221 | **0.097** |\n| StainTools (SPAMS) | 16.6 | N/A |\n\n\n## Use Cases and Tips\n* For details, follow the example in demo.py\n* Normalizers are wrapped as `torch.nn.Module`, working similarly to a standalone neural network. This means that for a workflow involving dataloader with multiprocessing, the normalizer\n (Note that CUDA has poor support in multiprocessing, and therefore it may not be the best practice to perform GPU-accelerated on-the-fly stain transformation in pytorch's dataset/dataloader)\n\n* `concentration_method='ls'` (i.e., `torch.linalg.lstsq`) can be efficient for batches of many smaller input (e.g., `256x256`) in terms of width and height. However, it may fail on GPU for a single larger input image (width and height). This happens even if the \nthe total number of pixels of the image is fewer than the aforementioned batch of multiple smaller input. Therefore, `concentration_method='ls'` could be suitable to deal with huge amount of small images in batches on the fly.\n\n```python\nimport cv2\nimport torch\nfrom torchvision.transforms import ToTensor\nfrom torch_staintools.normalizer import NormalizerBuilder\nfrom torch_staintools.augmentor import AugmentorBuilder\nimport os\nseed = 0\ntorch.manual_seed(seed)\ntorch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)\n\n# cpu or gpu\ndevice = torch.device(\"cuda:0\")\n\nroot_dir = '.'\ntarget = cv2.imread(os.path.join(root_dir, 'test_images/TCGA-33-4547-01Z-00-DX7.'\n '91be6f90-d9ab-4345-a3bd-91805d9761b9_8270_5932_0.png'))\n# shape: Height (H) x Width (W) x Channel (C, for RGB C=3)\ntarget = cv2.cvtColor(target, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)\nnorm = cv2.imread(os.path.join(root_dir, 'test_images/TCGA-95-8494-01Z-00-DX1.'\n '716299EF-71BB-4095-8F4D-F0C2252CE594_5932_5708_0.png'))\n# shape: HWC\nnorm = cv2.cvtColor(norm, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)\n\n\n# shape: Batch x Channel x Height x Width (BCHW); in the showcase here batch size is 1 (B=1) - scaled to [0, 1] torch.float32\ntarget_tensor = ToTensor()(target).unsqueeze(0).to(device)\n\n# shape: BCHW - scaled to [0, 1] torch.float32\nnorm_tensor = ToTensor()(norm).unsqueeze(0).to(device)\n\n# ######## Normalization\n# create the normalizer - using vahadane. Alternatively can use 'macenko' or 'reinhard'.\n# note this is equivalent to:\n# from torch_staintools.normalizer.separation import StainSeparation\n# normalizer_vahadane = StainSeparation.build('vahadane', **arguments)\n\n# we use the 'ista' (ISTA algorithm) to get the sparse solution of the factorization: STAIN_MATRIX * Concentration = OD\n# alternatively, 'cd' (coordinate descent) and 'ls' (least square from torch.linalg) is available.\n# Note that 'ls' does not can be much faster on batches of smaller input, but may fail on GPU for individual large input \n# in terms of width and height, regardless of the batch size\nnormalizer_vahadane = NormalizerBuilder.build('vahadane', concentration_method='ista')\n# move the normalizer to the device (CPU or GPU)\nnormalizer_vahadane = normalizer_vahadane.to(device)\n# fit. For macenko and vahadane this step will compute the stain matrix and concentration\nnormalizer_vahadane.fit(target_tensor)\n# transform\n# BCHW - scaled to [0, 1] torch.float32\noutput = normalizer_vahadane(norm_tensor)\n\n# ###### Augmentation\n# augment by: alpha * concentration + beta, while alpha is uniformly randomly sampled from (1 - sigma_alpha, 1 + sigma_alpha),\n# and beta is uniformly randomly sampled from (-sigma_beta, sigma_beta).\naugmentor = AugmentorBuilder.build('vahadane',\n # fix the random number generator seed for reproducibility.\n rng=314159,\n # the luminosity threshold to find the tissue region to augment\n # if set to None means all pixels are treated as tissue\n luminosity_threshold=0.8,\n # herein we use 'ista' to compute the concentration\n concentration_method='ista',\n sigma_alpha=0.2,\n sigma_beta=0.2, target_stain_idx=(0, 1),\n # this allows to cache the stain matrix if it's too time-consuming to recompute.\n # e.g., if using Vahadane algorithm\n use_cache=True,\n # size limit of cache. -1 means no limit (stain matrix is often small in size, e.g., 2 x 3)\n cache_size_limit=-1,\n # if specified, the augmentor will load the cached stain matrices from file system.\n load_path=None,\n )\n# move augmentor to the corresponding device\naugmentor = augmentor.to(device)\n\nnum_augment = 5\n# multiple copies of different random augmentation of the same tile may be generated\nfor _ in range(num_augment):\n # B x C x H x W\n # use a list of Hashable key (e.g., str) to map the batch input to its corresponding stain matrix in cache.\n # this key should be unique, e.g., using the filename of the input tile.\n # leave it as None if no caching is intended, even if use_cache is enabled.\n # note since the inputs are all batchified, the cache_key are in form of a list, with each element in the \n # list corresponding to a data point in the batch.\n aug_out = augmentor(norm_tensor, cache_keys=['some unique key'])\n # do anything to the augmentation output\n \n# dump the cache of stain matrices for future usage\naugmentor.dump_cache('./cache.pickle')\n\n# fast batch operation\ntile_size = 512\ntiles: torch.Tensor = norm_tensor.unfold(2, tile_size, tile_size)\\\n .unfold(3, tile_size, tile_size).reshape(1, 3, -1, tile_size, tile_size).squeeze(0).permute(1, 0, 2, 3).contiguous()\nprint(tiles.shape)\n# use macenko normalization as example\nnormalizer_macenko = NormalizerBuilder.build('macenko', use_cache=True,\n # use least square solver, along with cache, to perform\n # normalization on-the-fly\n concentration_method='ls')\nnormalizer_macenko = normalizer_macenko.to(device)\nnormalizer_macenko.fit(target_tensor)\nnormalizer_macenko(tiles)\n\n```\n## Stain Matrix Caching\nAs elaborated in the below in the running time benchmark of fitting, computation of stain matrix could be time-consuming.\nTherefore, for both `Augmentor` and `Normalizer`, an in-memory (device-specified) cache is implemented to store the previously computed stain matrices (typically with size 2 x 3 in H&E/RGB cases).\nTo enable the feature, the `use_cache` must be enabled, should you use the factory builders to instantiate the `Normalizer` or `Augmentor`.\nUpon the normalization/augmentation procedure, a unique cache_key corresponding to the image input must be defined (e.g., file name).\nSince both `Normalizer` and `Augmentor` are designed as `torch.nn.Module` to accept batch inputs (tensors of shape B x C x H x W), a list of cache_keys must be given along with the batch image\ninputs during the forward passing:\n```\nnormalizer_vahadane(input_batch, cache_keys=list_of_keys_corresponding_to_input_batch)\naugmentor(input_batch, cache_keys=list_of_keys_corresponding_to_input_batch)\n\n```\nThe next time `Normalizer` or `Augmentor` process the images, the corresponding stain matrices will be queried and fetched from cache if they are stored already, rather than recomputing from scratch.\n\n\n## Acknowledgments\n* Some codes are derived from [torchvahadane](https://github.com/cwlkr/torchvahadane), [torchstain](https://github.com/EIDOSLAB/torchstain), and [StainTools](https://github.com/Peter554/StainTools)\n* Sample images in the demo and ReadMe.md are selected from [The Cancer Genome Atlas Program(TCGA)](https://www.cancer.gov/ccg/research/genome-sequencing/tcga) dataset.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "MIT",
"summary": "GPU-accelerated stain normalization and augmentation",
"version": "1.0.4",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/CielAl/torch-staintools"
},
"split_keywords": [],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "90ffd801fc1c9708612a1ac243ae79d25d7f8a72208f50cea286bf0a02931856",
"md5": "62b4c5901c3e91d0d87f652ce5c94ec5",
"sha256": "55bcb290e9a6fc193abb8cba714e014e29f03f5156985dbc45af750cc3837e91"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "torch_staintools-1.0.4-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "62b4c5901c3e91d0d87f652ce5c94ec5",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"size": 47878,
"upload_time": "2024-01-12T11:44:05",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-01-12T11:44:05.953314Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/90/ff/d801fc1c9708612a1ac243ae79d25d7f8a72208f50cea286bf0a02931856/torch_staintools-1.0.4-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "74e5b6726e12d86e7c0264d5470cb7026f4e13d7111393e69228060e35191755",
"md5": "47215465b7c98ccdf258a919021bbc30",
"sha256": "40bb5b541bc8e240212aa2753d821137cebc19c621342fdeca224f064e6a73f5"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "torch-staintools-1.0.4.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "47215465b7c98ccdf258a919021bbc30",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.10",
"size": 38538,
"upload_time": "2024-01-12T11:44:07",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-01-12T11:44:07.173732Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/74/e5/b6726e12d86e7c0264d5470cb7026f4e13d7111393e69228060e35191755/torch-staintools-1.0.4.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-01-12 11:44:07",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "CielAl",
"github_project": "torch-staintools",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"requirements": [],
"lcname": "torch-staintools"
}
