
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/41725089)
# Visvis - the object oriented approach to visualization
[Visvis](http://github.com/almarklein/visvis) is a pure Python library
for visualization of 1D to 4D data in an object oriented way.
Essentially, visvis is an object oriented layer of Python on top of
OpenGl, thereby combining the power of OpenGl with the usability of
Python. A Matlab/Matplotlib-like interface in the form of a set of functions allows
easy creation of objects (e.g. `plot()`, `imshow()`, `volshow()`, `surf()`).
## Status
Visvis has been relatively stable for several years. I am still maintaining it
trying to make sure it keeps working, but do not plan on making any major changes. Visvis will not make use of modern OpenGL. It's API might be a bit idosyncratic (e.g. methods are UpperCamelCase) because I started working on Visvis before I knew about PEP8.
See [Vispy](https://github.com/vispy/vispy/) for a similar (but more modern) visualization library.
I am now working on [PyGfx](https://github.com/pygfx/pygfx), which is better in almost every way. A bit lower level though, but people are starting to build higher level API's on top of it ...
## Installation
Visvis is cross-platform and runs on Python 2.x and Python 3.x. It
depends on numpy, pyopengl.
Installation is best done via pip (``pip install visvis``) or conda (``conda install visvis``).
You also need a GUI backend, either of these will do:
* GLFW -> recommended, runs on asyncio, install using `pip install glfw`
* Qt: PySide6, Pyside2, Pyside, PyQt5, or PyQt4
* Wx
* GTK
* FLTK
## How visvis works
With visvis a range of different data can be visualized by simply adding
[world objects](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/cls_Wobject) to
a scene (i.e. an
[axes](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/cls_Axes)). These world
objects can be
anything from plots
([lines](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_plotting) with
markers), to
[images](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_images), 3D
rendered
[volumes](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_volumes), shaded
[meshes](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_meshes), or you
can program your own world object class.
If required, these data can also be
[moved](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_fourDimensions)
in time.
## Example
[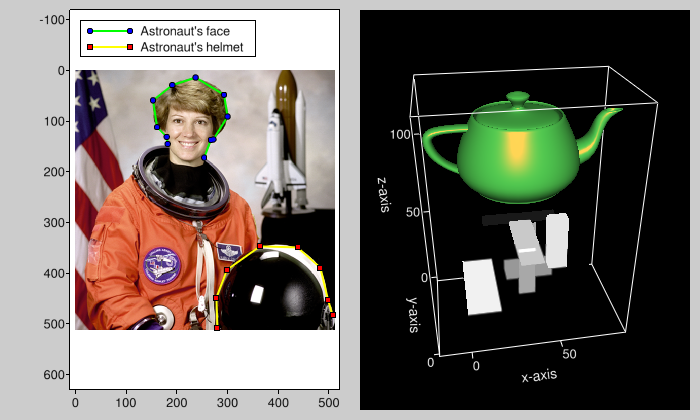](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_overview)
Click on the figure to see the [code](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_overview) and how one can interact with the figure.
## Documentation
The docs are on the [wiki](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki).
Online documentation is available for all
[classes](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/classes) and
[functions](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/functions). Any
questions can be asked in the visvis [discussion
group](http://groups.google.com/group/visvis).
At EuroScipy 2012, I gave a talk about Visvis. The long version of the
presentation can be seen [here](https://docs.google.com/presentation/pub?id=17J5IVIoh2zQk49ycYh__CYpi33aWi0oSljI_MnYByeg&start=false&loop=false&delayms=3000).
## License
Visvis makes use of the liberal BSD license. See license.txt for details.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "visvis",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=2.7",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "visualization, opengl, 2d, 3d, medical imaging",
"author": "Almar Klein",
"author_email": null,
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/4f/a3/9b438a534934c45861c01f8333f897c7679270f779af8b773cb9618c02e6/visvis-1.15.0.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "\n[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/41725089)\n\n# Visvis - the object oriented approach to visualization\n\n[Visvis](http://github.com/almarklein/visvis) is a pure Python library\nfor visualization of 1D to 4D data in an object oriented way.\nEssentially, visvis is an object oriented layer of Python on top of\nOpenGl, thereby combining the power of OpenGl with the usability of\nPython. A Matlab/Matplotlib-like interface in the form of a set of functions allows\neasy creation of objects (e.g. `plot()`, `imshow()`, `volshow()`, `surf()`).\n\n\n## Status\n\nVisvis has been relatively stable for several years. I am still maintaining it\ntrying to make sure it keeps working, but do not plan on making any major changes. Visvis will not make use of modern OpenGL. It's API might be a bit idosyncratic (e.g. methods are UpperCamelCase) because I started working on Visvis before I knew about PEP8.\n\nSee [Vispy](https://github.com/vispy/vispy/) for a similar (but more modern) visualization library.\n\nI am now working on [PyGfx](https://github.com/pygfx/pygfx), which is better in almost every way. A bit lower level though, but people are starting to build higher level API's on top of it ...\n\n\n## Installation\n\nVisvis is cross-platform and runs on Python 2.x and Python 3.x. It\ndepends on numpy, pyopengl.\n\nInstallation is best done via pip (``pip install visvis``) or conda (``conda install visvis``).\n\nYou also need a GUI backend, either of these will do:\n* GLFW -> recommended, runs on asyncio, install using `pip install glfw`\n* Qt: PySide6, Pyside2, Pyside, PyQt5, or PyQt4\n* Wx\n* GTK\n* FLTK\n\n\n## How visvis works\n\nWith visvis a range of different data can be visualized by simply adding\n[world objects](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/cls_Wobject) to\na scene (i.e. an\n[axes](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/cls_Axes)). These world\nobjects can be\nanything from plots\n([lines](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_plotting) with\nmarkers), to\n[images](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_images), 3D\nrendered\n[volumes](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_volumes), shaded\n[meshes](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_meshes), or you\ncan program your own world object class.\nIf required, these data can also be\n[moved](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_fourDimensions)\nin time.\n\n\n## Example\n[](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_overview)\n\nClick on the figure to see the [code](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/example_overview) and how one can interact with the figure.\n\n\n## Documentation\n\nThe docs are on the [wiki](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki).\nOnline documentation is available for all\n[classes](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/classes) and\n[functions](https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki/functions). Any\nquestions can be asked in the visvis [discussion\ngroup](http://groups.google.com/group/visvis).\n\nAt EuroScipy 2012, I gave a talk about Visvis. The long version of the\npresentation can be seen [here](https://docs.google.com/presentation/pub?id=17J5IVIoh2zQk49ycYh__CYpi33aWi0oSljI_MnYByeg&start=false&loop=false&delayms=3000).\n\n\n## License\n\nVisvis makes use of the liberal BSD license. See license.txt for details.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "The object oriented approach to visualization ",
"version": "1.15.0",
"project_urls": {
"Documentation": "https://github.com/almarklein/visvis/wiki",
"Homepage": "https://github.com/almarklein/visvis",
"Repository": "https://github.com/almarklein/visvis"
},
"split_keywords": [
"visualization",
" opengl",
" 2d",
" 3d",
" medical imaging"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "93717432d9b5c385e586591dc94dff00a9829e3f5a92415e5179405f079f4340",
"md5": "cd1d0d7043a4247f6bf0dacdb3142196",
"sha256": "ca884b5e025ca1565a91de310d473d08deae9428bc654ff459ff554c03322168"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "visvis-1.15.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "cd1d0d7043a4247f6bf0dacdb3142196",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py2.py3",
"requires_python": ">=2.7",
"size": 4888963,
"upload_time": "2025-01-20T15:43:52",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-01-20T15:43:52.970235Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/93/71/7432d9b5c385e586591dc94dff00a9829e3f5a92415e5179405f079f4340/visvis-1.15.0-py2.py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": null,
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "4fa39b438a534934c45861c01f8333f897c7679270f779af8b773cb9618c02e6",
"md5": "c1c748b6d63c07018e1ad30592706937",
"sha256": "aa013c62ea54ae4d170096e1fced7c3697b1d05c2fe6b38e822af0a986422a39"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "visvis-1.15.0.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "c1c748b6d63c07018e1ad30592706937",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=2.7",
"size": 4830638,
"upload_time": "2025-01-20T15:43:57",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2025-01-20T15:43:57.672992Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/4f/a3/9b438a534934c45861c01f8333f897c7679270f779af8b773cb9618c02e6/visvis-1.15.0.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2025-01-20 15:43:57",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "almarklein",
"github_project": "visvis",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"lcname": "visvis"
}
