# visualkeras for Keras / TensorFlow
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/visualkeras)
[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/visualkeras)
## Introduction
Visualkeras is a Python package to help visualize Keras (either standalone or included in tensorflow) neural network architectures. It allows easy styling to fit most
needs. This module supports layered style architecture generation which is great for CNNs (Convolutional Neural
Networks), and a graph style architecture, which works great for most models including plain feed-forward networks.
For help in citing this project, refer [here](#citation-header).
## Model Support
| Mode | Sequential | Functional | Subclassed models |
|---|---|---|---|
| `visualkeras.layered_view()` | yes<sup>(1)</sup> | partially<sup>(1,2)</sup> | not tested |
| `visualkeras.graph_view()` | yes | yes | not tested |
<sup>1</sup>: Any tensor with more than 3 dimensions will be rendered as 3D tensor with elongated z-axis.
<sup>2</sup>: Only linear models where each layer has no more than one in or output. Non-linear models will be shown in sequential order.
## Version Support
We currently only support Keras versions 2 and above. We plan to add support for Keras version 1 in the coming updates.
## Installation
To install published releases from PyPi (last updated: July 19, 2024) execute:
```bash
pip install visualkeras
```
To update visualkeras to the latest version, add the `--upgrade` flag to the above commands.
If you want the latest (potentially unstable) features you can also directly install from the github master branch:
```bash
pip install git+https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras
```
## Usage
Generating neural network architectures is easy:
```python
import visualkeras
model = ...
visualkeras.layered_view(model).show() # display using your system viewer
visualkeras.layered_view(model, to_file='output.png') # write to disk
visualkeras.layered_view(model, to_file='output.png').show() # write and show
```
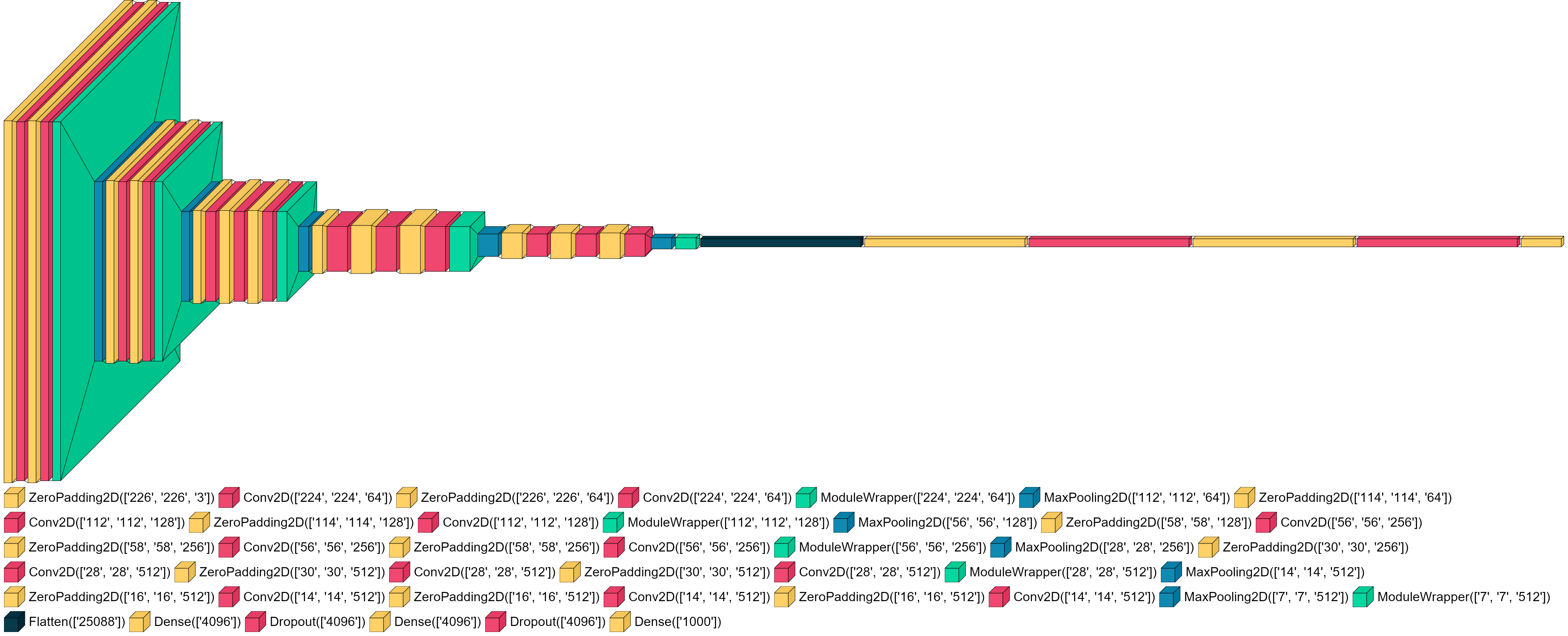
To help understand some of the most important parameters we are going to use a VGG16 CNN architecture (see [example.py](https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras/blob/master/examples/vgg16.py)).
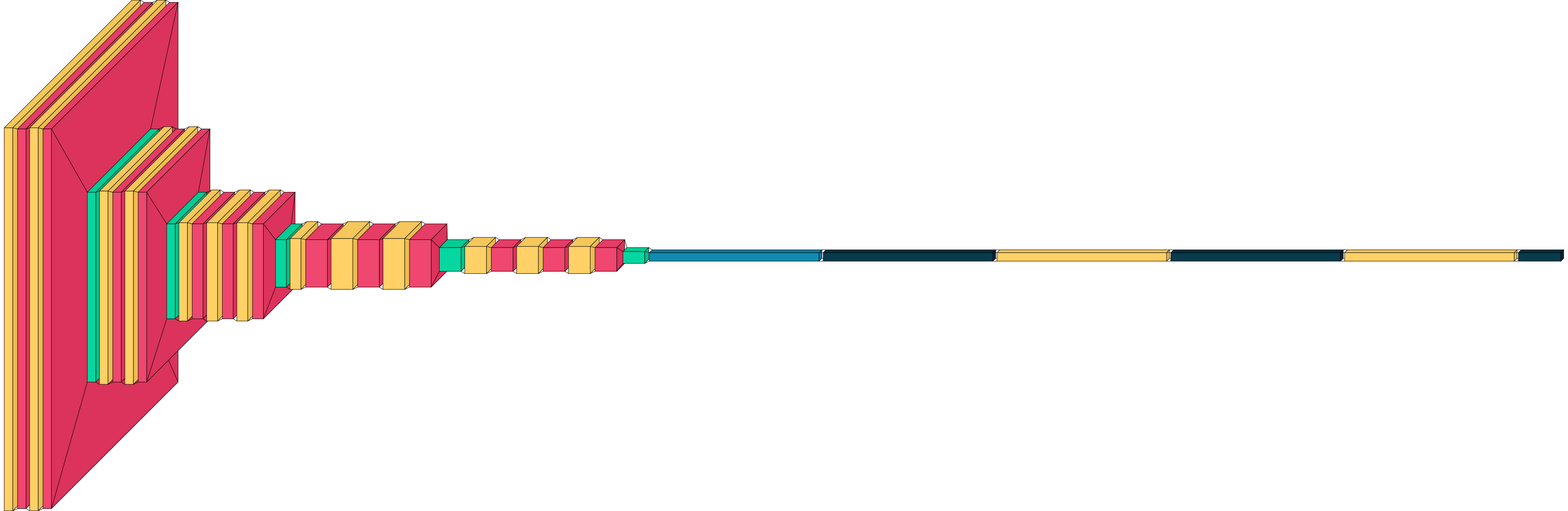
###### Default
```python
visualkeras.layered_view(model)
```
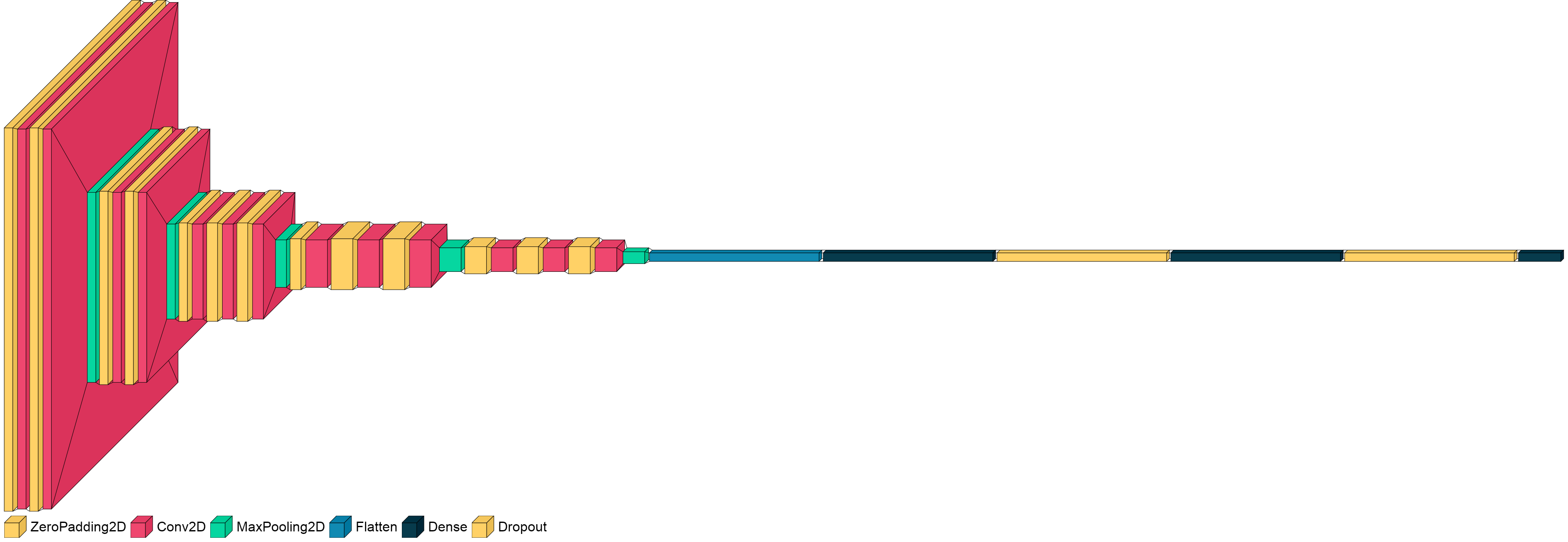
###### Legend
You can set the legend parameter to describe the relationship between color and layer types. It is also possible to pass
a custom `PIL.ImageFont` to use (or just leave it out and visualkeras will use the default PIL font). Please note that
you may need to provide the full path of the desired font depending on your OS.
```python
from PIL import ImageFont
font = ImageFont.truetype("arial.ttf", 32) # using comic sans is strictly prohibited!
visualkeras.layered_view(model, legend=True, font=font) # font is optional!
```
###### Flat Style
```python
visualkeras.layered_view(model, draw_volume=False)
```
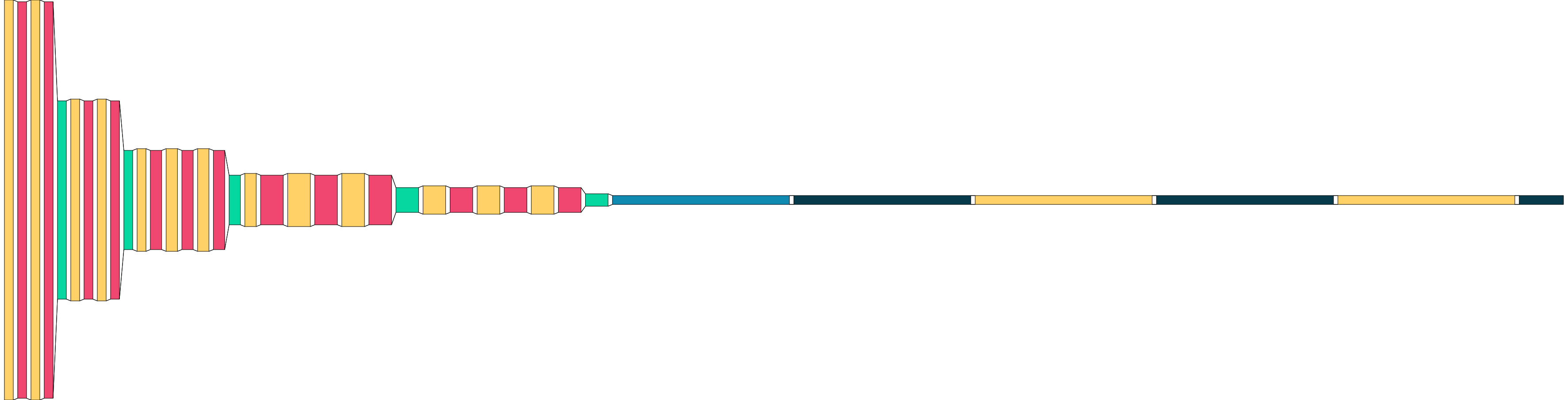

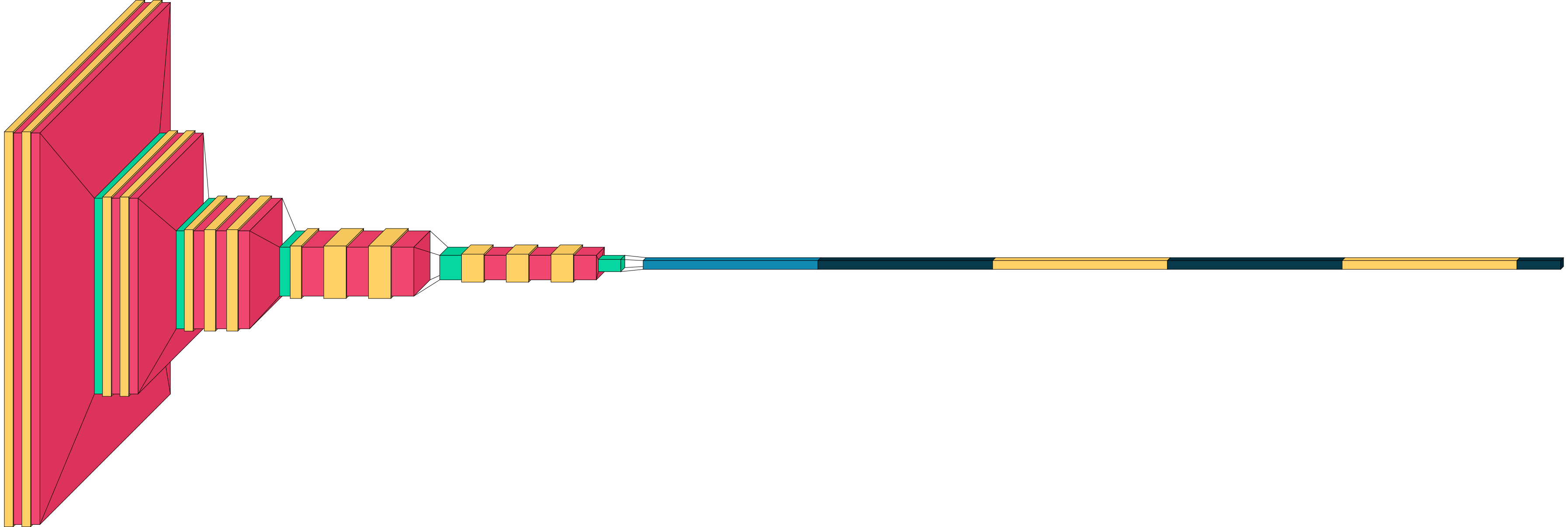
###### Spacing and logic grouping
The global distance between two layers can be controlled with `spacing`. To generate logical groups a special dummy
keras layer `visualkeras.SpacingDummyLayer()` can be added.
```python
model = ...
...
model.add(visualkeras.SpacingDummyLayer(spacing=100))
...
visualkeras.layered_view(model, spacing=0)
```
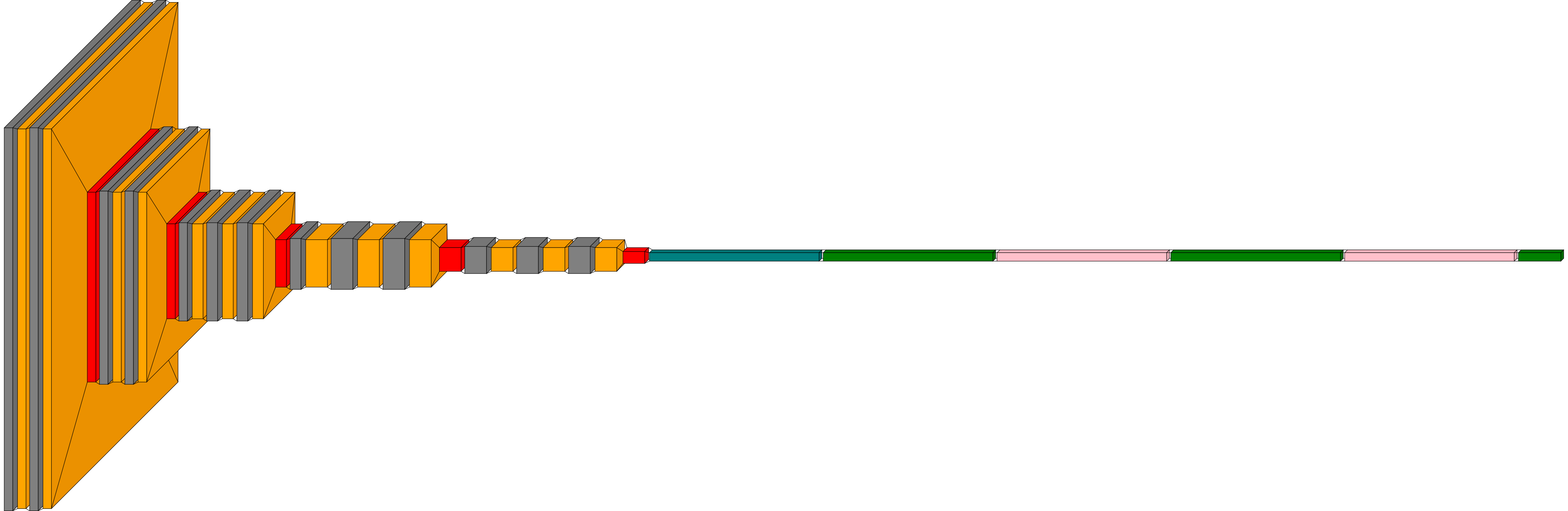
###### Custom color map
It is possible to provide a custom color map for fill and outline per layer type.
```python
from tensorflow.python.keras.layers import Dense, Conv2D, Flatten, Dropout, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D
from collections import defaultdict
color_map = defaultdict(dict)
color_map[Conv2D]['fill'] = 'orange'
color_map[ZeroPadding2D]['fill'] = 'gray'
color_map[Dropout]['fill'] = 'pink'
color_map[MaxPooling2D]['fill'] = 'red'
color_map[Dense]['fill'] = 'green'
color_map[Flatten]['fill'] = 'teal'
visualkeras.layered_view(model, color_map=color_map)
```
###### Hiding layers
Some models may consist of too many layers to visualize or to comprehend the model. In this case it can be helpful to
hide (ignore) certain layers of the keras model without modifying it. Visualkeras allows ignoring layers by their type
(`type_ignore`) or index in the keras layer sequence (`index_ignore`).
```python
visualkeras.layered_view(model, type_ignore=[ZeroPadding2D, Dropout, Flatten])
```
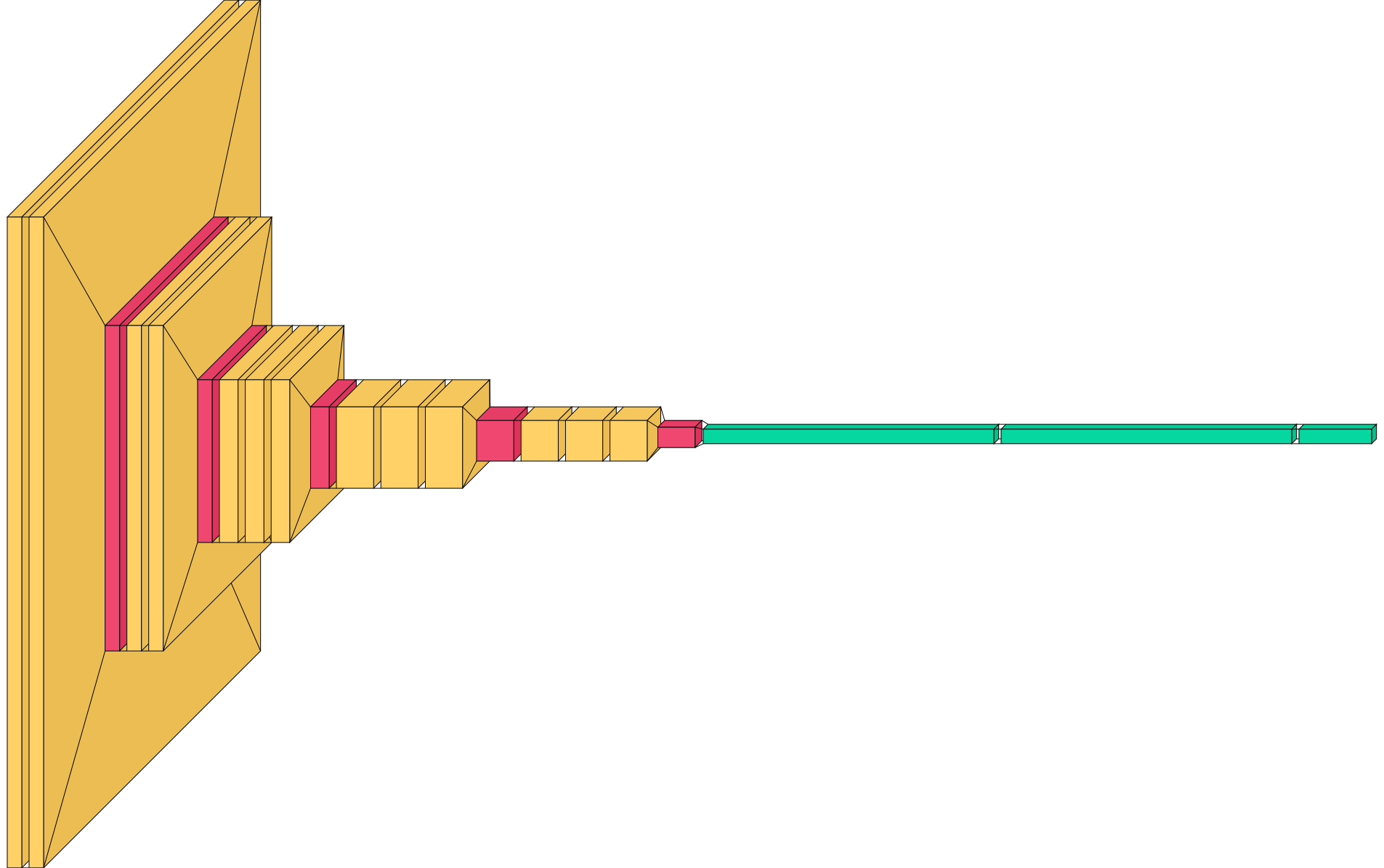
###### Scaling dimensions
Visualkeras computes the size of each layer by the output shape. Values are transformed into pixels. Then, scaling is
applied. By default visualkeras will enlarge the x and y dimension and reduce the size of the z dimensions as this has
deemed visually most appealing. However, it is possible to control scaling using `scale_xy` and `scale_z`. Additionally,
to prevent to small or large options minimum and maximum values can be set (`min_xy`, `min_z`, `max_xy`, `max_z`).
```python
visualkeras.layered_view(model, scale_xy=1, scale_z=1, max_z=1000)
```

_Note: Scaled models may hide the true complexity of a layer, but are visually more appealing._
###### Drawing information text
With the `text_callable` argument a function can be passed to the `layered_view` function which can be used to draw text below or above a specific layer. The function should have to following properties:
- Accepts two arguments: First the index of the layer in the model. This index ignores layers listed in `type_ignore`, `index_ignore` and also ignores layers of class `SpacingDummyLayer`. The second arguments is the layer object used in the model at the index given in the first argument
- Returns two arguments: The first return value is a string containing the text to be drawn. The second return value is a bool value indicating if the text is to be drawn above the box representing the layer.
The following function aims to describe the names of layers and their dimensionality. It would produce the output shown in the figure below:
```python
def text_callable(layer_index, layer):
# Every other piece of text is drawn above the layer, the first one below
above = bool(layer_index%2)
# Get the output shape of the layer
output_shape = [x for x in list(layer.output_shape) if x is not None]
# If the output shape is a list of tuples, we only take the first one
if isinstance(output_shape[0], tuple):
output_shape = list(output_shape[0])
output_shape = [x for x in output_shape if x is not None]
# Variable to store text which will be drawn
output_shape_txt = ""
# Create a string representation of the output shape
for ii in range(len(output_shape)):
output_shape_txt += str(output_shape[ii])
if ii < len(output_shape) - 2: # Add an x between dimensions, e.g. 3x3
output_shape_txt += "x"
if ii == len(output_shape) - 2: # Add a newline between the last two dimensions, e.g. 3x3 \n 64
output_shape_txt += "\n"
# Add the name of the layer to the text, as a new line
output_shape_txt += f"\n{layer.name}"
# Return the text value and if it should be drawn above the layer
return output_shape_txt, above
```
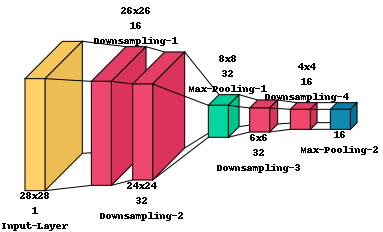
_Note: Use the `padding` argument to avoid long text being cut off at the left or right edge of the image. Also use `SpacingDummyLayers` to avoid interleaving text of different layers._
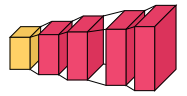
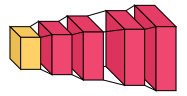
###### Reversed view
In certain use cases, it may be useful to reverse the view of the architecture so we look at the back of each layer. For example, when visualizing a decoder-like architecture. In such cases, we can switch draw_reversed to True. The following two figures show the same model with draw_reversed set to False and True, respectively.
```python
visualkeras.layered_view(model, draw_reversed=False) # Default behavior
```
```python
visualkeras.layered_view(model, draw_reversed=True)
```
###### Show layer dimensions (in the legend)
It is possible to display layer dimensions in the legend. To do so, set `legend=True` and `show_dimension=True` in `layered_view`. This is a simpler alternative to creating a callable for the `text_callable` argument to display dimensions above or below each layer.
```python
visualkeras.layered_view(model, legend=True, show_dimension=True)
```
## FAQ
###### Feature X documented here does not work
The main branch may be ahead of pypi. Consider upgrading to the latest (perhaps unstable) build as discussed in _Installation_.
###### Installing aggdraw fails
This is most likely due to missing gcc / g++ components (e.g. on Elementary OS). Try installing them via your package
manager, e.g.:
```bash
sudo apt-get install gcc
sudo apt-get install g++
```
###### .show() doesn't open a window
You have probably not configured your default image viewer. You can install imagemagick via most package managers:
```bash
sudo apt-get install imagemagick
```
## Future Features
These are features we plan to add in the future. If you're up for it, open an issue about a feature and code up a PR to add it!
- [ ] Multi-modal model support
- [ ] ResNet visualizations
- [ ] Concatenation visualizations
- [ ] More professional and academic visualizations for `graph_view` ([example](https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras/blob/master/figures/professional_diagram_sample.png))
- [ ] Annotate repeated layers or blocks (e.g., overarching double-arrow line w/ "3x" over it)
- [ ] Automated testing with GitHub actions
<h2 id="citation-header"> Citation </h2>
If you find this project helpful for your research please consider citing it in your publication as follows.
```
@misc{Gavrikov2020VisualKeras,
author = {Gavrikov, Paul},
title = {visualkeras},
year = {2020},
publisher = {GitHub},
journal = {GitHub repository},
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras}},
}
```
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras",
"name": "visualkeras",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.6",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": null,
"author": "Paul Gavrikov",
"author_email": "paul.gavrikov@hs-offenburg.de",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/b3/77/79dac1f5a765973d86167e02dc6973fda58198294fc24900f7450d3a7853/visualkeras-0.1.4.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "# visualkeras for Keras / TensorFlow\r\n\r\n[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/visualkeras)\r\n[](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/visualkeras)\r\n\r\n## Introduction\r\nVisualkeras is a Python package to help visualize Keras (either standalone or included in tensorflow) neural network architectures. It allows easy styling to fit most \r\nneeds. This module supports layered style architecture generation which is great for CNNs (Convolutional Neural \r\nNetworks), and a graph style architecture, which works great for most models including plain feed-forward networks.\r\nFor help in citing this project, refer [here](#citation-header).\r\n\r\n## Model Support\r\n\r\n| Mode | Sequential | Functional | Subclassed models |\r\n|---|---|---|---|\r\n| `visualkeras.layered_view()` | yes<sup>(1)</sup> | partially<sup>(1,2)</sup> | not tested |\r\n| `visualkeras.graph_view()` | yes | yes | not tested |\r\n\r\n<sup>1</sup>: Any tensor with more than 3 dimensions will be rendered as 3D tensor with elongated z-axis.\r\n\r\n<sup>2</sup>: Only linear models where each layer has no more than one in or output. Non-linear models will be shown in sequential order.\r\n\r\n## Version Support\r\n\r\nWe currently only support Keras versions 2 and above. We plan to add support for Keras version 1 in the coming updates.\r\n\r\n## Installation\r\nTo install published releases from PyPi (last updated: July 19, 2024) execute:\r\n```bash\r\npip install visualkeras\r\n```\r\nTo update visualkeras to the latest version, add the `--upgrade` flag to the above commands.\r\n\r\nIf you want the latest (potentially unstable) features you can also directly install from the github master branch:\r\n```bash\r\npip install git+https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras\r\n```\r\n\r\n## Usage\r\n\r\nGenerating neural network architectures is easy:\r\n```python\r\nimport visualkeras\r\n\r\nmodel = ...\r\n\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model).show() # display using your system viewer\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, to_file='output.png') # write to disk\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, to_file='output.png').show() # write and show\r\n```\r\n\r\nTo help understand some of the most important parameters we are going to use a VGG16 CNN architecture (see [example.py](https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras/blob/master/examples/vgg16.py)).\r\n\r\n###### Default\r\n```python\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model)\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Legend\r\n\r\nYou can set the legend parameter to describe the relationship between color and layer types. It is also possible to pass\r\na custom `PIL.ImageFont` to use (or just leave it out and visualkeras will use the default PIL font). Please note that \r\nyou may need to provide the full path of the desired font depending on your OS.\r\n\r\n```python\r\nfrom PIL import ImageFont\r\n\r\nfont = ImageFont.truetype(\"arial.ttf\", 32) # using comic sans is strictly prohibited!\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, legend=True, font=font) # font is optional!\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Flat Style\r\n```python\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, draw_volume=False)\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Spacing and logic grouping\r\nThe global distance between two layers can be controlled with `spacing`. To generate logical groups a special dummy \r\nkeras layer `visualkeras.SpacingDummyLayer()` can be added.\r\n```python\r\n\r\nmodel = ...\r\n...\r\nmodel.add(visualkeras.SpacingDummyLayer(spacing=100))\r\n...\r\n\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, spacing=0)\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Custom color map\r\nIt is possible to provide a custom color map for fill and outline per layer type.\r\n```python\r\nfrom tensorflow.python.keras.layers import Dense, Conv2D, Flatten, Dropout, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D\r\nfrom collections import defaultdict\r\n\r\ncolor_map = defaultdict(dict)\r\ncolor_map[Conv2D]['fill'] = 'orange'\r\ncolor_map[ZeroPadding2D]['fill'] = 'gray'\r\ncolor_map[Dropout]['fill'] = 'pink'\r\ncolor_map[MaxPooling2D]['fill'] = 'red'\r\ncolor_map[Dense]['fill'] = 'green'\r\ncolor_map[Flatten]['fill'] = 'teal'\r\n\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, color_map=color_map)\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Hiding layers\r\nSome models may consist of too many layers to visualize or to comprehend the model. In this case it can be helpful to \r\nhide (ignore) certain layers of the keras model without modifying it. Visualkeras allows ignoring layers by their type\r\n (`type_ignore`) or index in the keras layer sequence (`index_ignore`).\r\n```python\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, type_ignore=[ZeroPadding2D, Dropout, Flatten])\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Scaling dimensions\r\nVisualkeras computes the size of each layer by the output shape. Values are transformed into pixels. Then, scaling is \r\napplied. By default visualkeras will enlarge the x and y dimension and reduce the size of the z dimensions as this has \r\ndeemed visually most appealing. However, it is possible to control scaling using `scale_xy` and `scale_z`. Additionally, \r\nto prevent to small or large options minimum and maximum values can be set (`min_xy`, `min_z`, `max_xy`, `max_z`). \r\n```python\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, scale_xy=1, scale_z=1, max_z=1000)\r\n```\r\n\r\n_Note: Scaled models may hide the true complexity of a layer, but are visually more appealing._\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Drawing information text \r\nWith the `text_callable` argument a function can be passed to the `layered_view` function which can be used to draw text below or above a specific layer. The function should have to following properties:\r\n\r\n- Accepts two arguments: First the index of the layer in the model. This index ignores layers listed in `type_ignore`, `index_ignore` and also ignores layers of class `SpacingDummyLayer`. The second arguments is the layer object used in the model at the index given in the first argument\r\n\r\n- Returns two arguments: The first return value is a string containing the text to be drawn. The second return value is a bool value indicating if the text is to be drawn above the box representing the layer.\r\n\r\nThe following function aims to describe the names of layers and their dimensionality. It would produce the output shown in the figure below:\r\n```python\r\ndef text_callable(layer_index, layer):\r\n # Every other piece of text is drawn above the layer, the first one below\r\n above = bool(layer_index%2)\r\n\r\n # Get the output shape of the layer\r\n output_shape = [x for x in list(layer.output_shape) if x is not None]\r\n\r\n # If the output shape is a list of tuples, we only take the first one\r\n if isinstance(output_shape[0], tuple):\r\n output_shape = list(output_shape[0])\r\n output_shape = [x for x in output_shape if x is not None]\r\n\r\n # Variable to store text which will be drawn \r\n output_shape_txt = \"\"\r\n\r\n # Create a string representation of the output shape\r\n for ii in range(len(output_shape)):\r\n output_shape_txt += str(output_shape[ii])\r\n if ii < len(output_shape) - 2: # Add an x between dimensions, e.g. 3x3\r\n output_shape_txt += \"x\"\r\n if ii == len(output_shape) - 2: # Add a newline between the last two dimensions, e.g. 3x3 \\n 64\r\n output_shape_txt += \"\\n\"\r\n\r\n # Add the name of the layer to the text, as a new line\r\n output_shape_txt += f\"\\n{layer.name}\"\r\n\r\n # Return the text value and if it should be drawn above the layer\r\n return output_shape_txt, above\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n_Note: Use the `padding` argument to avoid long text being cut off at the left or right edge of the image. Also use `SpacingDummyLayers` to avoid interleaving text of different layers._\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Reversed view\r\nIn certain use cases, it may be useful to reverse the view of the architecture so we look at the back of each layer. For example, when visualizing a decoder-like architecture. In such cases, we can switch draw_reversed to True. The following two figures show the same model with draw_reversed set to False and True, respectively.\r\n\r\n```python\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, draw_reversed=False) # Default behavior\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n```python\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, draw_reversed=True)\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n###### Show layer dimensions (in the legend)\r\nIt is possible to display layer dimensions in the legend. To do so, set `legend=True` and `show_dimension=True` in `layered_view`. This is a simpler alternative to creating a callable for the `text_callable` argument to display dimensions above or below each layer.\r\n\r\n```python\r\nvisualkeras.layered_view(model, legend=True, show_dimension=True)\r\n```\r\n\r\n\r\n\r\n## FAQ\r\n\r\n###### Feature X documented here does not work\r\nThe main branch may be ahead of pypi. Consider upgrading to the latest (perhaps unstable) build as discussed in _Installation_. \r\n\r\n###### Installing aggdraw fails\r\nThis is most likely due to missing gcc / g++ components (e.g. on Elementary OS). Try installing them via your package \r\nmanager, e.g.:\r\n```bash\r\nsudo apt-get install gcc\r\nsudo apt-get install g++\r\n```\r\n\r\n###### .show() doesn't open a window\r\n\r\nYou have probably not configured your default image viewer. You can install imagemagick via most package managers:\r\n```bash\r\nsudo apt-get install imagemagick\r\n```\r\n\r\n## Future Features\r\nThese are features we plan to add in the future. If you're up for it, open an issue about a feature and code up a PR to add it!\r\n- [ ] Multi-modal model support\r\n- [ ] ResNet visualizations\r\n- [ ] Concatenation visualizations\r\n- [ ] More professional and academic visualizations for `graph_view` ([example](https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras/blob/master/figures/professional_diagram_sample.png))\r\n- [ ] Annotate repeated layers or blocks (e.g., overarching double-arrow line w/ \"3x\" over it)\r\n- [ ] Automated testing with GitHub actions\r\n\r\n<h2 id=\"citation-header\"> Citation </h2>\r\n\r\nIf you find this project helpful for your research please consider citing it in your publication as follows.\r\n```\r\n@misc{Gavrikov2020VisualKeras,\r\n author = {Gavrikov, Paul},\r\n title = {visualkeras},\r\n year = {2020},\r\n publisher = {GitHub},\r\n journal = {GitHub repository},\r\n howpublished = {\\url{https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras}},\r\n}\r\n```\r\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "Architecture visualization of Keras models",
"version": "0.1.4",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/paulgavrikov/visualkeras"
},
"split_keywords": [],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "9b6a7dc8a7da9ba0b6fcb8e4043e9665827a1a9e910f99425f94a5c51b924762",
"md5": "a4c8586d803358bac38ce531657bf2c1",
"sha256": "633fc1a3d781b5d9436beaef727f284628abf09b19ec47eb71639335a64c05a7"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "visualkeras-0.1.4-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "a4c8586d803358bac38ce531657bf2c1",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.6",
"size": 17272,
"upload_time": "2024-11-24T19:28:51",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-11-24T19:28:51.027857Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/9b/6a/7dc8a7da9ba0b6fcb8e4043e9665827a1a9e910f99425f94a5c51b924762/visualkeras-0.1.4-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "b37779dac1f5a765973d86167e02dc6973fda58198294fc24900f7450d3a7853",
"md5": "083c7f17759ab521a99af876835ae2f2",
"sha256": "dfef675857bc043fc7ad20191b40be178d4af009be32c6d48563db272e34b085"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "visualkeras-0.1.4.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "083c7f17759ab521a99af876835ae2f2",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.6",
"size": 20247,
"upload_time": "2024-11-24T19:28:52",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-11-24T19:28:52.710523Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/b3/77/79dac1f5a765973d86167e02dc6973fda58198294fc24900f7450d3a7853/visualkeras-0.1.4.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-11-24 19:28:52",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "paulgavrikov",
"github_project": "visualkeras",
"travis_ci": true,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"lcname": "visualkeras"
}

