# ABToolkit
Set of tools for AA and AB tests, sample size estimation, confidence intervals estimation.
For continuous and discrete variables.
## Install using pip:
```pip install abtoolkit```
## Continuous variables analysis
#### Sample size estimation:
```
from abtoolkit.continuous.utils import estimate_sample_size_by_mde
estimate_sample_size_by_mde(
std=variable.std(),
alpha=alpha_level,
power=power,
mde=mde,
alternative="two-sided"
)
```
#### AA and AB tests simulation:
Using ```abtoolkit.continuous.simulation.StatTestsSimulation``` class you can simulate and check different stat-test,
compare them in terms of stat test power to choose the best test for your data. As result of simulation for each
stat test you will get the 1-st Type error estimation with confidence interval, 2-nd Type error estimation with
confidence interval and plot of p-value distribution for different tests.
```
from abtoolkit.continuous.simulation import StatTestsSimulation
simulation = StatTestsSimulation(
variable,
stattests_list=[
"ttest",
"diff_ttest",
"regression_test",
"cuped_ttest",
"did_regression_test",
"additional_vars_regression_test",
],
alternative=alternative,
experiments_num=experiments_num,
treatment_sample_size=sample_size,
treatment_split_proportion=0.2,
mde=mde,
alpha_level=alpha_level,
previous_values=previous_value,
cuped_covariant=previous_value,
additional_vars=[previous_value],
)
simulation.run() # Run simulation
simulation.print_results() # Print results of simulation
simulation.plot_p_values() # Plot p-values distribution
```
Output:
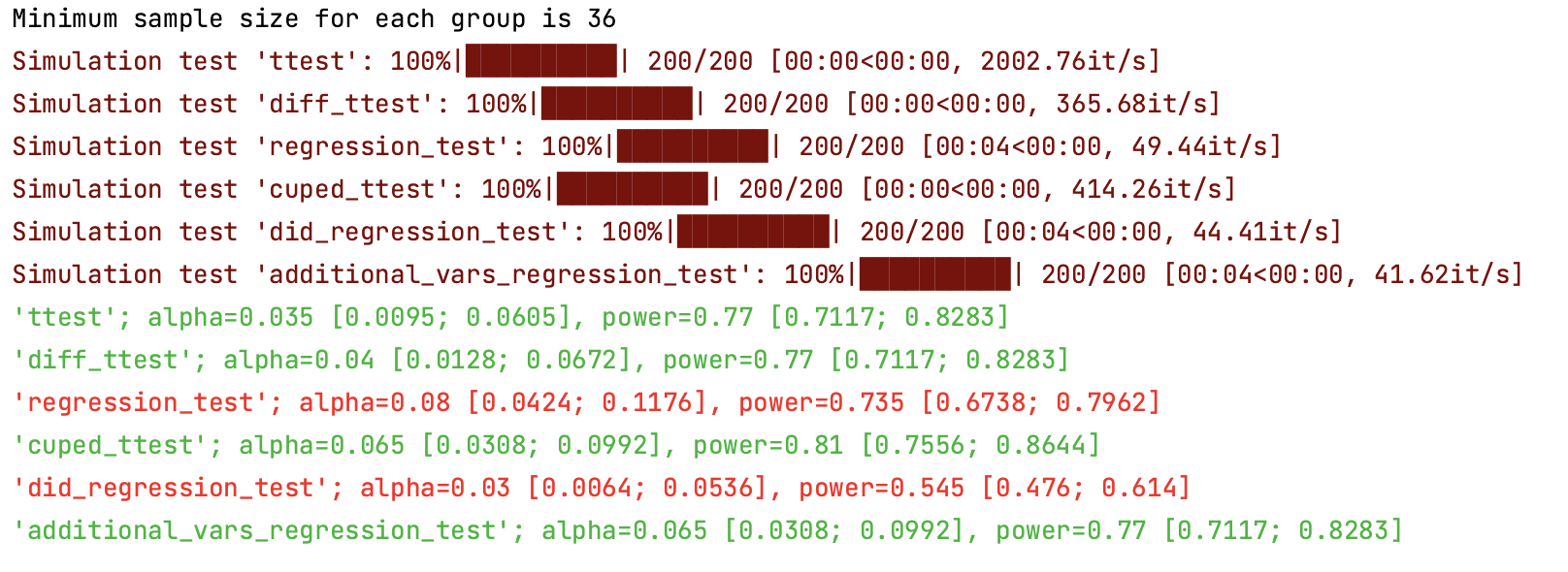
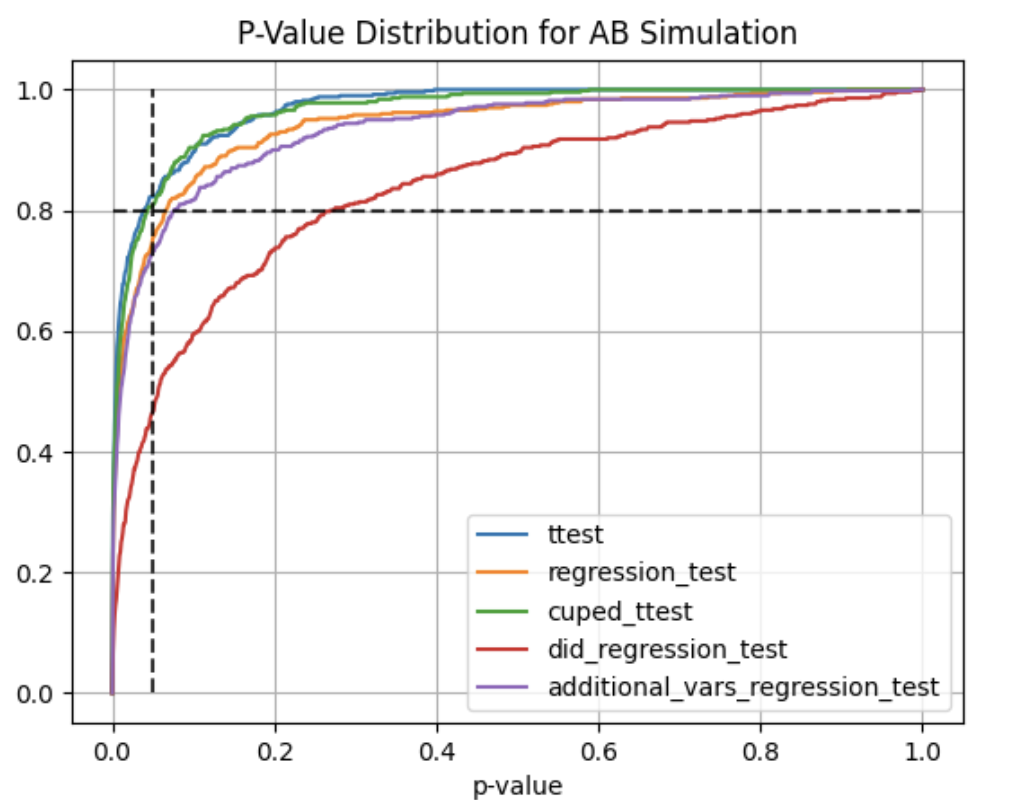
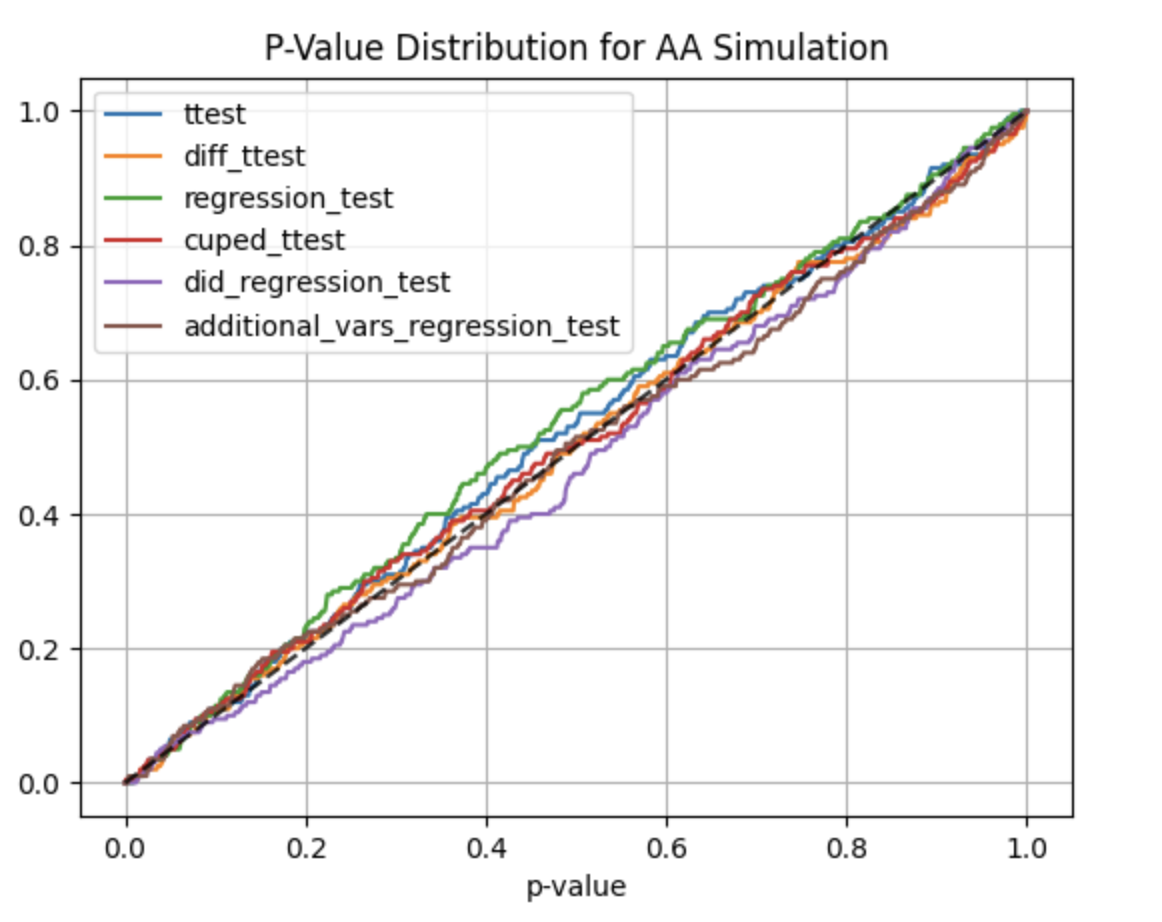
Full example of usage you can find in ```examples/continuous_var_analysis.py``` script.
#### Next stat tests implemented for treatment effect estimation:
- ***T-Test*** - estimates treatment effect by comparing variables between treatment and control groups.
- ***Difference T-Test*** - estimates treatment effect by comparing difference between actual and previous values
of variables in treatment and control groups.
- ***Regression Test*** - estimates treatment effect using linear regression by tested predicting variable.
Fact of treatment represented in model as binary flag (treated or not). Weight for this flag show significant
of treatment impact.
```y = bias + w * treated```
- ***Regression Difference-in-Difference Test*** - estimates treatment effect using linear regression by predicting
difference between treatment and control groups whist represented as difference between current variable value and
previous period variable value (two differences). Weight for treated and current variable values shows
significant of treatment. ```y = bias + w0 * treated + w1 * after + w2 * treated * after```
- ***CUPED*** - estimates treatment effect by comparing variables between treatment and control groups
and uses covariant to reduce variance and speedup test. ```y = y - Q * covariant```, where ```Q = cov(y, covariant) / var(covariant)```.
Cuped variable has same mean value (unbiased), but smaller variance, that speedup test.
- ***Regression with Additional Variables*** - estimates treatment effect using linear regression by predicting
tested variable with additional variables, which describe part of main variable variance and speedup test.
Fact of treatment represented in model as binary flag (treated or not). Weight for this flag show significant
of treatment impact.
```y = bias + w0 * treated + w1 * additional_variable1 + w2 * additional_variable2 + ...```
## Discrete variables analysis
#### Sample size estimation:
```
from abtoolkit.discrete.utils import estimate_sample_size_by_mde
estimate_sample_size_by_mde(
p,
sample_size,
alpha=0.05,
alternative="two-sided"
)
```
#### AA and AB tests simulation:
```
from abtoolkit.discrete.simulation import StatTestsSimulation
sim = StatTestsSimulation(
count=variable.sum(),
objects_num=variable.count(),
stattests_list=["conversion_ztest", "bayesian_test", "chi_square_test"],
alternative=alternative,
experiments_num=experiments_num, # Run each stattest 10 times
treatment_sample_size=sample_size,
treatment_split_proportion=0.5,
mde=mde, # Trying to detect this effect (very big for our simulated data)
alpha_level=alpha_level, # Fix alpha level on 5%
power=power,
bayesian_prior_positives=1,
bayesian_prior_negatives=1,
)
info = sim.run() # Get dictionary with information about tests
sim.print_results() # Print results of simulation
sim.plot_p_values() # Plot p-values distribution
```
Output:
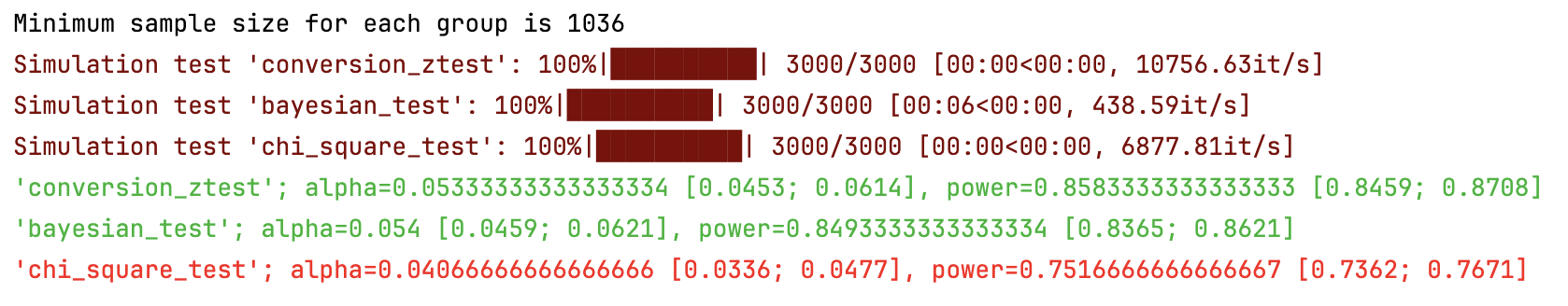
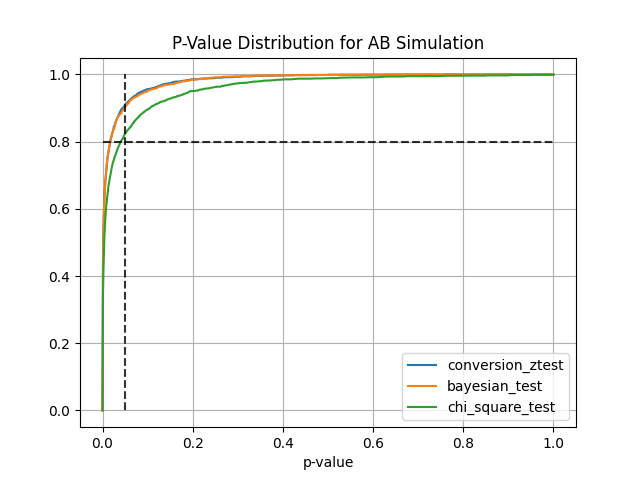
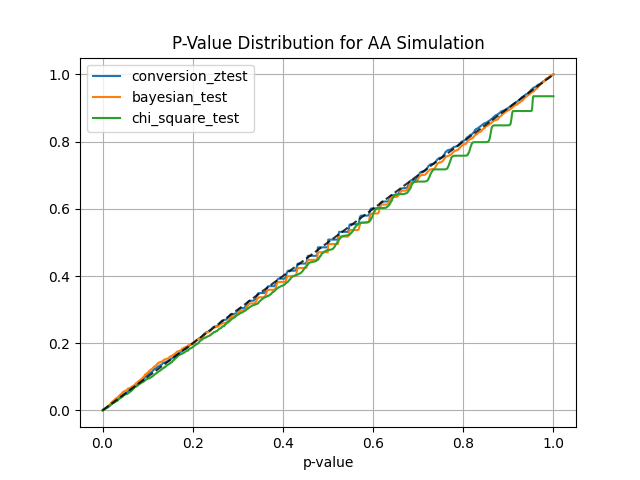
#### Next stat tests implemented for treatment effect estimation:
- ***Conversion Z-Test*** estimates treatment effect on conversion variable using z-test
- ***Bayesian Test*** estimates probability of difference between conversions according to prior knowledge
- ***Chi-Square Test*** estimates the significance of association between two categorical variables
## Another tools
#### Central Limit Theorem check
Helps you check if your variable meets the Central Limit Theorem and what sample size you need for it to meet.
```
from abtoolkit.utils import check_clt
import numpy as np
var = np.random.chisquare(df=2, size=10000)
p_value = check_clt(var, do_plot_distribution=True)
```
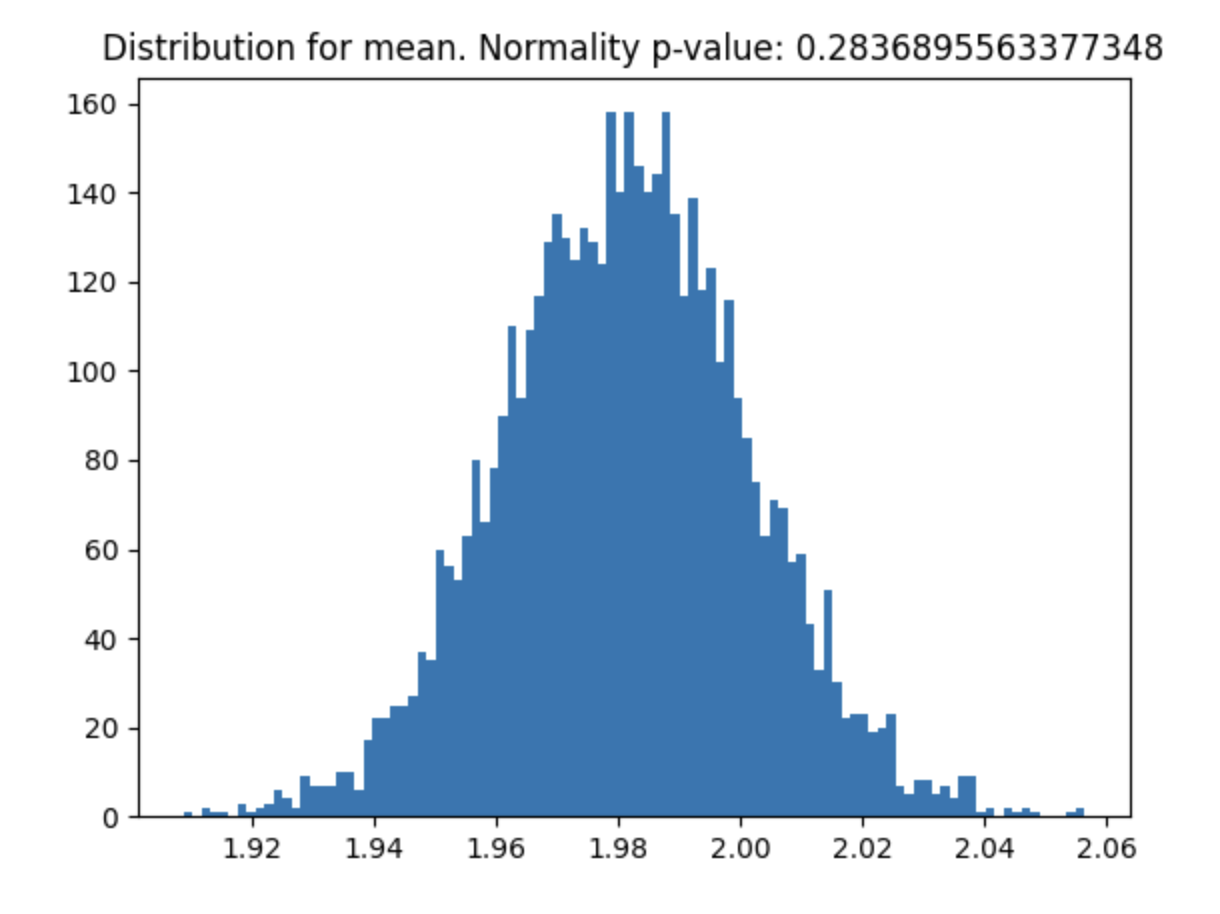
---
You can find examples of toolkit usage in [examples/](https://github.com/nikitosl/abtoolkit/tree/master/examples) directory.
Raw data
{
"_id": null,
"home_page": null,
"name": "abtoolkit",
"maintainer": null,
"docs_url": null,
"requires_python": ">=3.8",
"maintainer_email": null,
"keywords": "ab_test, cuped, did, ttest",
"author": null,
"author_email": "Nikita Altukhov <altuxov.nikita@gmail.com>",
"download_url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/76/77/c0e855bfc09bcab6517d40bcd35df7d46699942f7091aed365182f59c9a0/abtoolkit-2.0.0.tar.gz",
"platform": null,
"description": "# ABToolkit\nSet of tools for AA and AB tests, sample size estimation, confidence intervals estimation. \nFor continuous and discrete variables.\n\n## Install using pip:\n```pip install abtoolkit```\n\n## Continuous variables analysis\n#### Sample size estimation:\n```\nfrom abtoolkit.continuous.utils import estimate_sample_size_by_mde\n\nestimate_sample_size_by_mde(\n std=variable.std(),\n alpha=alpha_level, \n power=power, \n mde=mde,\n alternative=\"two-sided\"\n)\n```\n\n#### AA and AB tests simulation:\nUsing ```abtoolkit.continuous.simulation.StatTestsSimulation``` class you can simulate and check different stat-test, \ncompare them in terms of stat test power to choose the best test for your data. As result of simulation for each \nstat test you will get the 1-st Type error estimation with confidence interval, 2-nd Type error estimation with \nconfidence interval and plot of p-value distribution for different tests.\n\n```\nfrom abtoolkit.continuous.simulation import StatTestsSimulation\nsimulation = StatTestsSimulation(\n variable,\n stattests_list=[\n \"ttest\",\n \"diff_ttest\",\n \"regression_test\",\n \"cuped_ttest\",\n \"did_regression_test\",\n \"additional_vars_regression_test\",\n ], \n alternative=alternative,\n experiments_num=experiments_num,\n treatment_sample_size=sample_size,\n treatment_split_proportion=0.2,\n mde=mde,\n alpha_level=alpha_level,\n\n previous_values=previous_value,\n cuped_covariant=previous_value,\n additional_vars=[previous_value],\n )\nsimulation.run() # Run simulation\nsimulation.print_results() # Print results of simulation\nsimulation.plot_p_values() # Plot p-values distribution\n```\nOutput:\n\n\n\n\nFull example of usage you can find in ```examples/continuous_var_analysis.py``` script.\n\n#### Next stat tests implemented for treatment effect estimation:\n- ***T-Test*** - estimates treatment effect by comparing variables between treatment and control groups.\n- ***Difference T-Test*** - estimates treatment effect by comparing difference between actual and previous values \nof variables in treatment and control groups.\n- ***Regression Test*** - estimates treatment effect using linear regression by tested predicting variable. \nFact of treatment represented in model as binary flag (treated or not). Weight for this flag show significant \nof treatment impact.\n```y = bias + w * treated```\n- ***Regression Difference-in-Difference Test*** - estimates treatment effect using linear regression by predicting\ndifference between treatment and control groups whist represented as difference between current variable value and \nprevious period variable value (two differences). Weight for treated and current variable values shows \nsignificant of treatment. ```y = bias + w0 * treated + w1 * after + w2 * treated * after```\n- ***CUPED*** - estimates treatment effect by comparing variables between treatment and control groups \nand uses covariant to reduce variance and speedup test. ```y = y - Q * covariant```, where ```Q = cov(y, covariant) / var(covariant)```. \nCuped variable has same mean value (unbiased), but smaller variance, that speedup test.\n- ***Regression with Additional Variables*** - estimates treatment effect using linear regression by predicting \ntested variable with additional variables, which describe part of main variable variance and speedup test. \nFact of treatment represented in model as binary flag (treated or not). Weight for this flag show significant \nof treatment impact.\n```y = bias + w0 * treated + w1 * additional_variable1 + w2 * additional_variable2 + ...```\n\n\n## Discrete variables analysis\n#### Sample size estimation:\n```\nfrom abtoolkit.discrete.utils import estimate_sample_size_by_mde\n\nestimate_sample_size_by_mde(\n p, \n sample_size, \n alpha=0.05,\n alternative=\"two-sided\"\n)\n```\n#### AA and AB tests simulation:\n```\nfrom abtoolkit.discrete.simulation import StatTestsSimulation\n\nsim = StatTestsSimulation(\n count=variable.sum(),\n objects_num=variable.count(),\n stattests_list=[\"conversion_ztest\", \"bayesian_test\", \"chi_square_test\"],\n alternative=alternative,\n experiments_num=experiments_num, # Run each stattest 10 times\n treatment_sample_size=sample_size,\n treatment_split_proportion=0.5,\n mde=mde, # Trying to detect this effect (very big for our simulated data)\n alpha_level=alpha_level, # Fix alpha level on 5%\n power=power,\n bayesian_prior_positives=1,\n bayesian_prior_negatives=1,\n)\ninfo = sim.run() # Get dictionary with information about tests\nsim.print_results() # Print results of simulation\nsim.plot_p_values() # Plot p-values distribution\n```\nOutput:\n\n\n\n\n#### Next stat tests implemented for treatment effect estimation:\n- ***Conversion Z-Test*** estimates treatment effect on conversion variable using z-test\n- ***Bayesian Test*** estimates probability of difference between conversions according to prior knowledge\n- ***Chi-Square Test*** estimates the significance of association between two categorical variables\n\n## Another tools\n#### Central Limit Theorem check\nHelps you check if your variable meets the Central Limit Theorem and what sample size you need for it to meet.\n```\nfrom abtoolkit.utils import check_clt\nimport numpy as np\n\nvar = np.random.chisquare(df=2, size=10000)\np_value = check_clt(var, do_plot_distribution=True)\n```\n\n\n---\nYou can find examples of toolkit usage in [examples/](https://github.com/nikitosl/abtoolkit/tree/master/examples) directory.\n",
"bugtrack_url": null,
"license": null,
"summary": "Package with tools for AB testing",
"version": "2.0.0",
"project_urls": {
"Homepage": "https://github.com/nikitosl/abtoolkit",
"Issues": "https://github.com/nikitosl/abtoolkit/issues"
},
"split_keywords": [
"ab_test",
" cuped",
" did",
" ttest"
],
"urls": [
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "674167c2aaee4e65afd7811306aeb1de56a81fc922e5fb15b96d46a514ddaf2f",
"md5": "cbcdb922d4e82368de99218d785d8f78",
"sha256": "2f40800313225ea059d47876ebfae23fa5989991863169e64b8fa10541536a1f"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "abtoolkit-2.0.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "cbcdb922d4e82368de99218d785d8f78",
"packagetype": "bdist_wheel",
"python_version": "py3",
"requires_python": ">=3.8",
"size": 559300,
"upload_time": "2024-11-21T07:16:24",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-11-21T07:16:24.600262Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/67/41/67c2aaee4e65afd7811306aeb1de56a81fc922e5fb15b96d46a514ddaf2f/abtoolkit-2.0.0-py3-none-any.whl",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
},
{
"comment_text": "",
"digests": {
"blake2b_256": "7677c0e855bfc09bcab6517d40bcd35df7d46699942f7091aed365182f59c9a0",
"md5": "360db8c05a2229313dcd8bc0d3e03dd8",
"sha256": "97a21b189d7c30ac2521949486ec9eded39430d91a2b6e96fdec50eb7800f2b4"
},
"downloads": -1,
"filename": "abtoolkit-2.0.0.tar.gz",
"has_sig": false,
"md5_digest": "360db8c05a2229313dcd8bc0d3e03dd8",
"packagetype": "sdist",
"python_version": "source",
"requires_python": ">=3.8",
"size": 550854,
"upload_time": "2024-11-21T07:16:26",
"upload_time_iso_8601": "2024-11-21T07:16:26.349252Z",
"url": "https://files.pythonhosted.org/packages/76/77/c0e855bfc09bcab6517d40bcd35df7d46699942f7091aed365182f59c9a0/abtoolkit-2.0.0.tar.gz",
"yanked": false,
"yanked_reason": null
}
],
"upload_time": "2024-11-21 07:16:26",
"github": true,
"gitlab": false,
"bitbucket": false,
"codeberg": false,
"github_user": "nikitosl",
"github_project": "abtoolkit",
"travis_ci": false,
"coveralls": false,
"github_actions": false,
"requirements": [
{
"name": "pandas",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"2.2.1"
]
]
},
{
"name": "numpy",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"1.26.4"
]
]
},
{
"name": "statsmodels",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"0.14.1"
]
]
},
{
"name": "scipy",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"1.12.0"
]
]
},
{
"name": "linearmodels",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"5.4"
]
]
},
{
"name": "tqdm",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"4.66.2"
]
]
},
{
"name": "matplotlib",
"specs": [
[
">=",
"3.8.3"
]
]
}
],
"lcname": "abtoolkit"
}
