
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/248040662)
[](https://github.com/pha4ge/hAMRonization/blob/master/docs/subgrant/PHA4GE_AMR_SubGrant_Documentation.pdf)
[](https://github.com/pha4ge/hAMRonization/blob/master/docs/subgrant/PHA4GE_hAMRonization_espan%CC%83ol.pdf)
# hAMRonization
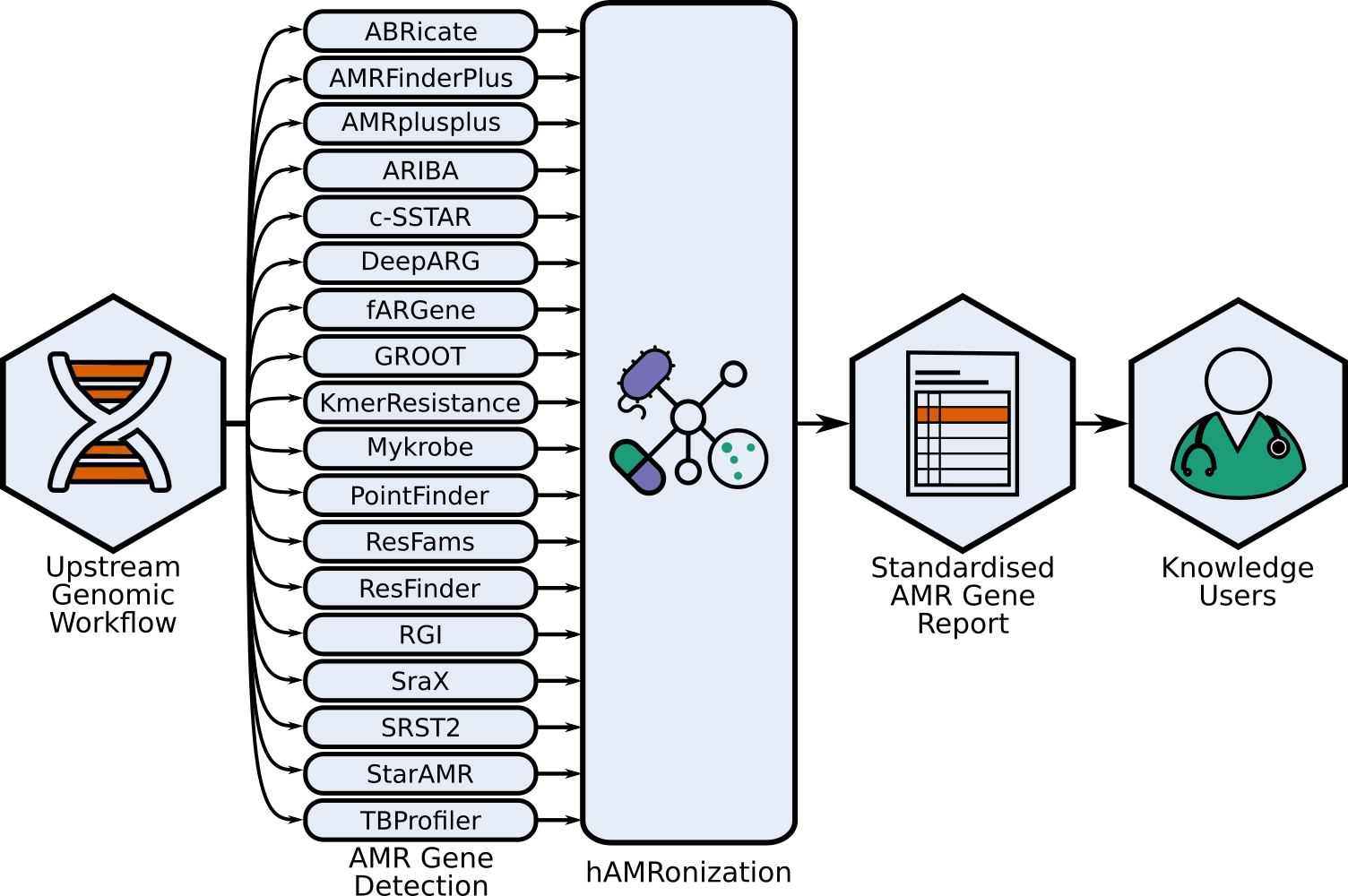
This repo contains the hAMRonization module and CLI parser tools combine the outputs of
18 (as of 2022-09-25) disparate antimicrobial resistance gene detection tools into a single unified format.
This is an implementation of the [hAMRonization AMR detection specification scheme](docs/hAMRonization_specification_details.csv) which supports gene presence/absence resistance and mutational resistance (if supported by the underlying tool).
This supports a variety of summary options including an [interactive summary](https://finlaymagui.re/assets/interactive_report_demo.html).
## Installation
This tool requires python>=3.7 and [pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/)
and the latest release can be installed directly from pip, conda, docker, this repository, or from the galaxy toolshed:
```
pip install hAMRonization
```
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/hamronization)
[](https://img.shields.io/pypi/dm/hAMRonization)
Or
```
conda create --name hamronization --channel conda-forge --channel bioconda --channel defaults hamronization
```



Or to install using docker:
```
docker pull finlaymaguire/hamronization:latest
```
Or to install the latest development version:
```
git clone https://github.com/pha4ge/hAMRonization
pip install hAMRonization
```
Alternatively, hAMRonization can also be installed and used in [galaxy](https://galaxyproject.org/) via the [galaxy toolshed](https://toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/view/iuc/suite_hamronization/904ab154f8f4).
## Usage
**NOTE**: Only the output format used in the "last updated" version of the AMR prediction tool has been tested for accuracy. Older tool versions or updates which lead to a change in output format may not work.
In theory, this should only be a problem with major version changes but not all tools follow semantic versioning.
If you encounter any issues with newer tool versions then please create an issue in this repository.
```
usage: hamronize <tool> <options>
Convert AMR gene detection tool output(s) to hAMRonization specification format
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-v, --version show program's version number and exit
Tools with hAMRonizable reports:
{abricate,amrfinderplus,amrplusplus,ariba,csstar,deeparg,fargene,groot,kmerresistance,resfams,resfinder,mykrobe,pointfinder,rgi,srax,srst2,staramr,tbprofiler,summarize}
abricate hAMRonize abricate's output report i.e., OUTPUT.tsv
amrfinderplus hAMRonize amrfinderplus's output report i.e., OUTPUT.tsv
amrplusplus hAMRonize amrplusplus's output report i.e., gene.tsv
ariba hAMRonize ariba's output report i.e., OUTDIR/OUTPUT.tsv
csstar hAMRonize csstar's output report i.e., OUTPUT.tsv
deeparg hAMRonize deeparg's output report i.e.,
OUTDIR/OUTPUT.mapping.ARG
fargene hAMRonize fargene's output report i.e., retrieved-
genes-*-hmmsearched.out
groot hAMRonize groot's output report i.e., OUTPUT.tsv (from `groot
report`)
kmerresistance hAMRonize kmerresistance's output report i.e., OUTPUT.res
resfams hAMRonize resfams's output report i.e., resfams.tblout
resfinder hAMRonize resfinder's output report i.e.,
ResFinder_results_tab.txt
mykrobe hAMRonize mykrobe's output report i.e., OUTPUT.json
pointfinder hAMRonize pointfinder's output report i.e.,
PointFinder_results.txt
rgi hAMRonize rgi's output report i.e., OUTPUT.txt or
OUTPUT_bwtoutput.gene_mapping_data.txt
srax hAMRonize srax's output report i.e., sraX_detected_ARGs.tsv
srst2 hAMRonize srst2's output report i.e., OUTPUT_srst2_report.tsv
staramr hAMRonize staramr's output report i.e., resfinder.tsv
tbprofiler hAMRonize tbprofiler's output report i.e., OUTPUT.results.json
summarize Provide a list of paths to the reports you wish to summarize
```
To look at a specific tool e.g. `abricate`:
```
>hamronize abricate -h
usage: hamronize abricate <options>
Applies hAMRonization specification to output from abricate (OUTPUT.tsv)
positional arguments:
report Path to tool report
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--format FORMAT Output format (tsv or json)
--output OUTPUT Output location
--analysis_software_version ANALYSIS_SOFTWARE_VERSION
Input string containing the analysis_software_version for abricate
--reference_database_version REFERENCE_DATABASE_VERSION
Input string containing the reference_database_version for abricate
```
Therefore, hAMRonizing abricates output:
```
hamronize abricate ../test/data/raw_outputs/abricate/report.tsv --reference_database_version 3.2.5 --analysis_software_version 1.0.0 --format json
```
To parse multiple reports from the same tool at once just give a list of reports as the argument,
and they will be concatenated appropriately (i.e. only one header for tsv)
```
hamronize rgi --input_file_name rgi_report --analysis_software_version 6.0.0 --reference_database_version 3.2.5 test/data/raw_outputs/rgi/rgi.txt test/data/raw_outputs/rgibwt/Kp11_bwtoutput.gene_mapping_data.txt
```
You can summarize hAMRonized reports regardless of format using the 'summarize'
function:
```
> hamronize summarize -h
usage: hamronize summarize <options> <list of reports>
Concatenate and summarize AMR detection reports
positional arguments:
hamronized_reports list of hAMRonized reports
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-t {tsv,json,interactive}, --summary_type {tsv,json,interactive}
Which summary report format to generate
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Output file path for summary
```
This will take a list of report and create single sorted report in the
specified format just containing the unique entries across input reports.
This can handle mixed json and tsv hamronized report formats.
```
hamronize summarize -o combined_report.tsv -t tsv abricate.json ariba.tsv
```
The [interactive summary](https://finlaymagui.re/assets/interactive_report_demo.html) option will produce an html file that can be opened within the browser for navigable data exploration (feature developed
with @alexmanuele).
### Using within scripts
Alternatively, hAMRonization can be used within scripts (the metadata must contain the mandatory metadata that is not included in that tool's output, this can be checked by looking at the CLI flags in `hamronize <tool> --help`):
```
import hAMRonization
metadata = {"analysis_software_version": "1.0.1", "reference_database_version": "2019-Jul-28"}
parsed_report = hAMRonization.parse("abricate_report.tsv", metadata, "abricate")
```
The `parsed_report` is then a generator that yields hAMRonized result objects from the parsed report:
```
for result in parsed_report:
print(result)
```
Alternatively, you can use the `.write` attribute to export all results left in the generator to a file (if a filepath isn't provided, this will write to stdout).
```parsed_report.write('hAMRonized_abricate_report.tsv')```
You can also output a `json` formatted hAMRonized report:
`parsed_report.write('all_hAMRonized_abricate_report.json', output_format='json')`
If you want to write multiple reports to one file, this `.write` method can accept `append_mode=True` to append rather than overwrite the output file and not include the header (in tsv format).
`parsed_report.write('all_hAMRonized_abricate_report.tsv', append_mode=True)`
### Implemented Parsers
Currently implemented parsers and the last tool version for which they have been validated:
1. [abricate](hAMRonization/AbricateIO.py): last updated for v1.0.0
2. [amrfinderplus](hAMRonization/AmrFinderPlusIO.py): last updated for v3.10.40
3. [amrplusplus](hAMRonization/AmrPlusPlusIO.py): last updated for c6b097a
4. [ariba](hAMRonization/AribaIO.py): last updated for v2.14.6
5. [csstar](hAMRonization/CSStarIO.py): last updated for v2.1.0
6. [deeparg](hAMRonization/DeepArgIO.py): last updated for v1.0.2
7. [fargene](hAMRonization/FARGeneIO.py): last updated for v0.1
8. [groot](hAMRonization/GrootIO.py): last updated for v1.1.2
9. [kmerresistance](hAMRonization/KmerResistanceIO.py): late updated for v2.2.0
10. [mykrobe](test/data/raw_outputs/mykrobe/report.json): last updated for v0.8.1
11. [pointfinder](hAMRonization/PointFinderIO.py): last updated for v4.1.0
12. [resfams](hAMRonization/ResFamsIO.py): last updated for hmmer v3.3.2
13. [resfinder](hAMRonization/ResFinderIO.py): last updated for v4.1.0
14. [rgi](hAMRonization/RgiIO.py) (includes RGI-BWT) last updated for v5.2.0
15. [srax](hAMRonization/SraxIO.py): last updated for v1.5
16. [srst2](hAMRonization/Srst2IO.py): last updated for v0.2.0
17. [staramr](hAMRonization/StarAmrIO.py): last updated for v0.8.0
18. [tbprofilder](test/data/raw_outputs/tbprofiler/tbprofiler.json): last updated for v3.0.8
## Implementation Details
### hAMRonizedResult Data Structure
The hAMRonization specification is implemented in the [hAMRonizedResult dataclass](https://github.com/pha4ge/harmonized-amr-parsers/blob/master/hAMRonization/hAMRonization/hAMRonizedResult.py#L6).
This is a simple datastructure that uses positional and key-word args to distinguish mandatory from optional hAMRonization fields.
It also uses type-hinting to validate the supplied values are of the correct type
Each parser follows a similar strategy, using a common interface.
This has been designed to match the `biopython` `SeqIO` `parse` function
>>> import hAMRonization
>>> filename = "abricate_report.tsv"
>>> metadata = {"analysis_software_version": "1.0.1", "reference_database_version": "2019-Jul-28"}
>>> for result in hAMRonization.parse(filename, metadata, "abricate"):
... print(result)
Where the final argument to the `hAMRonization.parse` command is whichever tool is being parsed.
### hAMRonizedResultIterator
An abstract iterator is then implemented to ingest a given AMR tool's report
(via the appropriate subclassed implementation), hAMRonize results i.e. translate the
original inputs to the fields in the hAMRonization specification, and yield a stream of
hAMRonizedResult dataclasses.
This iterator also implements a write function to enable outputting the contents
to a output stream or filehandle in either tsv or json format.
### Tool-specific Iterators
Each tool has a specific subclass of this abstract hAMRonizedResultIterator e.g. `AbricateIO.AbricateIterator`.
These include an attribute containing the mapping of the tools original output report fields to the hAMRonized specification fields (`self.field_mapping`), as well as handling specifying any additional required metadata.
The `parse` method of these subclasses then implements the tool-specific parsing logic required.
This is typically a simple `csv.DictReader` but can be more complex such as the json parsing of `resfinder` output,
or the modification of output fields required to better fit some tools into the hAMRonization specification.
## Contributing
We welcome contributions for users in any form (from github issues flagging problems/requests) to pull requests of bug fixes or adding new parsers.
## Setting up a Development Environment
First fork this repository and set up a development environment (replacing `YOURUSERNAME` with your github username:
```
git clone https://github.com/YOURUSERNAME/hAMRonization
conda create -n hAMRonization
conda activate hAMRonization
cd hAMRonization
pip install pytest flake8
pip install -e .
```
## Testing and Linting
On every commit github actions automatically runs tests and linting to check
the code.
You can manually run these in your development environment as well.
To run a full set of integration tests:
pushd test
bash run_integration_test.sh
popd
To run unit tests that verify parsing validity for each tool
as well as generation of valid summaries you can use pytest:
pip install pytest
pushd test
pytest
popd
Finally to run linting and check whether your code matches the project
code style:
pushd hAMRonization
flake8 . --count --select=E9,F63,F7,F82 --show-source --statistics
flake8 . --count --exit-zero --max-complexity=20 --max-line-length=127 --statistics
popd
## Adding a new parser
If you wish to add a parser for a new tool here are the main steps required:
1. Add an entry into `_RequiredToolMetadata` and `_FormatToIterator` in `hAMRonziation/__init__.py` which points to the appropriate `ToolNameIO.py` containing the tool's Iterator subclass
2. In `ToolNameIO.py` add a `required_metadata` list containing any mandatory fields not implemented by the tool
3. Then add a class `ToolNameIterator(hAMRonizedResultIterator)` and implement the `__init__` methods with the approriate mapping (`self.field_mapping`), and metadata (`self.metadata`).
4. To this class, add a `parse` method which reads an opened file stream into a dictionary per line/result (matching the keys of `self.field_mapping`) and yields the output of `self.hAMRonize` being applied to that dictionary.
5. To add a CLI parser for the tool, create a python file in the `parsers` directory:
```
from hAMRonization import Interfaces
if __name__ == '__main__':
Interfaces.cli_parser('toolname')
```
Alternatively, the `hAMRonized_parser.py` can be used as a common script interface to all implemented parsers.
6. Finally, following the template in `test/test_parsing_validity.py`, please generate a unit test that ensures the parser is working as you intend it to!
If you have any questions about any of this or need any help, please file an issue.
## FAQ
* What's the difference between an Antimicrobial Resistance 'Result' and 'Report'?
* For the purposes of this project, a 'Report' is an output file (or collection of files) from an AMR analysis tool.
A 'Result' is a single entry in a report. For example, a single line in an abricate report file is a single Antimicrobial
Resistance 'Result'.
### Known Issues
Here are some known issues that we would welcome input on trying to solve!
#### Limitations of specification
- mandatory fields: `gene_symbol` and `gene_name` are confusing and not usually both present (only consistently used in AFP). Means tools either need 1:2 mapping i.e. single output field maps to both `gene_symbol` and `gene_name` OR have fragile text splitting of single field that won't be robust to databases changes. Current solution is 1:2 mapping e.g. staramr
- inconsistent nomenclature of terms being used in specification fields: target, query, subject, reference. Need to stick to one name for sequence with which the database is being searched, and one the hit that results from that search.
- `sequence_identity`: is sequence type specific %id amino acids != %id nucleotide but does this matter?
- `coverage_depth` seems to include both tool fields that are average depth of read and just plain overall read-count,
- `contig_id` isn't general enough when some tools this ID naturally corresponds to a `read_name` (deepARG), individual ORF (resfams), or protein sequence (AFP with protein input): *change to `query_id_name` or similar?*
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": "https://github.com/pha4ge/hAMRonization",
"name": "hAMRonization",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.7",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "Genomics, Antimicrobial resistance, Antibiotic, Standardization",
"author": "Finlay Maguire",
"author_email": "finlaymaguire@gmail.com",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/36/b9/3931330917401735c1cae8cb651978bb6f35a38dbca5f1f54f43fe1a0942/hamronization-1.1.7.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "\n[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/248040662)\n[](https://github.com/pha4ge/hAMRonization/blob/master/docs/subgrant/PHA4GE_AMR_SubGrant_Documentation.pdf)\n[](https://github.com/pha4ge/hAMRonization/blob/master/docs/subgrant/PHA4GE_hAMRonization_espan%CC%83ol.pdf)\n\n\n# hAMRonization \n\nThis repo contains the hAMRonization module and CLI parser tools combine the outputs of \n18 (as of 2022-09-25) disparate antimicrobial resistance gene detection tools into a single unified format.\n\nThis is an implementation of the [hAMRonization AMR detection specification scheme](docs/hAMRonization_specification_details.csv) which supports gene presence/absence resistance and mutational resistance (if supported by the underlying tool).\n\nThis supports a variety of summary options including an [interactive summary](https://finlaymagui.re/assets/interactive_report_demo.html).\n\n\n\n\n## Installation\n\nThis tool requires python>=3.7 and [pandas](https://pandas.pydata.org/)\nand the latest release can be installed directly from pip, conda, docker, this repository, or from the galaxy toolshed:\n```\npip install hAMRonization\n```\n[](https://badge.fury.io/py/hamronization)\n[](https://img.shields.io/pypi/dm/hAMRonization)\n\nOr\n\n```\nconda create --name hamronization --channel conda-forge --channel bioconda --channel defaults hamronization\n```\n\n\n\n\n\nOr to install using docker:\n```\ndocker pull finlaymaguire/hamronization:latest\n```\n\nOr to install the latest development version:\n```\ngit clone https://github.com/pha4ge/hAMRonization\npip install hAMRonization\n```\n\nAlternatively, hAMRonization can also be installed and used in [galaxy](https://galaxyproject.org/) via the [galaxy toolshed](https://toolshed.g2.bx.psu.edu/view/iuc/suite_hamronization/904ab154f8f4).\n\n## Usage\n\n**NOTE**: Only the output format used in the \"last updated\" version of the AMR prediction tool has been tested for accuracy. Older tool versions or updates which lead to a change in output format may not work. \nIn theory, this should only be a problem with major version changes but not all tools follow semantic versioning.\nIf you encounter any issues with newer tool versions then please create an issue in this repository.\n\n```\nusage: hamronize <tool> <options>\n\nConvert AMR gene detection tool output(s) to hAMRonization specification format\n\noptions:\n -h, --help show this help message and exit\n -v, --version show program's version number and exit\n\nTools with hAMRonizable reports:\n {abricate,amrfinderplus,amrplusplus,ariba,csstar,deeparg,fargene,groot,kmerresistance,resfams,resfinder,mykrobe,pointfinder,rgi,srax,srst2,staramr,tbprofiler,summarize}\n abricate hAMRonize abricate's output report i.e., OUTPUT.tsv\n amrfinderplus hAMRonize amrfinderplus's output report i.e., OUTPUT.tsv\n amrplusplus hAMRonize amrplusplus's output report i.e., gene.tsv\n ariba hAMRonize ariba's output report i.e., OUTDIR/OUTPUT.tsv\n csstar hAMRonize csstar's output report i.e., OUTPUT.tsv\n deeparg hAMRonize deeparg's output report i.e.,\n OUTDIR/OUTPUT.mapping.ARG\n fargene hAMRonize fargene's output report i.e., retrieved-\n genes-*-hmmsearched.out\n groot hAMRonize groot's output report i.e., OUTPUT.tsv (from `groot\n report`)\n kmerresistance hAMRonize kmerresistance's output report i.e., OUTPUT.res\n resfams hAMRonize resfams's output report i.e., resfams.tblout\n resfinder hAMRonize resfinder's output report i.e.,\n ResFinder_results_tab.txt\n mykrobe hAMRonize mykrobe's output report i.e., OUTPUT.json\n pointfinder hAMRonize pointfinder's output report i.e.,\n PointFinder_results.txt\n rgi hAMRonize rgi's output report i.e., OUTPUT.txt or\n OUTPUT_bwtoutput.gene_mapping_data.txt\n srax hAMRonize srax's output report i.e., sraX_detected_ARGs.tsv\n srst2 hAMRonize srst2's output report i.e., OUTPUT_srst2_report.tsv\n staramr hAMRonize staramr's output report i.e., resfinder.tsv\n tbprofiler hAMRonize tbprofiler's output report i.e., OUTPUT.results.json\n summarize Provide a list of paths to the reports you wish to summarize\n```\n\nTo look at a specific tool e.g. `abricate`:\n```\n>hamronize abricate -h \nusage: hamronize abricate <options>\n\nApplies hAMRonization specification to output from abricate (OUTPUT.tsv)\n\npositional arguments:\n report Path to tool report\n\noptional arguments:\n -h, --help show this help message and exit\n --format FORMAT Output format (tsv or json)\n --output OUTPUT Output location\n --analysis_software_version ANALYSIS_SOFTWARE_VERSION\n Input string containing the analysis_software_version for abricate\n --reference_database_version REFERENCE_DATABASE_VERSION\n Input string containing the reference_database_version for abricate\n\n```\n\nTherefore, hAMRonizing abricates output:\n```\nhamronize abricate ../test/data/raw_outputs/abricate/report.tsv --reference_database_version 3.2.5 --analysis_software_version 1.0.0 --format json\n```\n\nTo parse multiple reports from the same tool at once just give a list of reports as the argument,\nand they will be concatenated appropriately (i.e. only one header for tsv)\n\n```\nhamronize rgi --input_file_name rgi_report --analysis_software_version 6.0.0 --reference_database_version 3.2.5 test/data/raw_outputs/rgi/rgi.txt test/data/raw_outputs/rgibwt/Kp11_bwtoutput.gene_mapping_data.txt\n```\n\nYou can summarize hAMRonized reports regardless of format using the 'summarize'\nfunction:\n\n```\n> hamronize summarize -h\nusage: hamronize summarize <options> <list of reports>\n\nConcatenate and summarize AMR detection reports\n\npositional arguments:\n hamronized_reports list of hAMRonized reports\n\noptional arguments:\n -h, --help show this help message and exit\n -t {tsv,json,interactive}, --summary_type {tsv,json,interactive}\n Which summary report format to generate\n -o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT\n Output file path for summary\n```\n\nThis will take a list of report and create single sorted report in the \nspecified format just containing the unique entries across input reports.\nThis can handle mixed json and tsv hamronized report formats.\n\n```\nhamronize summarize -o combined_report.tsv -t tsv abricate.json ariba.tsv\n```\n\nThe [interactive summary](https://finlaymagui.re/assets/interactive_report_demo.html) option will produce an html file that can be opened within the browser for navigable data exploration (feature developed\nwith @alexmanuele).\n\n### Using within scripts\n\nAlternatively, hAMRonization can be used within scripts (the metadata must contain the mandatory metadata that is not included in that tool's output, this can be checked by looking at the CLI flags in `hamronize <tool> --help`):\n\n```\nimport hAMRonization\nmetadata = {\"analysis_software_version\": \"1.0.1\", \"reference_database_version\": \"2019-Jul-28\"}\nparsed_report = hAMRonization.parse(\"abricate_report.tsv\", metadata, \"abricate\")\n```\n\nThe `parsed_report` is then a generator that yields hAMRonized result objects from the parsed report:\n\n```\nfor result in parsed_report:\n print(result)\n```\n\nAlternatively, you can use the `.write` attribute to export all results left in the generator to a file (if a filepath isn't provided, this will write to stdout).\n\n```parsed_report.write('hAMRonized_abricate_report.tsv')```\n\nYou can also output a `json` formatted hAMRonized report:\n\n`parsed_report.write('all_hAMRonized_abricate_report.json', output_format='json')`\n\nIf you want to write multiple reports to one file, this `.write` method can accept `append_mode=True` to append rather than overwrite the output file and not include the header (in tsv format).\n\n`parsed_report.write('all_hAMRonized_abricate_report.tsv', append_mode=True)`\n\n\n### Implemented Parsers\n\nCurrently implemented parsers and the last tool version for which they have been validated:\n\n1. [abricate](hAMRonization/AbricateIO.py): last updated for v1.0.0\n2. [amrfinderplus](hAMRonization/AmrFinderPlusIO.py): last updated for v3.10.40\n3. [amrplusplus](hAMRonization/AmrPlusPlusIO.py): last updated for c6b097a\n4. [ariba](hAMRonization/AribaIO.py): last updated for v2.14.6\n5. [csstar](hAMRonization/CSStarIO.py): last updated for v2.1.0\n6. [deeparg](hAMRonization/DeepArgIO.py): last updated for v1.0.2\n7. [fargene](hAMRonization/FARGeneIO.py): last updated for v0.1\n8. [groot](hAMRonization/GrootIO.py): last updated for v1.1.2\n9. [kmerresistance](hAMRonization/KmerResistanceIO.py): late updated for v2.2.0\n10. [mykrobe](test/data/raw_outputs/mykrobe/report.json): last updated for v0.8.1\n11. [pointfinder](hAMRonization/PointFinderIO.py): last updated for v4.1.0\n12. [resfams](hAMRonization/ResFamsIO.py): last updated for hmmer v3.3.2\n13. [resfinder](hAMRonization/ResFinderIO.py): last updated for v4.1.0\n14. [rgi](hAMRonization/RgiIO.py) (includes RGI-BWT) last updated for v5.2.0\n15. [srax](hAMRonization/SraxIO.py): last updated for v1.5\n16. [srst2](hAMRonization/Srst2IO.py): last updated for v0.2.0\n17. [staramr](hAMRonization/StarAmrIO.py): last updated for v0.8.0\n18. [tbprofilder](test/data/raw_outputs/tbprofiler/tbprofiler.json): last updated for v3.0.8\n\n## Implementation Details\n\n### hAMRonizedResult Data Structure\n\nThe hAMRonization specification is implemented in the [hAMRonizedResult dataclass](https://github.com/pha4ge/harmonized-amr-parsers/blob/master/hAMRonization/hAMRonization/hAMRonizedResult.py#L6).\n\nThis is a simple datastructure that uses positional and key-word args to distinguish mandatory from optional hAMRonization fields. \nIt also uses type-hinting to validate the supplied values are of the correct type\n\n\nEach parser follows a similar strategy, using a common interface.\nThis has been designed to match the `biopython` `SeqIO` `parse` function \n\n >>> import hAMRonization\n >>> filename = \"abricate_report.tsv\"\n >>> metadata = {\"analysis_software_version\": \"1.0.1\", \"reference_database_version\": \"2019-Jul-28\"}\n >>> for result in hAMRonization.parse(filename, metadata, \"abricate\"):\n ... print(result)\n\nWhere the final argument to the `hAMRonization.parse` command is whichever tool is being parsed.\n\n### hAMRonizedResultIterator\n\nAn abstract iterator is then implemented to ingest a given AMR tool's report\n(via the appropriate subclassed implementation), hAMRonize results i.e. translate the \noriginal inputs to the fields in the hAMRonization specification, and yield a stream of \nhAMRonizedResult dataclasses.\n\nThis iterator also implements a write function to enable outputting the contents \nto a output stream or filehandle in either tsv or json format.\n\n### Tool-specific Iterators\n\nEach tool has a specific subclass of this abstract hAMRonizedResultIterator e.g. `AbricateIO.AbricateIterator`.\n\nThese include an attribute containing the mapping of the tools original output report fields to the hAMRonized specification fields (`self.field_mapping`), as well as handling specifying any additional required metadata.\n\nThe `parse` method of these subclasses then implements the tool-specific parsing logic required.\nThis is typically a simple `csv.DictReader` but can be more complex such as the json parsing of `resfinder` output, \nor the modification of output fields required to better fit some tools into the hAMRonization specification.\n\n\n## Contributing \n\nWe welcome contributions for users in any form (from github issues flagging problems/requests) to pull requests of bug fixes or adding new parsers.\n\n## Setting up a Development Environment\n\nFirst fork this repository and set up a development environment (replacing `YOURUSERNAME` with your github username:\n\n```\ngit clone https://github.com/YOURUSERNAME/hAMRonization\nconda create -n hAMRonization \nconda activate hAMRonization\ncd hAMRonization\npip install pytest flake8\npip install -e .\n\n```\n## Testing and Linting\n\nOn every commit github actions automatically runs tests and linting to check\nthe code. \nYou can manually run these in your development environment as well.\n\nTo run a full set of integration tests:\n\n pushd test\n bash run_integration_test.sh\n popd\n\nTo run unit tests that verify parsing validity for each tool\nas well as generation of valid summaries you can use pytest:\n\n pip install pytest\n pushd test\n pytest\n popd\n\nFinally to run linting and check whether your code matches the project\ncode style:\n\n pushd hAMRonization\n flake8 . --count --select=E9,F63,F7,F82 --show-source --statistics\n flake8 . --count --exit-zero --max-complexity=20 --max-line-length=127 --statistics\n popd\n\n## Adding a new parser\n\nIf you wish to add a parser for a new tool here are the main steps required:\n\n1. Add an entry into `_RequiredToolMetadata` and `_FormatToIterator` in `hAMRonziation/__init__.py` which points to the appropriate `ToolNameIO.py` containing the tool's Iterator subclass\n\n2. In `ToolNameIO.py` add a `required_metadata` list containing any mandatory fields not implemented by the tool\n\n3. Then add a class `ToolNameIterator(hAMRonizedResultIterator)` and implement the `__init__` methods with the approriate mapping (`self.field_mapping`), and metadata (`self.metadata`).\n\n4. To this class, add a `parse` method which reads an opened file stream into a dictionary per line/result (matching the keys of `self.field_mapping`) and yields the output of `self.hAMRonize` being applied to that dictionary.\n\n5. To add a CLI parser for the tool, create a python file in the `parsers` directory:\n\n ```\n from hAMRonization import Interfaces\n if __name__ == '__main__': \n Interfaces.cli_parser('toolname')\n ```\n\nAlternatively, the `hAMRonized_parser.py` can be used as a common script interface to all implemented parsers. \n\n6. Finally, following the template in `test/test_parsing_validity.py`, please generate a unit test that ensures the parser is working as you intend it to!\n\nIf you have any questions about any of this or need any help, please file an issue.\n\n## FAQ\n\n* What's the difference between an Antimicrobial Resistance 'Result' and 'Report'?\n * For the purposes of this project, a 'Report' is an output file (or collection of files) from an AMR analysis tool.\n A 'Result' is a single entry in a report. For example, a single line in an abricate report file is a single Antimicrobial\n Resistance 'Result'.\n \n### Known Issues\n\nHere are some known issues that we would welcome input on trying to solve!\n\n#### Limitations of specification\n\n- mandatory fields: `gene_symbol` and `gene_name` are confusing and not usually both present (only consistently used in AFP). Means tools either need 1:2 mapping i.e. single output field maps to both `gene_symbol` and `gene_name` OR have fragile text splitting of single field that won't be robust to databases changes. Current solution is 1:2 mapping e.g. staramr\n\n- inconsistent nomenclature of terms being used in specification fields: target, query, subject, reference. Need to stick to one name for sequence with which the database is being searched, and one the hit that results from that search.\n\n- `sequence_identity`: is sequence type specific %id amino acids != %id nucleotide but does this matter?\n\n- `coverage_depth` seems to include both tool fields that are average depth of read and just plain overall read-count, \n\n- `contig_id` isn't general enough when some tools this ID naturally corresponds to a `read_name` (deepARG), individual ORF (resfams), or protein sequence (AFP with protein input): *change to `query_id_name` or similar?*\n\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": "LGPLv3",
"summary": "Tool to convert and summarize AMR gene detection outputs using the hAMRonization specification",
"version": "1.1.7",
"project_urls": {
"Download": "https://github.com/pha4ge/archive/v1.1.7.tar.gz",
"Homepage": "https://github.com/pha4ge/hAMRonization"
},
"split_keywords": [
"genomics",
" antimicrobial resistance",
" antibiotic",
" standardization"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "f863ee82ba56f668d2022c1b5d2d41a7ab1bbb50a43e04d059156d62b2202997",
"md5": "a4e9fb84a3b184fb864252f84a6511b5",
"sha256": "df1f2804f04c591fedd5532af7d40ee310da88b1f5fd1c6b1f311161f99516b5"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "hAMRonization-1.1.7-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "a4e9fb84a3b184fb864252f84a6511b5",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.7",
"size": 45550,
"upload_time": "2024-05-21T21:13:02",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-05-21T21:13:02.463484Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/f8/63/ee82ba56f668d2022c1b5d2d41a7ab1bbb50a43e04d059156d62b2202997/hAMRonization-1.1.7-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "36b93931330917401735c1cae8cb651978bb6f35a38dbca5f1f54f43fe1a0942",
"md5": "a357de669cd70474a51acfe8d0ee35bf",
"sha256": "9560e891772da7b339655d92cb7cdd112236175a0a5bd3fbccf9619f13e74a22"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "hamronization-1.1.7.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "a357de669cd70474a51acfe8d0ee35bf",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.7",
"size": 43426,
"upload_time": "2024-05-21T21:13:04",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-05-21T21:13:04.427472Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/36/b9/3931330917401735c1cae8cb651978bb6f35a38dbca5f1f54f43fe1a0942/hamronization-1.1.7.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-05-21 21:13:04",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "pha4ge",
"github_project": "hAMRonization",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": true,
"lcname": "hamronization"
}
